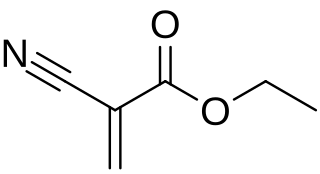
Cyanoacrylates are a family of strong fast-acting adhesives with industrial, medical, and household uses. They are derived from ethyl cyanoacrylate and related esters. The cyanoacrylate group in the monomer rapidly polymerize in the presence of water to form long, strong chains. They have some minor toxicity.

Methyl isocyanate (MIC) is an organic compound with the molecular formula CH3NCO. Synonyms are isocyanatomethane, methyl carbylamine and MIC. Methyl isocyanate is an intermediate chemical in the production of carbamate pesticides (such as carbaryl, carbofuran, methomyl, and aldicarb). It has also been used in the production of rubbers and adhesives. As a highly toxic and irritating material, it is extremely hazardous to human health. It was the principal toxicant involved in the Bhopal disaster, which killed 2,259 people initially and officially 20,000 people in total.
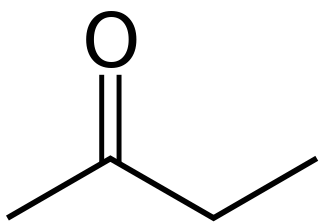
Butanone, also known as methyl ethyl ketone (MEK), is an organic compound with the formula CH3C(O)CH2CH3. This colourless liquid ketone has a sharp, sweet odor reminiscent of acetone. It is produced industrially on a large scale, but occurs in nature only in trace amounts. It is partially soluble in water, and is commonly used as an industrial solvent. It is an isomer of another solvent, tetrahydrofuran.

Poly(methyl methacrylate) (PMMA), also known as acrylic, acrylic glass, or plexiglass, as well as by the trade names Crylux, Plexiglas, Acrylite, Astariglas, Lucite, Perclax, and Perspex, among several others, is a transparent thermoplastic often used in sheet form as a lightweight or shatter-resistant alternative to glass. The same material can be used as a casting resin or in inks and coatings, among many other uses.

Polypropylene (PP), also known as polypropene, is a thermoplastic polymer used in a wide variety of applications. It is produced via chain-growth polymerization from the monomer propylene.
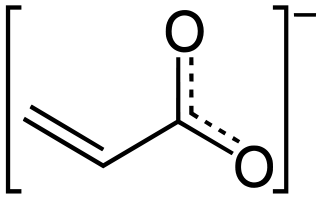
Acrylates (IUPAC: prop-2-enoates) are the salts, esters, and conjugate bases of acrylic acid. The acrylate ion is the anion CH2=CHCOO−. Often, acrylate refers to esters of acrylic acid, the most common member being methyl acrylate. These acrylates contain vinyl groups. These compounds are of interest because they are bifunctional: the vinyl group is susceptible to polymerization and the carboxylate group carries myriad functionalities. Modified acrylates are also numerous, some examples being methacrylates (CH2=C(CH3)CO2R) and cyanoacrylates (CH2=C(CN)CO2R). Acrylate can also refer to polyacrylates prepared through the polymerization of the vinyl groups of acrylate monomers.

Parathion, also called parathion-ethyl or diethyl parathion and locally known as "Folidol", is an organophosphate insecticide and acaricide. It was originally developed by IG Farben in the 1940s. It is highly toxic to non-target organisms, including humans, so its use has been banned or restricted in most countries. The basic structure is shared by parathion methyl.

3-Pentanone is a simple, symmetrical dialkyl ketone. It is a colorless liquid ketone with an odor like that of acetone. It is soluble in about 25 parts water, but miscible with organic solvents.

Hydroquinone, also known as benzene-1,4-diol or quinol, is an aromatic organic compound that is a type of phenol, a derivative of benzene, having the chemical formula C6H4(OH)2. It has two hydroxyl groups bonded to a benzene ring in a para position. It is a white granular solid. Substituted derivatives of this parent compound are also referred to as hydroquinones. The name "hydroquinone" was coined by Friedrich Wöhler in 1843.

Methyl methacrylate (MMA) is an organic compound with the formula CH2=C(CH3)COOCH3. This colorless liquid, the methyl ester of methacrylic acid (MAA), is a monomer produced on a large scale for the production of poly(methyl methacrylate) (PMMA).

p-Xylene (para-xylene) is an aromatic hydrocarbon. It is one of the three isomers of dimethylbenzene known collectively as xylenes. The p- stands for para-, indicating that the two methyl groups in p-xylene occupy the diametrically opposite substituent positions 1 and 4. It is in the positions of the two methyl groups, their arene substitution pattern, that it differs from the other isomers, o-xylene and m-xylene. All have the same chemical formula C6H4(CH3)2. All xylene isomers are colorless and highly flammable. The odor threshold of p-xylene is 0.62 parts per million (ppm).

N-Methyl-2-pyrrolidone (NMP) is an organic compound consisting of a 5-membered lactam. It is a colorless liquid, although impure samples can appear yellow. It is miscible with water and with most common organic solvents. It also belongs to the class of dipolar aprotic solvents such as dimethylformamide and dimethyl sulfoxide. It is used in the petrochemical and plastics industries as a solvent, exploiting its nonvolatility and ability to dissolve diverse materials.

Methyl vinyl ketone (MVK, IUPAC name: butenone) is the organic compound with the formula CH3C(O)CH=CH2. It is a reactive compound classified as an enone, in fact the simplest example thereof. It is a colorless, flammable, highly toxic liquid with a pungent odor. It is soluble in water and polar organic solvents. It is a useful intermediate in the synthesis of other compounds.
Synthetic resins are industrially produced resins, typically viscous substances that convert into rigid polymers by the process of curing. In order to undergo curing, resins typically contain reactive end groups, such as acrylates or epoxides. Some synthetic resins have properties similar to natural plant resins, but many do not.

Nitroethane is an organic compound having the chemical formula C2H5NO2. Similar in many regards to nitromethane, nitroethane is an oily liquid at standard temperature and pressure. Pure nitroethane is colorless and has a fruity odor.

Methyl cyanoacrylate (MCA) is an organic compound that contains several functional groups: a methyl ester, a nitrile, and an alkene. It is a colorless liquid with low viscosity. Its chief use is as the main component of cyanoacrylate glues. It can be encountered under many trade names. Methyl cyanoacrylate is less commonly encountered than ethyl cyanoacrylate.
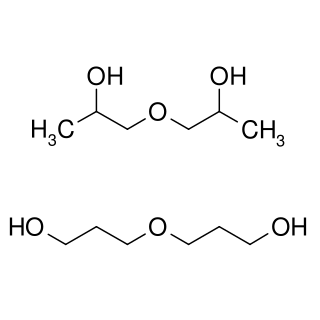
Dipropylene glycol is a mixture of three isomeric chemical compounds, 4-oxa-2,6-heptandiol, 2-(2-hydroxy-propoxy)-propan-1-ol, and 2-(2-hydroxy-1-methyl-ethoxy)-propan-1-ol. It is a colorless, nearly odorless liquid with a high boiling point and low toxicity.
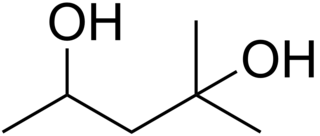
2-Methyl-2,4-pentanediol (MPD) is an organic compound with the formula (CH3)2C(OH)CH2CH(OH)CH3. This colourless liquid is a chiral diol. It is produced industrially from diacetone alcohol by hydrogenation. Total European and USA production was 15000 tonnes in 2000.

Swaminathan Sivaram is an Indian polymer chemist, inventor, institution builder and a former director of the National Chemical Laboratory, Pune. He is known for his pioneering work on alkylation of tertiary alkyl halides with trialkylaluminum and olefin polymerization and holds the highest number of US patents by an Indian working outside the US. He is a fellow of several significant professional organizations. The Government of India awarded him the fourth highest civilian honour of the Padma Shri, in 2006, for his contributions to Indian science.

Methyldichlorophosphine (alternatively known as dichloro(methyl)phosphane and methyl phosphonous dichloride) is an organophosphorus compound with the chemical formula CH3Cl2P. It is a colorless, corrosive, flammable, and highly reactive liquid with a pungent odor. It is also extremely toxic if inhaled, can cause burns upon contact with the skin and eyes, and releases fumes of hydrochloric acid in moist environments.



















