
An electron and an electron hole that are attracted to each other by the Coulomb force can form a bound state called an exciton. It is an electrically neutral quasiparticle that exists mainly in condensed matter, including insulators, semiconductors, some metals, but also in certain atoms, molecules and liquids. The exciton is regarded as an elementary excitation that can transport energy without transporting net electric charge.

Luminescence is a spontaneous emission of radiation from an electronically or vibrationally excited species not in thermal equilibrium with its environment. A luminescent object emits cold light in contrast to incandescence, where an object only emits light after heating. Generally, the emission of light is due to the movement of electrons between different energy levels within an atom after excitation by external factors. However, the exact mechanism of light emission in vibrationally excited species is unknown.

Photoluminescence is light emission from any form of matter after the absorption of photons. It is one of many forms of luminescence and is initiated by photoexcitation, hence the prefix photo-. Following excitation, various relaxation processes typically occur in which other photons are re-radiated. Time periods between absorption and emission may vary: ranging from short femtosecond-regime for emission involving free-carrier plasma in inorganic semiconductors up to milliseconds for phosphoresence processes in molecular systems; and under special circumstances delay of emission may even span to minutes or hours.
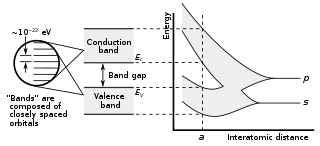
In solid-state physics and solid-state chemistry, a band gap, also called a bandgap or energy gap, is an energy range in a solid where no electronic states exist. In graphs of the electronic band structure of solids, the band gap refers to the energy difference between the top of the valence band and the bottom of the conduction band in insulators and semiconductors. It is the energy required to promote an electron from the valence band to the conduction band. The resulting conduction-band electron are free to move within the crystal lattice and serve as charge carriers to conduct electric current. It is closely related to the HOMO/LUMO gap in chemistry. If the valence band is completely full and the conduction band is completely empty, then electrons cannot move within the solid because there are no available states. If the electrons are not free to move within the crystal lattice, then there is no generated current due to no net charge carrier mobility. However, if some electrons transfer from the valence band to the conduction band, then current can flow. Therefore, the band gap is a major factor determining the electrical conductivity of a solid. Substances having large band gaps are generally insulators, those with small band gaps are semiconductor, and conductors either have very small band gaps or none, because the valence and conduction bands overlap to form a continuous band.

A scintillator is a material that exhibits scintillation, the property of luminescence, when excited by ionizing radiation. Luminescent materials, when struck by an incoming particle, absorb its energy and scintillate. Sometimes, the excited state is metastable, so the relaxation back down from the excited state to lower states is delayed. The process then corresponds to one of two phenomena: delayed fluorescence or phosphorescence. The correspondence depends on the type of transition and hence the wavelength of the emitted optical photon.

Quantum dots (QDs) or semiconductor nanocrystals are semiconductor particles a few nanometres in size with optical and electronic properties that differ from those of larger particles via quantum mechanical effects. They are a central topic in nanotechnology and materials science. When a quantum dot is illuminated by UV light, an electron in the quantum dot can be excited to a state of higher energy. In the case of a semiconducting quantum dot, this process corresponds to the transition of an electron from the valence band to the conductance band. The excited electron can drop back into the valence band releasing its energy as light. This light emission (photoluminescence) is illustrated in the figure on the right. The color of that light depends on the energy difference between the conductance band and the valence band, or the transition between discrete energy states when the band structure is no longer well-defined in QDs.
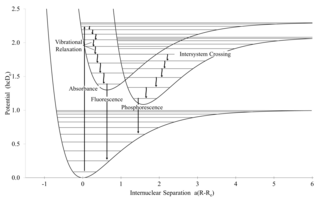
Intersystem crossing (ISC) is an isoenergetic radiationless process involving a transition between the two electronic states with different spin multiplicity.

An F-center or color center or Farbe center is a type of crystallographic defect in which an anionic vacancy in a crystal lattice is occupied by one or more unpaired electrons. Electrons in such a vacancy in a crystal lattice tend to absorb light in the visible spectrum such that a material that is usually transparent becomes colored. The greater the number of F centers, the more intense the color of the compound. F centers are a type of color center.
Organic semiconductors are solids whose building blocks are pi-bonded molecules or polymers made up by carbon and hydrogen atoms and – at times – heteroatoms such as nitrogen, sulfur and oxygen. They exist in the form of molecular crystals or amorphous thin films. In general, they are electrical insulators, but become semiconducting when charges are injected from appropriate electrodes or are introduced by doping or photoexcitation.
In solid-state physics of semiconductors, carrier generation and carrier recombination are processes by which mobile charge carriers are created and eliminated. Carrier generation and recombination processes are fundamental to the operation of many optoelectronic semiconductor devices, such as photodiodes, light-emitting diodes and laser diodes. They are also critical to a full analysis of p-n junction devices such as bipolar junction transistors and p-n junction diodes.

Photosensitizers are light absorbers that alter the course of a photochemical reaction. They usually are catalysts. They can function by many mechanisms, sometimes they donate an electron to the substrate, sometimes they abstract a hydrogen atom from the substrate. At the end of this process, the photosensitizer returns to its ground state, where it remains chemically intact, poised to absorb more light. One branch of chemistry which frequently utilizes photosensitizers is polymer chemistry, using photosensitizers in reactions such as photopolymerization, photocrosslinking, and photodegradation. Photosensitizers are also used to generate prolonged excited electronic states in organic molecules with uses in photocatalysis, photon upconversion and photodynamic therapy. Generally, photosensitizers absorb electromagnetic radiation consisting of infrared radiation, visible light radiation, and ultraviolet radiation and transfer absorbed energy into neighboring molecules. This absorption of light is made possible by photosensitizers' large de-localized π-systems, which lowers the energy of HOMO and LUMO orbitals to promote photoexcitation. While many photosensitizers are organic or organometallic compounds, there are also examples of using semiconductor quantum dots as photosensitizers.

Photoexcitation is the production of an excited state of a quantum system by photon absorption. The excited state originates from the interaction between a photon and the quantum system. Photons carry energy that is determined by the wavelengths of the light that carries the photons. Objects that emit light with longer wavelengths, emit photons carrying less energy. In contrast to that, light with shorter wavelengths emit photons with more energy. When the photon interacts with a quantum system, it is therefore important to know what wavelength one is dealing with. A shorter wavelength will transfer more energy to the quantum system than longer wavelengths.

A quantum dot solar cell (QDSC) is a solar cell design that uses quantum dots as the captivating photovoltaic material. It attempts to replace bulk materials such as silicon, copper indium gallium selenide (CIGS) or cadmium telluride (CdTe). Quantum dots have bandgaps that are adjustable across a wide range of energy levels by changing their size. In bulk materials, the bandgap is fixed by the choice of material(s). This property makes quantum dots attractive for multi-junction solar cells, where a variety of materials are used to improve efficiency by harvesting multiple portions of the solar spectrum.
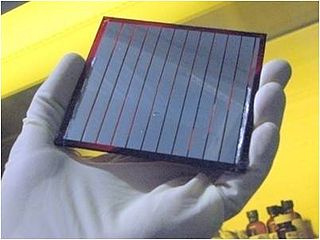
An organic solar cell (OSC) or plastic solar cell is a type of photovoltaic that uses organic electronics, a branch of electronics that deals with conductive organic polymers or small organic molecules, for light absorption and charge transport to produce electricity from sunlight by the photovoltaic effect. Most organic photovoltaic cells are polymer solar cells.

Solid is one of the four fundamental states of matter along with liquid, gas, and plasma. The molecules in a solid are closely packed together and contain the least amount of kinetic energy. A solid is characterized by structural rigidity and resistance to a force applied to the surface. Unlike a liquid, a solid object does not flow to take on the shape of its container, nor does it expand to fill the entire available volume like a gas. The atoms in a solid are bound to each other, either in a regular geometric lattice, or irregularly. Solids cannot be compressed with little pressure whereas gases can be compressed with little pressure because the molecules in a gas are loosely packed.

Transition-metal dichalcogenide (TMD or TMDC) monolayers are atomically thin semiconductors of the type MX2, with M a transition-metal atom (Mo, W, etc.) and X a chalcogen atom (S, Se, or Te). One layer of M atoms is sandwiched between two layers of X atoms. They are part of the large family of so-called 2D materials, named so to emphasize their extraordinary thinness. For example, a MoS2 monolayer is only 6.5 Å thick. The key feature of these materials is the interaction of large atoms in the 2D structure as compared with first-row transition-metal dichalcogenides, e.g., WTe2 exhibits anomalous giant magnetoresistance and superconductivity.
Lanthanide probes are a non-invasive analytical tool commonly used for biological and chemical applications. Lanthanides are metal ions which have their 4f energy level filled and generally refer to elements cerium to lutetium in the periodic table. The fluorescence of lanthanide salts is weak because the energy absorption of the metallic ion is low; hence chelated complexes of lanthanides are most commonly used. The term chelate derives from the Greek word for “claw,” and is applied to name ligands, which attach to a metal ion with two or more donor atoms through dative bonds. The fluorescence is most intense when the metal ion has the oxidation state of 3+. Not all lanthanide metals can be used and the most common are: Sm(III), Eu(III), Tb(III), and Dy(III).
Suning Wang was a Chinese-born Canadian chemist. She was a Professor of Chemistry, Research Chair and head of the Wang Group at Queen's University, Canada, having joined the Department of Chemistry at Queen's University in 1996. Wang worked on the development of new Organometallic chemistry and luminescent materials chemistry. Her research interests also included the work on organic Photovoltaics and Nanoparticle, stimuli-responsive materials as well as OLEDs. Wang and her group developed a simple method of producing graphene-like lattice through light exposure, which may contribute to a huge field of future use. Wang held several patents related to the application of luminescent compounds and boron compounds.
Thermally activated delayed fluorescence (TADF) is a process through which a molecular species in a non-emitting excited state can incorporate surrounding thermal energy to change states and only then undergo light emission. The TADF process usually involves an excited molecular species in a triplet state, which commonly has a forbidden transition to the ground state termed phosphorescence. By absorbing nearby thermal energy the triplet state can undergo reverse intersystem crossing (RISC) converting it to a singlet state, which can then de-excite to the ground state and emit light in a process termed fluorescence. Along with fluorescent and phosphorescent compounds, TADF compounds are one of the three main light-emitting materials used in organic light-emitting diodes (OLEDs). Although most TADF molecules rely on the RISC from a triplet state to a singlet state, some of them take advantage of RISC processes between states with other spin multiplicities instead, for example from a quartet state to a doublet state.

Perovskite nanocrystals are a class of semiconductor nanocrystals, which exhibit unique characteristics that separate them from traditional quantum dots. Perovskite nanocrystals have an ABX3 composition where A = cesium, methylammonium (MA), or formamidinium (FA); B = lead or tin; and X = chloride, bromide, or iodide.














