Related Research Articles

William Redington Hewlett was an American engineer and the co-founder, with David Packard, of the Hewlett-Packard Company (HP).

Gordon Earle Moore was an American businessman, engineer, and the co-founder and emeritus chairman of Intel Corporation. He proposed Moore's law which makes the observation that the number of transistors in an integrated circuit (IC) doubles about every two years.

David Packard was an American electrical engineer and co-founder, with Bill Hewlett, of Hewlett-Packard (1939), serving as president (1947–64), CEO (1964–68), and chairman of the board of HP. He served as U.S. Deputy Secretary of Defense from 1969 to 1971 during the Nixon administration. Packard served as president of the Uniformed Services University of the Health Sciences (USU) from 1976 to 1981 and chairman of its board of regents from 1973 to 1982. He was a member of the Trilateral Commission. Packard was the recipient of the Presidential Medal of Freedom in 1988 and is noted for many technological innovations and philanthropic endeavors.

Nagavara Ramarao Narayana Murthy is an Indian billionaire businessman. He is one of the seven co-founders of Infosys, and has previously served as the chairman, chief executive officer (CEO), president, and chief mentor of the company before retiring and taking the title chairman emeritus. As of April 2023, his net worth was estimated to be $4.1 billion, making him the 711th richest person in the world according to Forbes.
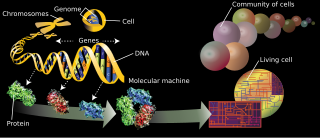
The branches of science known informally as omics are various disciplines in biology whose names end in the suffix -omics, such as genomics, proteomics, metabolomics, metagenomics, phenomics and transcriptomics. Omics aims at the collective characterization and quantification of pools of biological molecules that translate into the structure, function, and dynamics of an organism or organisms.

Bradford Parkinson is an American engineer and inventor, retired United States Air Force Colonel and Emeritus Professor at Stanford University. He is best known as the lead architect, advocate and developer, with early contributions from Ivan Getting and Roger Easton, of the Air Force NAVSTAR program, better known as Global Positioning System.

Personalized medicine, also referred to as precision medicine, is a medical model that separates people into different groups—with medical decisions, practices, interventions and/or products being tailored to the individual patient based on their predicted response or risk of disease. The terms personalized medicine, precision medicine, stratified medicine and P4 medicine are used interchangeably to describe this concept though some authors and organisations use these expressions separately to indicate particular nuances.

George McDonald Church is an American geneticist, molecular engineer, chemist, serial entrepreneur, and pioneer in personal genomics and synthetic biology. He is the Robert Winthrop Professor of Genetics at Harvard Medical School, Professor of Health Sciences and Technology at Harvard University and Massachusetts Institute of Technology, and a founding member of the Wyss Institute for Biologically Inspired Engineering at Harvard. Through his Harvard lab Church has co-founded around 50 biotech companies pushing the boundaries of innovation in the world of life sciences and making his lab as a hotbed of biotech startup activity in Boston. In 2018, the Church lab at Harvard made a record by spinning off 16 biotech companies in one year. The Church lab works on research projects that are distributed in diverse areas of modern biology like developmental biology, neurobiology, info processing, medical genetics, genomics, gene therapy, diagnostics, chemistry & bioengineering, space biology & space genetics, and ecosystem. Research and technology developments at the Church lab have impacted or made direct contributions to nearly all "next-generation sequencing (NGS)" methods and companies. In 2017, Time magazine listed him in Time 100, the list of 100 most influential people in the world. In 2022, he was featured among the most influential people in biopharma by Fierce Pharma, and was listed among the top 8 famous geneticists of all time in human history. As of January 2023, Church serves as a member of the Bulletin of the Atomic Scientists' Board of Sponsors, established by Albert Einstein.
Illumina, Inc. is an American biotechnology company, headquartered in San Diego, California, and it serves more than 140 countries. Incorporated on April 1, 1998, Illumina develops, manufactures, and markets integrated systems for the analysis of genetic variation and biological function. The company provides a line of products and services that serves the sequencing, genotyping and gene expression, and proteomics markets.

William James Dally is an American computer scientist and educator. Since 2021, he has been a member of the President’s Council of Advisors on Science and Technology (PCAST).

Whole genome sequencing (WGS), also known as full genome sequencing, complete genome sequencing, or entire genome sequencing, is the process of determining the entirety, or nearly the entirety, of the DNA sequence of an organism's genome at a single time. This entails sequencing all of an organism's chromosomal DNA as well as DNA contained in the mitochondria and, for plants, in the chloroplast.
Sequenom is an American company based in San Diego, California. It develops enabling molecular technologies, and highly sensitive laboratory genetic tests for NIPT. Sequenom's wholly owned subsidiarity, Sequenom Center for Molecular Medicine (SCMM), offers multiple clinical molecular genetics tests to patients, including MaterniT21, plus a noninvasive prenatal test for trisomy 21, trisomy 18, and trisomy 13, and the SensiGene RHD Fetal RHD genotyping test.

Christofer "Chris" Toumazou, FRS, FREng, FMedSci, FIET, FIEEE, FCGI, FRSM, CEng is a British Cypriot electronic engineer.

Paul Garrett Kaminski is a technologist and former U.S. government official, best known for his leading role in the development of stealth aircraft.
Natera, Inc. is a clinical genetic testing company based in Austin, Texas that specializes in non-invasive, cell-free DNA (cfDNA) testing technology, with a focus on women’s health, cancer, and organ health. Natera’s proprietary technology combines novel molecular biology techniques with a suite of bioinformatics software that allows detection down to a single molecule in a tube of blood. Natera operates CAP-accredited laboratories certified under the Clinical Laboratory Improvement Amendments (CLIA) in San Carlos, California and Austin, Texas.

Euan Angus Ashley is a Scottish physician, scientist, author, and founder based at Stanford University in California where he is Associate Dean in the School of Medicine and holds the Roger and Joelle Burnell Chair of Genomics and Precision Health. He is known for helping establish the field of medical genomics.

In genetics, a polygenic score (PGS), also called a polygenic index (PGI), polygenic risk score (PRS), genetic risk score, or genome-wide score, is a number that summarizes the estimated effect of many genetic variants on an individual's phenotype, typically calculated as a weighted sum of trait-associated alleles. It reflects an individual's estimated genetic predisposition for a given trait and can be used as a predictor for that trait. In other words, it gives an estimate of how likely an individual is to have a given trait only based on genetics, without taking environmental factors into account. Polygenic scores are widely used in animal breeding and plant breeding due to their efficacy in improving livestock breeding and crops. In humans, polygenic scores are typically generated from genome-wide association study (GWAS) data.

James Julius Spilker Jr. was an American engineer and a consulting professor in the Aeronautics and Astronautics Department at Stanford University. He was one of the principal architects of the Global Positioning System (GPS). He was a co-founder of the space communications company Stanford Telecommunications, and was most recently executive chairman of AOSense Inc., Sunnyvale, CA.

Marty Bradley is an American aerospace engineer who specializes in advanced propulsion, electric aircraft, and sustainable aviation. He is a fellow of the American Institute of Aeronautics and Astronautics (AIAA), an adjunct professor of aerospace and mechanical engineering practice at the University of Southern California (USC), and a sustainable aviation consultant.
References
- ↑ "Matthew Rabinowitz". World Economic Forum. Retrieved 25 January 2023.
- ↑ "Patents by Inventor Matthew Rabinowitz". JUSTIA Patents.
- ↑ "Peer-reviewed Publications". Natera. Natera. Retrieved 25 January 2023.
- 1 2 "Bernard (Bokkie) Rabinowitz" (PDF). The Scientific Electronic Library Online. Retrieved 7 April 2023.
- ↑ "Feed In Tariff for Renewable Energy, Private Members' Bill". Inkatha Freedom Party.
- ↑ "Inventory of the private collection of Inkatha Freeadom Party" (PDF). University of the Free State.
- ↑ "Stanford eCorner - Irreverence Pays Benefits" (PDF). eCorner.
- ↑ Bleby, Michael (22 August 2007). "South Africa: Delicate Detective Work At the Genetic Frontier" . Retrieved 25 January 2023.
- 1 2 "Matthew Rabinowitz - IEEE Xplore". IEEE. Retrieved 5 April 2023.
- ↑ "Broadbase Software to Buy Panop.com". The New York Times. 8 July 2000. Retrieved 25 January 2023.
- ↑ Brown, Steven E.F. (15 April 2008). "Rosum Corp. raises $15 million". San Francisco Business Times. Retrieved 25 January 2023.
- ↑ Rabinowitz, Matthew; Spilker, James J. (December 2004). "Augmenting GPS with Television Signals for Reliable Indoor Positioning". Navigation. pp. 269–282. doi:10.1002/j.2161-4296.2004.tb00358.x . Retrieved 29 May 2023.
- ↑ Anderson, Chris (25 August 2021). "Much More than Child's Play". Inside Precision Medicine. Retrieved 29 May 2023.
- ↑ "Matthew Rabinowitz, Natera Co-Founder and Executive Chairman of the Board, Makes Additional Investment in Natera". Business Insider. 16 May 2022. Retrieved 25 January 2023.
- ↑ "Matthew Rabinowitz, Natera Co-Founder and Executive Chairman of the Board, Makes Additional Investment in Natera". Yahoo Finance. 16 May 2022. Retrieved 25 January 2023.
- ↑ "How a Family Tragedy Inspired This Founder to Help Pregnant Women". Inc. Retrieved 5 April 2023.
- ↑ "About - MyOme". MyOme. MyOme. Retrieved 25 January 2023.
- ↑ Kumar, Akash (2022). "Whole-genome risk prediction of common diseases in human preimplantation embryos". Nature Medicine. Nature.com. 28 (3): 513–516. doi:10.1038/s41591-022-01735-0. PMC 8938270 . PMID 35314819.
- ↑ "Scientists say they can read nearly the whole genome of an IVF-created embryo". www.science.org. Retrieved 29 May 2023.
- ↑ Ray, Forest (15 June 2022). "MyOme Develops Cross-Ancestry Breast Cancer Polygenic Risk Score, Plans Product Launch". GenomeWeb. Retrieved 25 January 2023.
- ↑ "Matthew Rabinowitz". Sequoia Capital. Retrieved 25 January 2023.
- ↑ Diphoko, Wesley (5 April 2022). "This SA born Venture Capitalist is taking over the world". Fast Company. Retrieved 25 January 2023.
- ↑ "NatureEye helps conservation while delivering a unique experience". NatureEye. NatureEye. Retrieved 25 January 2023.
- ↑ Zhavoronkov, Alex (31 October 2022). "This Harvard Female Scientist Wants To Use Genetics To Reverse The Age Of Your Skin". Forbes. Retrieved 25 January 2023.
- ↑ Tozzi, John (26 April 2013). "Innovator: Matt Rabinowitz Sifts Gene Data for Healthy Pregnancies". Bloomberg. Retrieved 25 January 2023.
- ↑ White, Tracie. "Rock solid science, passion help fuel successful startups". Scope Blog - Stanford Medicine. Stanford Medicine. Retrieved 25 January 2023.
- ↑ "Matthew Rabinowitz | Innovators Under 35". www.innovatorsunder35.com. Retrieved 7 April 2023.
- ↑ "2006 Scott Helt Memorial Award For the best paper published in the IEEE Transactions on Broadcasting". IEEE. December 2006. pp. 417–417. doi:10.1109/TBC.2006.887344 . Retrieved 7 April 2023.
- ↑ "World Economic Forum - 2006 Tech Pioneers in Information Technology". World Bank. Retrieved 7 April 2023.
- ↑ "Technology Pioneers 2014" (PDF). WEF. Retrieved 7 April 2023.
- ↑ "2012-2018 Winners". Edison Awards. Retrieved 7 April 2023.