Related Research Articles

The Ferrymead Railway is a New Zealand heritage railway built upon the track formation of New Zealand's first public railway, from Ferrymead to Christchurch, which opened on 1 December 1863. On the opening of the line to Lyttelton on 9 December 1867, the Ferrymead Railway became the Ferrymead Branch and was closed shortly thereafter. In 1964, rail enthusiasts began relaying track on the historic formation and the new 3 ft 6 in narrow gauge. Ferrymead Railway officially reopened in 1977. It now operates steam, diesel and electric trains regularly and is recognised as one of the most significant rail preservation sites in New Zealand.

The Puffing Billy Railway is a 2 ft 6 in narrow gauge heritage railway in the southern foothills of the Dandenong Ranges in Melbourne, Australia. The railway was one of the five narrow gauge lines of the Victorian Railways which opened around the beginning of the 20th century. It is close to the city of Melbourne and is one of the most popular steam heritage railways in the world, attracting tourists from Australia and overseas. The railway aims to preserve and restore the line and its operation as closely as possible to the way it was in the first three decades of its existence, but with particular emphasis on the early 1920s.

Kensington railway station is a commuter railway station on the Craigieburn line, which is part of the Melbourne railway network. It serves the northern suburb of Kensington, in Melbourne, Victoria, Australia. Kensington station is a ground level unstaffed station, featuring two side platforms. It opened on 1 November 1860, with the current station provided in 1871. It initially closed on 1 July 1864, then reopened on 9 October 1871.

Newmarket railway station is a commuter railway station on the Craigieburn line, which is part of the Melbourne railway network. It serves the northern suburb of Flemington, in Melbourne, Victoria, Australia. Newmarket station is an elevated unstaffed station, featuring two side platforms. It opened on 1 November 1860, with the current station provided in 1871. It initially closed on 1 July 1864, then reopened on 9 October 1871.

Ascot Vale railway station is a commuter railway station on the Craigieburn line, which is part of the Melbourne railway network. It serves the northern suburb of Ascot Vale, in Melbourne, Victoria, Australia. Ascot Vale station is a ground level unstaffed station, featuring two side platforms. It opened on 1 November 1860, with the current station provided in 1871. It initially closed on 1 July 1864, then reopened on 9 October 1871.

Moonee Ponds railway station is a commuter railway station on the Craigieburn line, which is part of the Melbourne railway network. It serves the northern suburb of Moonee Ponds, in Melbourne, Victoria, Australia. Moonee Ponds station is a ground level unstaffed station, featuring two side platforms. It opened on 1 November 1860, with the current station provided in 1882. It initially closed on 1 July 1864, then reopened in 9 October 1871.

The Flemington Racecourse line is a commuter railway line in the city of Melbourne, Victoria, Australia. Operated by Metro Trains Melbourne, it is the city's shortest metropolitan railway line at 7.8 kilometres (4.8 mi). The line runs from Flinders Street station in central Melbourne to Flemington Racecourse station, situated next to the racecourse in the city's north west, serving a total of 5 stations. The line operates only during special events, with services as frequent as every 4 minutes during peak periods of those special events. Trains on the Flemington Racecourse line run with two three-car formations of Comeng, Siemens Nexas, or X'Trapolis 100 trainsets.

The Melbourne rail network is a metropolitan suburban and freight rail system serving the city of Melbourne, Victoria, Australia. The metropolitan rail network is centred around the Melbourne central business district (CBD) and consists of 222 railway stations across 16 lines, which served a patronage of 99.5 million over the year 2021–2022. It is the core of the larger Victorian railway network, with regional links to both intrastate and interstate rail systems.
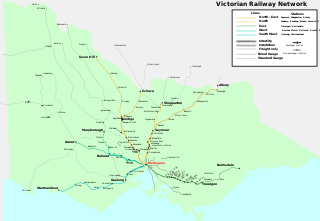
Rail transport in the Australian state of Victoria is provided by a number of railway operators who operate over the government-owned railway lines. The network consists of 2,357 km of Victorian broad gauge lines, and 1,912 km of standard gauge freight and interstate lines; the latter increasing with gauge conversion of the former. Historically, a few experimental 762 mm gauge lines were built, along with various private logging, mining and industrial railways. The rail network radiates from the state capital, Melbourne, with main interstate links to Sydney and to Adelaide, as well as major lines running to regional centres, upgraded as part of the Regional Fast Rail project.

The Craigieburn line is a commuter railway line in the city of Melbourne, Victoria, Australia. Operated by Metro Trains Melbourne, it is the city's seventh shortest metropolitan railway line at 27.0 kilometres (16.8 mi). The line runs from Flinders Street station in central Melbourne to Craigieburn station in the north, serving 21 stations via North Melbourne, Essendon, and Broadmeadows. The line operates for approximately 19 hours a day with 24 hour service available on Friday and Saturday nights. During peak hour, headways of up to 5 minutes are operated with services every 20–30 minutes during off-peak hours. Trains on the Craigieburn line run with a two three-car formations of Comeng or Siemens Nexas trainsets.

Flemington is an inner-city suburb in Melbourne, Victoria, Australia, 5 km (3.1 mi) north-west of Melbourne's Central Business District, located within the Cities of Melbourne and Moonee Valley local government areas. Flemington recorded a population of 7,025 at the 2021 census.

Kensington is an inner-city suburb in Melbourne, Victoria, Australia, 4 km (2.5 mi) north-west of Melbourne's Central Business District, located within the City of Melbourne local government area. Kensington recorded a population of 10,745 at the 2021 census.

The Victorian Railways (VR), trading from 1974 as VicRail, was the state-owned operator of most rail transport in the Australian state of Victoria from 1859 to 1983. The first railways in Victoria were private companies, but when these companies failed or defaulted, the Victorian Railways was established to take over their operations. Most of the lines operated by the Victorian Railways were of 5 ft 3 in. However, the railways also operated up to five 2 ft 6 in narrow gauge lines between 1898 and 1962, and a 4 ft 8+1⁄2 instandard gauge line between Albury and Melbourne from 1961.
The South Gippsland railway line is a partially closed railway line in Victoria, Australia. It was first opened in 1892, branching from the Orbost line at Dandenong, and extending to Port Albert. Much of it remained open until December 1994. Today, only the section between Dandenong and Cranbourne remains open for use. The section of the line from Nyora to Leongatha was used by the South Gippsland Tourist Railway until it ceased operations in 2016. The section from Nyora to Welshpool, with extension trail to Port Welshpool and a portion of the former line at Koo Wee Rup, have been converted into the Great Southern Rail Trail.
The Port Melbourne railway line is a former railway line in Melbourne, Australia, opened in September 1854, that is now a light rail line. It was instigated by the Melbourne and Hobson's Bay Railway Company to carry passengers arriving in Victoria at Station Pier and to alleviate the high cost of shipping goods using small vessels up the Yarra River to Melbourne. The line's conversion to light rail occurred in 1987; it is now served by tram route 109.
The Canterbury Provincial Railways was an early part of the railways of New Zealand. Built by the Canterbury Provincial government mainly to the broad gauge of 5 ft 3 in, the railway reached most of the Canterbury region by the time the province was abolished in 1876. Edward Dobson, the Provincial Engineer from 1854 to 1868, was the designer and overseer.
The North East railway line is a railway line in Victoria, Australia. The line runs from Southern Cross railway station on the western edge of the Melbourne central business district to Albury railway station in the border settlement of Albury-Wodonga, serving the cities of Wangaratta and Seymour, and smaller towns in northeastern Victoria.
The Tocumwal railway line is a 1,600 mm gauge railway line in Victoria, Australia. The line runs between the border town of Tocumwal in New South Wales to Southern Cross station in Melbourne. The line is used by various passenger and freight trains serving the northern suburbs of Melbourne and northern regions of Victoria.
The Victorian Railways L class was a class of 2-4-0ST passenger locomotives operated by the Victorian Railways between 1861 and 1906, built by both George England and Co., Newcastle upon Tyne, England and Slaughter, Gruning & Co., Bristol, England.
This was a group of 18 2-4-0WT passenger steam locomotives, built by Robert Stephenson & Company and an extra locomotive built from spare parts supplied with the other 18. These locomotives not only provided the bulk workforce of the early private railway operators in Victoria, but upon their withdrawal they once again proved themselves as useful as contractors locos building some of the railway lines for the then expanding Victorian Railway network.