
Maverick County is a county located in the U.S. state of Texas. As of the 2020 census, its population was 57,887. Its county seat is Eagle Pass. The county was created in 1856 and organized in 1871. It is named for Samuel Maverick, cattleman and state legislator.

Coahuila, formally Coahuila de Zaragoza, officially the Free and Sovereign State of Coahuila de Zaragoza, is one of the 32 states of Mexico.

Piedras Negras is a city and seat of the surrounding municipality of the same name in the Mexican state of Coahuila. It stands at the northeastern edge of Coahuila on the Mexico–United States border, across the Rio Grande from Eagle Pass in the U.S. state of Texas. In the 2015 census the city had a population of 163,595 inhabitants, while the metropolitan area had a population of 245,155 inhabitants. The Piedras Negras and the Eagle Pass areas are connected by the Eagle Pass–Piedras Negras International Bridge, Camino Real International Bridge, and the Union Pacific International Railroad Bridge.
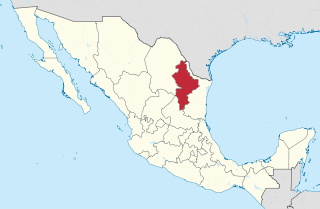
Nuevo León is a state in northeast Mexico. The state borders the Mexican states of Tamaulipas, Coahuila, Zacatecas, and San Luis Potosi, and has an extremely narrow international border with the U.S. state of Texas. With a population of 5.78 million people, it is the seventh-most populous federal entity in Mexico and the fourteenth most densely populated as of 2020. Nuevo León is the 13th-largest federal entity in Mexico by area, with a total land area of 64,156 square kilometers.

Adolfo Tomás Ruiz Cortines was a Mexican politician who served as President of Mexico from 1952 to 1958. A member of the Institutional Revolutionary Party (PRI), he previously served as Governor of Veracruz and Secretary of the Interior. During his presidency, which constituted the Mexican Miracle, women gained the right to vote, and he instigated numerous public health, education, infrastructure, and works projects.

Ignacio Anaya García was a Mexican maître d' who invented the popular Tex-Mex dish nachos at the Victory Club restaurant a couple miles from the border of Texas in Mexico in 1940. After nachos grew in popularity Anaya was promoted to chef, and he eventually started his own restaurant in the 1960s.

The Belisario Domínguez Medal of Honor is the highest award bestowed by the Mexican Senate.
Rafael Rojas is a Costa Rican former male fashion model and actor. He is known for his work in telenovelas, theater, and Mexican cinema.

The Mirador del Obispado is located at the top of the Cerro del Obispado in the northern city of Monterrey, Mexico. It features the biggest bandera monumental in Mexico. The hill and the lookout receive their name from the building constructed in the middle of the hill by the end of the 18th century, the Palacio del Obispado.

The National Professional Basketball League, officially known as the Liga Caliente LNBP for sponsorship reasons, is the top professional basketball league in Mexico. The league was founded in 2000 with 10 teams.
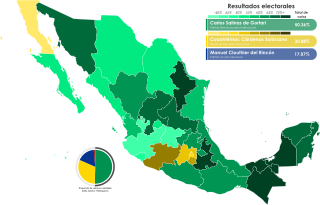
General elections were held in Mexico on 6 July 1988. They were the first competitive presidential elections in Mexico since the Institutional Revolutionary Party (PRI) took power in 1929. The elections were widely considered to have been fraudulent, with Salinas de Gortari and the PRI resorting to electoral tampering to remain in power.

General elections were held in Mexico on 7 July 1952. The presidential elections were won by Adolfo Ruiz Cortines, who received 74.3% of the vote. In the Chamber of Deputies election, the Institutional Revolutionary Party won 151 of the 161 seats. These were the last presidential elections in Mexico in which women were not allowed to vote.

Coras Fútbol Club commonly known as Coras de Tepic is a football club that plays in the Mexican football league system Mexican Liga Premier (third-tier). The club was founded in the late 1950s as Deportivo Tepic and is based in Piedras Negras, Coahuila, Mexico.
The Serie A has 34 teams divided into two groups. For the 2023–24 season, it will be a return of a season-long tournament consisting of 34 total matches played home & away and the liguilla. The top 7 teams from each group at the end of the season will play in the Liguilla for a spot to play for promotion to Liga de Expansión MX provided that their stadiums meet the requirements to ascend.
Events in the year 1983 in Mexico.
Events in the year 1962 in Mexico.
This is a list of events that happened in 2017 in Mexico. The article also lists the most important political leaders during the year at both federal and state levels.
This is a list of events that happened in 2018 in Mexico. The article also lists the most important political leaders during the year at both federal and state levels.
This article lists events occurring in Mexico during the year 2021. The article lists the most important political leaders during the year at both federal and state levels and will include a brief year-end summary of major social and economic issues. Cultural events, including major sporting events, are also listed. For a more expansive list of political events, see 2021 in Mexican politics and government.
This article lists events occurring in Mexico during the year 2022. The article lists the most important political leaders during the year at both federal and state levels and will include a brief year-end summary of major social and economic issues. Cultural events, including major sporting events, are also listed.












