
Iron(III) chloride is the inorganic compound with the formula. Also called ferric chloride, it is a common compound of iron in the +3 oxidation state. The anhydrous compound is a crystalline solid with a melting point of 307.6 °C. The color depends on the viewing angle: by reflected light the crystals appear dark green, but by transmitted light they appear purple-red.

Lead(II) chloride (PbCl2) is an inorganic compound which is a white solid under ambient conditions. It is poorly soluble in water. Lead(II) chloride is one of the most important lead-based reagents. It also occurs naturally in the form of the mineral cotunnite.

Nickel(II) chloride (or just nickel chloride), is the chemical compound NiCl2. The anhydrous salt is yellow, but the more familiar hydrate NiCl2·6H2O is green. Nickel(II) chloride, in various forms, is the most important source of nickel for chemical synthesis. The nickel chlorides are deliquescent, absorbing moisture from the air to form a solution. Nickel salts have been shown to be carcinogenic to the lungs and nasal passages in cases of long-term inhalation exposure.

Iron(II) chloride, also known as ferrous chloride, is the chemical compound of formula FeCl2. It is a paramagnetic solid with a high melting point. The compound is white, but typical samples are often off-white. FeCl2 crystallizes from water as the greenish tetrahydrate, which is the form that is most commonly encountered in commerce and the laboratory. There is also a dihydrate. The compound is highly soluble in water, giving pale green solutions.

A sulfoxide is a chemical compound containing a sulfinyl (SO) functional group attached to two carbon atoms. It is a polar functional group. Sulfoxides are the oxidized derivatives of sulfides. Examples of important sulfoxides are alliin, a precursor to the compound that gives freshly crushed garlic its aroma, and dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO), a common solvent.

Scandium(III) chloride is the inorganic compound with the formula ScCl3. It is a white, high-melting ionic compound, which is deliquescent and highly water-soluble. Scandium(III) chloride is mainly of interest in the research laboratory. Both the anhydrous form and hexahydrate (ScCl3•6H2O) are commercially available.

Bismuthine (IUPAC name: bismuthane) is the chemical compound with the formula BiH3. As the heaviest analogue of ammonia (a pnictogen hydride), BiH3 is unstable, decomposing to bismuth metal well below 0 °C. This compound adopts the expected pyramidal structure with H-Bi-H angles of around 90°.

Platinum(II) chloride is the chemical compound PtCl2. It is an important precursor used in the preparation of other platinum compounds. It exists in two crystalline forms, but the main properties are somewhat similar: dark brown, insoluble in water, diamagnetic, and odorless.

Bismuth chloride (or butter of bismuth) is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula BiCl3. It is a covalent compound and is the common source of the Bi3+ ion. In the gas phase and in the crystal, the species adopts a pyramidal structure, in accord with VSEPR theory.
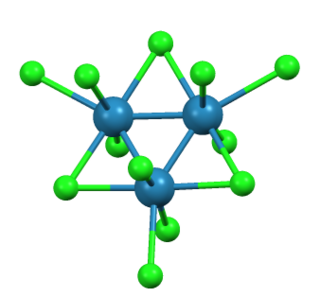
Trirhenium nonachloride is a compound with the formula ReCl3, sometimes also written Re3Cl9. It is a dark red hygroscopic solid that is insoluble in ordinary solvents. The compound is important in the history of inorganic chemistry as an early example of a cluster compound with metal-metal bonds. It is used as a starting material for synthesis of other rhenium complexes.
Molybdenum tetrachloride is the inorganic compound with the empirical formula MoCl4. The material exists as two polymorphs, a polymeric ("α") and a hexameric ("β") structure, although neither form is soluble in any solvent without degradation. In each polymorph, the Mo center is octahedral with two terminal chloride ligands and four doubly bridging ligands.

Bismuth is a chemical element with the symbol Bi and atomic number 83. It is a pentavalent post-transition metal and one of the pnictogens with chemical properties resembling its lighter group 15 siblings arsenic and antimony. Elemental bismuth may occur naturally, although its sulfide and oxide form important commercial ores. The free element is 86% as dense as lead. It is a brittle metal with a silvery white color when freshly produced, but surface oxidation can give it an iridescent tinge in numerous colours. Bismuth is the most naturally diamagnetic element, and has one of the lowest values of thermal conductivity among metals.
Bismuth pentafluoride is an inorganic compound with the formula BiF5. It is a white solid that is highly reactive. The compound is of interest to researchers but not of particular value.
Organobismuth chemistry is the chemistry of organometallic compounds containing a carbon to bismuth chemical bond. Applications are few. The main bismuth oxidation states are Bi(III) and Bi(V) as in all higher group 15 elements. The energy of a bond to carbon in this group decreases in the order P > As > Sb > Bi. The first reported use of bismuth in organic chemistry was in oxidation of alcohols by Challenger in 1934 (using Ph3Bi(OH)2). Knowledge about methylated species of bismuth in environmental and biological media is limited.

Bismuth oxychloride is an inorganic compound of bismuth with the formula BiOCl. It is a lustrous white solid used since antiquity, notably in ancient Egypt. Light wave interference from its plate-like structure gives a pearly iridescent light reflectivity similar to nacre. It is also known as pearl white.

In chemistry, subhalide usually refers to inorganic compounds that have a low halide:metal ratio, made possible by metal–metal bonding, sometimes extensive. Many compounds meet this definition.
Molecular oxohalides (oxyhalides) are a group of chemical compounds in which both oxygen and halogen atoms are attached to another chemical element A in a single molecule. They have the general formula AOmXn, X = F, Cl, Br, I. The element A may be a main group element, a transition element or an actinide. The term oxohalide, or oxyhalide, may also refer to minerals and other crystalline substances with the same overall chemical formula, but having an ionic structure.

Pentamethylbismuth (or pentamethylbismuthorane) is an organometalllic compound containing five methyl groups bound to a bismuth atom with formula Bi(CH3)5. It is an example of a hypervalent compound. The molecular shape is trigonal bipyramid.
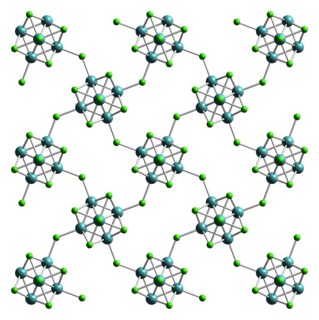
Tungsten(II) chloride is the inorganic compound with the formula W6Cl12. It is a polymeric cluster compound. The material dissolves in concentrated hydrochloric acid, forming (H3O)2[W6Cl14](H2O)x. Heating this salt gives yellow-brown W6Cl12. The structural chemistry resembles that observed for molybdenum(II) chloride.

Tungsten(III) chloride is the inorganic compound with the formula W6Cl18. It is a cluster compound. It is a brown solid, obtainable by chlorination of tungsten(II) chloride. Featuring twelve doubly bridging chloride ligands, the cluster adopts a structure related to the corresponding chlorides of niobium and tantalum. In contrast, W6Cl12 features eight triply bridging chlorides.

















