
Belarus, officially the Republic of Belarus, is a landlocked country in Eastern Europe. It is bordered by Russia to the east and northeast, Ukraine to the south, Poland to the west, and Lithuania and Latvia to the northwest. Covering an area of 207,600 square kilometres (80,200 sq mi) and with a population of 9.4 million, Belarus is the thirteenth-largest and the twentieth-most populous country in Europe. The country is administratively divided into seven regions. Minsk is the capital and largest city.

Moscow is the capital and largest city of Russia. The city stands on the Moskva River in Central Russia, with a population estimated at 12.4 million residents within the city limits, over 17 million residents in the urban area, and over 20 million residents in the metropolitan area. The city covers an area of 2,511 square kilometres (970 sq mi), while the urban area covers 5,891 square kilometres (2,275 sq mi), and the metropolitan area covers over 26,000 square kilometres (10,000 sq mi). Moscow is among the world's largest cities, being the largest city entirely in Europe, the largest urban area in Europe, the largest metropolitan area in Europe, and the largest city by land area on the European continent.

Russia, or the Russian Federation, is a country spanning Eastern Europe and North Asia. It is the largest country in the world, covering over 17 million square kilometres (6.6 sq mi), and encompassing more than one-eighth of the Earth's inhabited land area. Russia extends across eleven time zones, and has borders with sixteen sovereign nations. It has a population of 146.2 million; and is the most populous country in Europe, and the ninth-most populous country in the world. Moscow, the capital, is the largest city in Europe, while Saint Petersburg is the nation's second-largest city and cultural centre. Russians are the largest Slavic and European nation; they speak Russian, the most spoken Slavic language, and the most spoken native language in Europe.

Russian is an East Slavic language native to the Russian people of Eastern Europe. Part of the Indo-European language family, Russian is one of four living East Slavic languages, and also part of the larger Balto-Slavic branch. It is an official language in Russia, Belarus, Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, and is used widely throughout the Caucasus, Central Asia, and—to some extent—in the Baltic states. Russian was the de facto language of the Soviet Union (USSR) until its dissolution on 26 December 1991; Russian is used in an official capacity or in public life in all the post-Soviet nation-states. The language is one of the six official languages of the United Nations.

The Soviet Union, officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics (USSR), was a federal socialist state in Northern Eurasia that existed from 1922 to 1991. Nominally a union of multiple national Soviet republics, in practice its government and economy were highly centralized until its final years. It was a one-party state prior to 1990 governed by Communist Party of the Soviet Union, with Moscow as its capital in its largest republic, the Russian SFSR. Other major urban centers were Leningrad, Kiev, Minsk, Tashkent, Alma-Ata and Novosibirsk. It was the largest country in the world by surface area, spanning over 10,000 kilometers (6,200 mi) east to west across 11 time zones and over 7,200 kilometers (4,500 mi) north to south. Its territory included much of Eastern Europe, parts of Northern Europe and Western Asia, and all of Central and North Asia. Its five biomes were tundra, taiga, steppes, desert, and mountains. Its diverse population was officially known as the Soviet people.

Ukraine is a country in Eastern Europe. It is the second-largest country in Europe, after Russia, which it borders to the east and north-east. Ukraine also shares borders with Belarus to the north; Poland, Slovakia, and Hungary to the west; Romania and Moldova to the south; and has a coastline along the Sea of Azov and the Black Sea. It covers an area of 603,628 km2 (233,062 sq mi), with a population of about 41.5 million, and is the eighth-most populous country in Europe. The country's capital and largest city is Kyiv.

Vladimir Vladimirovich Putin is a Russian politician and former intelligence officer who is serving as the current president of Russia since 2012, previously being in the office from 1999 until 2008. He was also prime minister from 1999 to 2000 and again from 2008 to 2012. As of 2021, Putin is the second-longest serving European president, after Alexander Lukashenko of Belarus.

Catherine II, most commonly known as Catherine the Great, was empress regnant of All Russia from 1762 until 1796 – the country's longest-ruling female leader. She came to power following a coup d'état that overthrew her husband and second cousin, Peter III. Under her reign, Russia grew larger, its culture was revitalised, and it was recognised as one of the great powers of Europe.

The Crimean War was a military conflict fought from October 1853 to February 1856 in which Russia lost to an alliance made up of France, the Ottoman Empire, the United Kingdom and Sardinia. The immediate cause of the war involved the rights of Christian minorities in the Holy Land, then a part of the Ottoman Empire. The French promoted the rights of Roman Catholics, while Russia promoted those of the Eastern Orthodox Church. Longer-term causes involved the decline of the Ottoman Empire and the unwillingness of Britain and France to allow Russia to gain territory and power at the Ottoman Empire's expense. It has widely been noted that the causes, in one case involving an argument over a key, have never revealed a "greater confusion of purpose", yet they led to a war that stood out for its "notoriously incompetent international butchery".

Crimea is a peninsula located on the northern coast of the Black Sea in Eastern Europe that is almost completely surrounded by both the Black Sea and the smaller Sea of Azov to the northeast. Crimea is located south of the Ukrainian region of Kherson, to which it is connected by the Isthmus of Perekop, and west of the Russian region of Kuban, from which it is separated by the Strait of Kerch though linked by the Crimean Bridge since 2018. The Arabat Spit is located to the northeast, a narrow strip of land that separates a system of lagoons named Sivash from the Sea of Azov. Across the Black Sea to its west is Romania, and to its south, Turkey.

RT is a Russian state-controlled international television network funded by the federal tax budget of the Russian government. It operates pay television channels directed to audiences outside of Russia, as well as providing Internet content in English, Spanish, French, German, Arabic, and Russian.

The Russian Empire was a historical empire that extended across Eurasia and North America from 1721, following the end of the Great Northern War, until the Republic was proclaimed by the Provisional Government that took power after the February Revolution of 1917. The third-largest empire in history, at its greatest extent stretching over three continents, Europe, Asia, and North America, the Russian Empire was surpassed in size only by the British and Mongol empires. The rise of the Russian Empire coincided with the decline of neighboring rival powers: the Swedish Empire, the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, Persia and the Ottoman Empire. It played a major role in 1812–1814 in defeating Napoleon's ambitions to control Europe and expanded to the west and south, becoming one of the most powerful European empires of all time.

Saint Petersburg, formerly known as Petrograd (1914–1924) and later Leningrad (1924–1991), is the second-largest city in Russia. The city is situated on the Neva River, at the head of the Gulf of Finland on the Baltic Sea, with a population of roughly 5.4 million residents. It is the fourth-most populous city in Europe, the most populous city on the Baltic Sea, as well as the world's northernmost city with over 1 million residents. As an important Russian port on the Baltic Sea, it is governed as a federal city.

Nicholas II or Nikolai II Alexandrovich Romanov, known in the Russian Orthodox Church as Saint Nicholas the Passion-Bearer, was the last Emperor of All Russia, ruling from 1 November 1894 until his abdication on 15 March 1917. During his reign, Russia embarked on a series of reforms including the introduction of civil liberties, literacy programs, state representation, and initiatives to modernize the empire's infrastructure. Ultimately, this progress was undermined by Nicholas's commitment to autocratic rule, as well as defeats sustained by the Russian military in the Russo-Japanese war and World War I. By March 1917, public support for Nicholas had collapsed and he was forced to abdicate the throne, thereby ending the Romanov dynasty's 300-year rule of Russia.
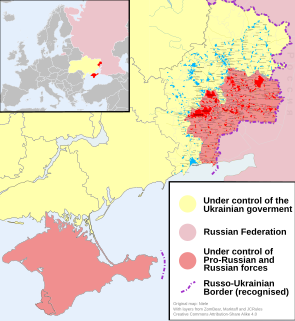
The Russo-Ukrainian War is an ongoing and protracted conflict between Russia and Ukraine that began in February 2014. The war has centered around the status of the Ukrainian regions of Crimea and Donbas.

The Crimean Peninsula, north of the Black Sea in Eastern Europe, was annexed by the Russian Federation between February and March 2014 and since then has been administered as two Russian federal subjects—the Republic of Crimea and the federal city of Sevastopol. The annexation from Ukraine followed a Russian military intervention in Crimea that took place in the aftermath of the 2014 Ukrainian revolution and was part of wider unrest across southern and eastern Ukraine.
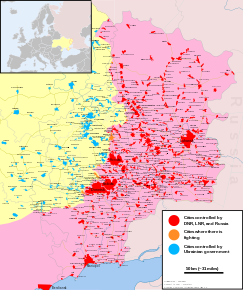
The war in Donbas, also known as the Donbas war, is an armed conflict in the Donbas region of Ukraine, part of the Ukrainian crisis and the broader Russo-Ukrainian War. From the beginning of March 2014, in the aftermath of the 2014 Ukrainian revolution and the Euromaidan movement, protests by Russia-backed anti-government separatist groups took place in the Donetsk and Luhansk oblasts of Ukraine, collectively called the Donbas region. These demonstrations, which followed the February–March 2014 annexation of Crimea by the Russian Federation, and which were part of a wider group of concurrent protests across southern and eastern Ukraine, escalated into an armed conflict between the separatist forces of the self-declared Donetsk and Luhansk People's Republics, and the Ukrainian government. While the initial protests were largely native expressions of discontent with the new Ukrainian government, Russia took advantage of them to launch a co-ordinated political and military campaign against Ukraine. Russian citizens led the separatist movement in Donetsk from April until August 2014, and were supported by volunteers and materiel from Russia. As the conflict escalated in May 2014, Russia employed a "hybrid approach", deploying a combination of disinformation tactics, irregular fighters, regular Russian troops, and conventional military support to destabilise the Donbas region. According to the Ukrainian government, at the height of the conflict in the summer of 2014, Russian paramilitaries were reported to make up between 15% to 80% of the combatants.

This is a timeline of events related to Russian interference in the 2016 United States elections.

The Special Counsel investigation was an investigation of Russian interference in the 2016 United States elections, of links between associates of Donald Trump and Russian officials, and of possible obstruction of justice by Trump and his associates. The investigation was conducted by special prosecutor Robert Mueller from May 2017 to March 2019. It was also called the Russia investigation, the Mueller probe, and the Mueller investigation. The Mueller investigation culminated with the Mueller Report, which concluded that though the Trump campaign welcomed Russian interference and expected to benefit from it, there was insufficient evidence to bring any conspiracy charges against Trump or his associates. The report did not reach a conclusion about possible obstruction of justice of Trump, citing a Justice Department guideline that prohibits the federal indictment of a sitting president. The investigation resulted in charges against 34 individuals and 3 companies, 8 guilty pleas, and a conviction at trial.

Sputnik V is a viral vector vaccine for COVID-19 developed by the Gamaleya Research Institute of Epidemiology and Microbiology. Registered on 11 August 2020 by the Russian Ministry of Health as Gam-COVID-Vac, Sputnik V is an adenovirus viral vector vaccine. The "V" designates the letter of the English alphabet, not the Roman numeral for five.


















