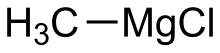 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name chlorido(methyl)magnesium | |
| Other names (chloromagnesio)methane | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.010.573 |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID | |
| UNII |
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| CH3MgCl | |
| Molar mass | 74.79 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | colorless solid |
| Reacts with water | |
| Solubility | soluble in diethyl ether and THF |
| Hazards | |
| Occupational safety and health (OHS/OSH): | |
Main hazards | Flammable, reacts violently with water, severe skin burns and serious eye damage |
| GHS labelling: | |
  | |
| Danger | |
| H225, H250, H260, H314 | |
| P210, P222, P223, P231+P232, P233, P240, P241, P242, P243, P260, P264, P280, P301+P330+P331, P302+P334, P303+P361+P353, P304+P340, P305+P351+P338, P310, P321, P335+P334, P363, P370+P378, P402+P404, P403+P235, P405, P422, P501 | |
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |
| Flash point | −17 °C (1 °F; 256 K) |
| Related compounds | |
Related compounds | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
Methylmagnesium chloride is an organometallic compound with the general formula CH3MgCl. This highly flammable, colorless, and moisture sensitive compound is the simplest Grignard reagent and is commercially available, usually as a solution in tetrahydrofuran.

