Related Research Articles

The Muslim period in the Indian subcontinent or Indo-Muslim period is conventionally said to have started in 712, after the conquest of Sindh and Multan by the Umayyad Caliphate under the military command of Muhammad ibn al-Qasim. It began in the Indian subcontinent in the course of a gradual conquest. The perfunctory rule by the Ghaznavids in Punjab was followed by Ghurids, and Sultan Muhammad of Ghor is generally credited with laying the foundation of Muslim rule in Northern India.

The Maratha Confederacy, also referred to as the Maratha Empire, was an early modern polity in the Indian subcontinent. It comprised the realms of the Peshwa and four major independent Maratha states often subordinate to the former. It was established in 1674 with the coronation of Shivaji as the Maratha Chhatrapati and recognised by Emperor Bahadur Shah I as a tributary state in 1707 following a prolonged rebellion. Following this, the Marathas continued to recognise the Mughal emperor as their nominal suzerain, similar to other contemporary Indian entities, though in practice, imperial politics at Delhi were largely influenced by the Marathas between 1737 and 1803.
Rajput, also called Thakur, is a large multi-component cluster of castes, kin bodies, and local groups, sharing social status and ideology of genealogical descent originating from the northern part of the Indian subcontinent. The term Rajput covers various patrilineal clans historically associated with warriorhood: several clans claim Rajput status, although not all claims are universally accepted. According to modern scholars, almost all Rajput clans originated from peasant or pastoral communities.

Mirza Nasir-ud-Din Muḥammad Shah was the thirteenth Mughal emperor from 1719 to 1748. He was son of Khujista Akhtar, the fourth son of Bahadur Shah I. After being chosen by the Sayyid Brothers of Barha, he ascended the throne at the young age of 16, under their strict supervision.

Balaji Baji Rao, often referred to as Nana Saheb I, was the 8th Peshwa of the Maratha Confederacy. He was appointed as Peshwa in 1740 upon the death of his father, the Peshwa Bajirao I.

Bahuchara Mata is a Hindu goddess of chastity and fertility in her maiden aspect, of the incarnation of the Hinglaj. The goddess grants favours, especially to male children, and cures diseases. Like other divinities in Gujarat and Rajasthan, Bahuchara is of Charan an origin. She is also considered the patroness of the hijra community. Her primary temple is located in Becharaji town in Mehsana district of Gujarat, India.
Parmar, also known as Panwar or Pawar, is a Kshatriya (Rajput) clan belonging to the Agnivansha lineage of Kshatriyas. They are primarily found in Northern and Central India, especially in Rajasthan, Gujarat, Madhya Pradesh, Punjab, Haryana, Uttarakhand, Himachal Pradesh, Uttar Pradesh, Bihar, Jharkhand, and North Maharashtra.

Patidar, formerly known as Kanbi, is an Indian land-owning and peasant caste and community native to Gujarat. The community comprises at multiple subcastes, most prominently the Levas and Kadvas. They form one of the dominant castes in Gujarat. The title of Patidar originally conferred to the land owning aristocratic class of Gujarati Kanbis; however, it was later applied en masse to the entirety of the Kanbi population who lay claim to a land owning identity, partly as a result of land reforms during the British Raj.
Garasia alternatively spelled Girasia, Girasiya or Garasiya, is a title used by tribal chieftains and members of other arms bearing lineages in India who held the villages as Giras granted by rulers.
The history of Gujarat began with Stone Age settlements followed by Chalcolithic and Bronze Age settlements like Indus Valley civilisation. Gujarat's coastal cities, chiefly Bharuch, served as ports and trading centers in the Nanda, Maurya, Satavahana and Gupta empires as well as during the Western Kshatrapas period. After the fall of the Gupta empire in the 6th century, Gujarat flourished as an independent Hindu-Buddhist state. The Maitraka dynasty, descended from a general of the Gupta empire, ruled the Kingdom of Valabhi the 6th to the 8th centuries, although they were ruled briefly by Harsha during the 7th century. The Arab rulers of Sindh sacked Vallabhi in 770, bringing the Kingdom of Valabhi to an end. In 775, the first Parsi (Zoroastrian) refugees arrived in Gujarat from Greater Iran.

The Gujarat Sultanate or Sultanate of Guzerat was a late medieval Islamic Indian kingdom in Western India, primarily in the present-day state of Gujarat. The kingdom was established in 1394 when Muzaffar Shah I, the Governor of Gujarat, declared independence from the Tughlaq dynasty of Delhi.

The Rathva or Rathwa is a Subcaste of the Koli caste found in the Indian state of Gujarat. Rathava Kolis were agriculturist by profession and turbulent by habits but now lives like Adivasis such as Bhil because of their neighborhood
The Kotwal also spelled as Cotwal, or Kotval, was a title used in medieval and early modern period for the leader of a Kot or fort. Kotwals often controlled the fort of a major town or an area of smaller towns on behalf of another ruler. It was similar in function to a British Indian Zaildar From Mughal times the title was given to the local ruler of a large town and the surrounding area. However, the title is also used for leaders in small villages as well. Kotwal has also been translated as Chief police officer. The post of Kotwal was known since ancient times as Kota pala who was the chief of Police.

Baroda State was a kingdom within the Maratha Confederacy and later a princely state in present-day Gujarat. It was ruled by the Gaekwad dynasty from its formation in 1721 until its accession to the newly formed Dominion of India. With the city of Baroda (Vadodara) as its capital, its relations with the British Raj authorities were managed by the Baroda Residency. The revenue of the state in 1901 was Rs. 13,661,000. Baroda merged into the Dominion of India on 1 May 1949, before which an interim government was formed in the state.
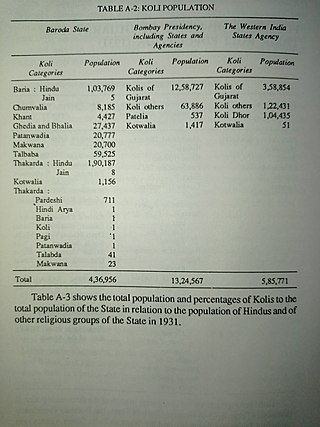
The Baria Koli, or Baraiya Koli, Bareeya Koli and Bariya Koli is a clan (Gotra) of the Koli caste found in the Indian State of Gujarat and Dadra and Nagar Haveli and Daman and Diu. the Devgad Baria was their Stronghold or given their name to Baria State in Gujarat.

The Koli is an Indian caste found in Rajasthan, Himachal Pradesh, Gujarat, Maharashtra, Uttar Pradesh, Haryana, Karnataka, Odisha and Jammu and Kashmir states in India. Koli is an agriculturist caste of Gujarat but in coastal areas they also work as fishermen along with agriculture. In the beginning of 20th century, the Koli caste was recognised as a denotified tribe under Criminal Tribes Act by the Indian Government because of their anti-social activities during World War I.

The Muslim Khatris are desandants of the Khatri community of Indian subcontinent which embraced Islam during medieval period. They are now mostly concentrated in Pakistani provinces of Punjab, Sindh, Azad Kashmir as well as northern India. The community is scattered throughout Punjab and Kutch region.
Modern historians agree that Rajputs consisted of a mix of various different social groups and different varnas. Rajputisation explains the process by which such diverse communities coalesced into the Rajput community.

The Chunvalia Koli, or Chuvalia Koli, Chunwalia Koli is a subcaste of the Koli caste, found in the Indian state of Gujarat. The Chunvalia Kolis were the first Indian caste to adopt the game of cricket in India. Chunvalia Kolis were classified as a Criminal Tribe under Criminal Tribes Act by government of the British Raj because of their purported anti-social behaviour and activities, such as alleged dacoity in Gujarat. During the First World War, Chunwalia Kolis were enlisted as soldiers in British Indian Army by the Bombay government of British India.
The Nathaji Patel was Gameti of the Chandap estate in Baroda State's territory during the British Raj in India. During the Indian rebellion of 1857, Nathaji Patel rose up against British rule and challenged the British authority in Baroda territory.
References
- ↑ Krishan, Shri (7 April 2005). Political Mobilization and Identity in Western India, 1934-47. New Delhi, India: SAGE Publishing India. ISBN 978-93-5280-307-1.
- ↑ Bhatnagar, Rashmi Dube; Dube, Renu; Dube, Reena (1 February 2012). Female Infanticide in India: A Feminist Cultural History. New Delhi, India, Asia: State University of New York Press. p. 266. ISBN 978-0-7914-8385-5.
- ↑ Shah, A. M. (2002). Exploring India's Rural Past: A Gujarat Village in the Early Nineteenth Century. New Delhi, India: Oxford University Press. p. 28-30. ISBN 978-0-19-565732-6.
- ↑ Lobo, Lancy (1995). The Thakors of North Gujarat: A Caste in the Village and the Region. New Delhi, India: Hindustan Publishing Corporation. p. 200. ISBN 978-81-7075-035-2.
- ↑ Dominance and State Power in Modern India: Decline of a Social Order (2nd ed.). New Delhi, India, Asia: Oxford University Press. 1989. p. 66. ISBN 978-0-19-562098-6.
- ↑ Patel, Govindlal Dalsukhbhai (1954). The Indian Land Problem and Legislation. New Delhi, India: N. M. Tripathi. p. 78.
- ↑ Kamerkar, Mani (1980). British Paramountcy: British-Baroda Relations, 1818-1848. New Delhi, India: Popular Prakashan. p. 33. ISBN 978-0-940500-75-4.
- ↑ Shah 2002, p. 39.
- ↑ Gidwani, Vinay Krishin (1996). Fluid Dynamics: An Essay on Canal Irrigation and the Processses of Agrarian Change in Matar Taluka (Gujarat). India. New Delhi, India: University of California, Berkeley. pp. 165–167.