Rewa Kantha Agency Last updated December 09, 2025 History The native states came under British subsidiary alliances after the Third Anglo-Maratha War of the early 19th century. [ 3]
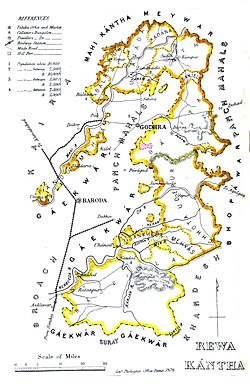
The total surface was 4,971.75 square miles, comprising 3,412 villages, with a population of 479,055, yielding 2,072,026 Rupees state revenue and paying 147,826 Rupees tribute (mostly to the Gaikwar Baroda State ).
In 1937 the princely states of the Rewa Kantha Agency were merged with Baroda State in order to form the Baroda and Gujarat States Agency , [ 4] which in turn merged in 1944 with the Western India States Agency as Baroda, Western India and Gujarat States Agency .
After the Independence of British India in 1947, split into India and Pakistan, the rulers of the states all agreed to accede to the Government of India and were integrated into Bombay State . Bombay state was split along linguistic lines in 1960, and Rewa Kantha became part of Gujarat , like Saurashtra State .
Princely States The number of separate states was 61, [ 2] mostly minor or petty states except for five. Many of them were under British influence; the largest one was Rajpipla . [ 2] [ 5]
The Agency also dealt with five first-class states named Chhota Udaipur State , Devgadh Bariya State , Santrampur , Lunawada State and Balasinor State . The total area of the states the agency related to was 12,877 km 2 (4,972 sq mi) . In 1901 their population was 479,065. Many of the inhabitants were Bhils and Kolis . [ 6]
Rewa Kantha division (includes all the main states; in direct relations with the Political Agent at Godhra)
Salute states :
Rajpipla (Nandod), First Class, title Maharaja, Hereditary salute of 13-guns Bari(y)a (Devgadh), Second Class, title Maharaol, Hereditary salute of 9-guns (11-guns personal) Lunavada , Second Class, title Maharana, Hereditary salute of 9-guns Balasinor , Second Class, title Nawab, Hereditary salute of 9-guns Sant (Sunth) (Rampur), Second Class, title Maharana, Hereditary salute of 9-guns Chhota Udepur , First Class, title Maharaja Maharawal, Hereditary Salute of 11 - guns Non-salute states :
Mehwas Only non-salute states: two geographical groups of minor or petty rural (e)states
Sankheda (near Narmada River )
Mandwa , Third Class (personal) / Fourth Class Gad Boriad , Third Class (personal) / Fourth Class Shanor , Fourth Class Vajiria , Fourth Class Vanmala , Fourth Class (personal) / Fifth Class Nangam , Fifth Class Uchad , Agar , Palasni , Khareda , Borkhad , Bhilodia : Vasan Virpur , Vora , Vasan Sewada , Virampura Alwa , Chorangla State , Sindhiapura , Bihora State , Vadia (Virampura), Dudhpur , Rampura , Jiral Kamsoli , Chudesar State , Pantalavdi : Rengan , Nalia , Nasvadi Pandu (near Mahi River ; all paying tribute to the Gaekwar Baroda State ) :
Bhadarwa , Third Class Umetha , Third (personal) / Fourth Class Sihora (Gujarat) Fourth Class Pandu , Fifth Class Chhaliar State , Mevli , Kanoda , Poicha , Dhari , Itwad , Gotardi , Litter Gothda State , Amrapur , Vakhtapur , Jesar , Moka Paginu Muvadu , Kasla Paginu Muvadu , Rajpur , Moti Varnol , Nahara Jumkha , Nani Varnol , Varnolmal , Angadh , the Dorka (e)states Fiscal Stamps In addition to those of Rewa Kantha Agency itself, revenue and/or court fee stamps were issued for the following native states :
in the Rewa Kantha Division (all) Rajpipla Balasinor Baria Lunavada Sant Chhota Udaipur Jambughoda Kadana Sanjeli in the Sankheda Mehwas (only these) Gad Boriad Naswadi Shanor Vajiria in the Pandu Mehwas (only these) Bhadarva Pandu Mewas Umeta Bakrol (Boru) Sources and external links
This page is based on this
Wikipedia article Text is available under the
CC BY-SA 4.0 license; additional terms may apply.
Images, videos and audio are available under their respective licenses.