The Queen Elizabeth Range is a rugged mountain range of the Transantarctic Mountains System, located in the Ross Dependency region of Antarctica.
Martin Glacier is a glacier, 3 nautical miles (6 km) wide and 9 nautical miles (17 km) long, which flows west and then northwest from the south side of Mount Lupa to the southeast corner of Rymill Bay where it joins Bertrand Ice Piedmont, on the west coast of Graham Land, Antarctica. It was first surveyed in 1936 by the British Graham Land Expedition (BGLE) under John Riddoch Rymill, and was resurveyed in 1948–1949 by the Falkland Islands Dependencies Survey. The glacier was named for James Hamilton Martin, a member of the British Australian and New Zealand Antarctic Research Expedition (1929–1931) under Sir Douglas Mawson, and first mate of the Penola during the BGLE.
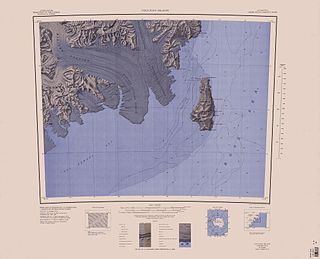
Borchgrevink Glacier is a large glacier in the Victory Mountains, Victoria Land, draining south between Malta Plateau and Daniell Peninsula, and thence projecting into Glacier Strait, Ross Sea, as a floating glacier tongue, the Borchgrevink Glacier Tongue, just south of Cape Jones. It was named by the New Zealand Geological Survey Antarctic Expedition, 1957–58, for Carsten Borchgrevink, leader of the British Antarctic Expedition, 1898–1900. Borchgrevink visited the area in February 1900 and first observed the seaward portion of the glacier.

Lambert Glacier is a major glacier in East Antarctica. At about 80 km (50 mi) wide, over 400 km (250 mi) long, and about 2,500 m (8,200 ft) deep, it is the world's largest glacier. It drains 8% of the Antarctic ice sheet to the east and south of the Prince Charles Mountains and flows northward to the Amery Ice Shelf. It flows in part of Lambert Graben and exits the continent at Prydz Bay.

The Prince Charles Mountains are a major group of mountains in Mac. Robertson Land in Antarctica, including the Athos Range, the Porthos Range, and the Aramis Range. The highest peak is Mount Menzies, with a height of 3,228 m (10,591 ft). Other prominent peaks are Mount Izabelle and Mount Stinear. These mountains, together with other scattered peaks, form an arc about 420 km (260 mi) long, extending from the vicinity of Mount Starlight in the north to Goodspeed Nunataks in the south.
The Grove Mountains are a large, scattered group of mountains and nunataks extending over an area of approximately 40 by 20 miles, located 100 miles (160 km) east of the Mawson Escarpment in American Highland, Antarctica. They were first photographed from the air by aircraft of U.S. Navy Operation Highjump, 1946–47, and named by the Antarctic Names Committee of Australia for Squadron Leader I.L. Grove, a Royal Australian Air Force pilot with the Australian National Antarctic Research Expeditions, who made a November 1958 landing in these mountains.
Cape Goodenough is an ice-covered cape marking the west side of the entrance to Porpoise Bay and forming the northernmost projection of Norths Highland in Antarctica. It was discovered by the British Australian New Zealand Antarctic Research Expedition under Douglas Mawson on an airplane flight in January 1931, and was named by Mawson for Admiral Sir William Goodenough, President of the Council of the Royal Geographical Society from 1930 to 1933.

Ninnis Glacier is a large, heavily hummocked and crevassed glacier descending steeply from the high interior to the sea in a broad valley, on George V Coast in Antarctica. It was discovered by the Australasian Antarctic Expedition (1911–14) under Douglas Mawson, who named it for Lieutenant B. E. S. Ninnis, who lost his life on the far east sledge journey of the expedition on 14 December 1912 through falling into the Black Crevasse in the glacier.
Mawson Peninsula is a high, narrow, ice-covered peninsula on the George V Coast, on the west side of the Slava Ice Shelf, Antarctica, terminating in Cape Hudson. It extends for over 30 nautical miles (56 km) in a northwesterly direction. The peninsula was photographed from the air by U.S. Navy Operation Highjump, 1946–47, and was sketched and photographed by Phillip Law of the Australian National Antarctic Research Expeditions who flew along it to its northern end in February 1959. It was named by the Antarctic Names Committee of Australia for Sir Douglas Mawson.
The Dismal Mountains are a group of nunataks about 35 miles (56 km) southwest of Rayner Peak in Antarctica. They were photographed from ANARE aircraft in 1956, and surveyed by G.A. Knuckey during a dog-sledge journey from Amundsen Bay to Mawson Station in December 1958. They are so named because the mountains are frequently shrouded in clouds.
Enderby Land is a projecting landmass of Antarctica. Its shore extends from Shinnan Glacier at about 67°55′S44°38′E to William Scoresby Bay at 67°24′S59°34′E, approximately 1⁄24 of the earth's longitude. It was first documented in western and eastern literature in February 1831 by John Biscoe aboard the whaling brig Tula, and named after the Enderby Brothers of London, the ship's owners who encouraged their captains to combine exploration with sealing.
Astronaut Glacier is a broad glacier, tributary to upper Aviator Glacier, flowing south-west and joining the latter just west of Parasite Cone in Victoria Land. It was named by the northern party of the New Zealand Geological Survey Antarctic Expedition, 1962–63, in association with nearby Aeronaut Glacier.
Barkell Platform is a narrow, level rock platform on the north end of Mawson Escarpment in Antarctica. This promontory, 1,285 metres (4,220 ft) high, was the site of a geodetic survey station during the Australian National Antarctic Research Expeditions Prince Charles Mountains survey in 1971. It was named for V.G. Barkell, helicopter pilot with the survey.
Campbell Peak is a peak, 2,415 metres (7,920 ft) high, standing 1.2 nautical miles (2.2 km) northeast of Mawson Peak, the summit of Heard Island. It was surveyed in 1948 by the Australian National Antarctic Research Expeditions (ANARE), who named it for Group-Captain Stuart A. Campbell, Royal Australian Air Force. Campbell visited Heard Island in 1929 as aircraft pilot with the British Australian and New Zealand Antarctic Research Expedition led by Douglas Mawson, and again as leader of ANARE when a research station was established on the island in December 1947.
Cave Bay is a 0.3-nautical-mile-wide (0.56 km) cove indenting the west side of Heard Island, an uninhabited Australian overseas territory in the Indian Ocean, between West Bay and South West Bay. The bay was formed by the erosion of an extinct volcanic crater of which Mount Andree forms the north side.

Dobbratz Glacier is a broad tributary glacier which drains the south part of the White Escarpment and flows northeast between the Watlack Hills and the Webers Peaks into Splettstoesser Glacier, in the Heritage Range. It was named by the University of Minnesota Geological Party, 1963–64, for Major Joseph Dobbratz, a United States Marine Corps pilot who supported the party.
The Franko Escarpment is a mostly snow-covered escarpment that runs north–south for 4 nautical miles (7 km) and forms the northeast edge of Lexington Table in the Forrestal Range of the Pensacola Mountains, Antarctica. It was named by the Advisory Committee on Antarctic Names in 1979 for Stephen J. Franko, a Grants and Contracts Officer with the National Science Foundation from 1967, with responsibility for all contracts in support of the United States Antarctic Research Program.
Tenaza Peak is a peak (1,345 m) located 2.5 nautical miles (4.6 km) east of Mount Pechell in the west-central part of Hedgpeth Heights, Anare Mountains, Antarctica. Mapped by United States Geological Survey (USGS) from surveys and U.S. Navy air photos, 1960–63. Named by Advisory Committee on Antarctic Names (US-ACAN) for Richard R. Tenaza, United States Antarctic Research Program (USARP) biologist at Hallett Station, 1967–68.
Casey Point is a narrow rock spur separating Sheraton Glacier and Arriens Glacier in the Mawson Escarpment, Antarctica. It was plotted from ANARE aerial photographs taken in 1956, 1960 and 1973, and named by the Australian Antarctic Names and Medals Committee after J. N. Casey, (then) Assistant Director (Geology) of the Bureau of Mineral Resources, Geology and Geophysics, Australian Department of Minerals and Energy, Canberra.






