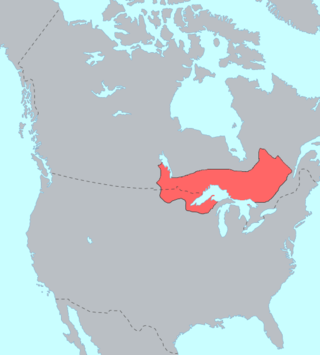
The Ojibwe are an Anishinaabe people whose homeland covers much of the Great Lakes region and the northern plains, extending into the subarctic and throughout the northeastern woodlands. Ojibweg, being Indigenous peoples of the Northeastern Woodlands and of the subarctic, are known by several names, including Ojibway or Chippewa. As a large ethnic group, several distinct nations also understand themselves to be Ojibwe as well, including the Saulteaux, Nipissings, and Oji-Cree.
Sandy Lake Band of Mississippi Chippewa are a historical Ojibwa tribe located in the upper Mississippi River basin, on and around Big Sandy Lake in what today is in Aitkin County, Minnesota. Though politically folded into the Mille Lacs Band of Ojibwe, thus no longer independently federally recognized, for decades, Sandy Lake Band members have been leading efforts to restore their independent Federal recognition.

The White Earth Indian Reservation is home to the White Earth Band, in northwestern Minnesota. It is the largest Indian reservation in the state by land area. The reservation includes all of Mahnomen County, plus parts of Becker and Clearwater counties in the northwest part of the state along the Wild Rice and White Earth rivers. The reservation's land area is 1,093 square miles (2,830 km2). The population was 9,726 as of the 2020 census, including off-reservation trust land. The White Earth Indian Reservation is one of six bands that make up the Minnesota Chippewa Tribe, their governing body for major administrative needs. It is about 225 miles (362 km) from Minneapolis–Saint Paul and roughly 65 miles (105 km) from Fargo–Moorhead.

The White Earth Band of the Minnesota Chippewa Tribe, also called the White Earth Nation, is a federally recognized Native American band located in northwestern Minnesota. The band's land base is the White Earth Indian Reservation.
Mille Lacs Indian Reservation is the popular name for the land-base for the Mille Lacs Band of Ojibwe in Central Minnesota, about 100 miles (160 km) north of Minneapolis-St. Paul. The contemporary Mille Lacs Band reservation has significant land holdings in Mille Lacs, Pine, Aitkin and Crow Wing counties, as well as other land holdings in Kanabec, Morrison, and Otter Tail Counties. Mille Lacs Indian Reservation is also the name of a formal Indian reservation established in 1855. It is one of the two formal reservations on which the contemporary Mille Lacs Band retains land holdings. The contemporary Mille Lacs band includes several aboriginal Ojibwe bands and villages, whose members reside in communities throughout central Minnesota.

The Mille Lacs Band of Ojibwe, also known as the Mille Lacs Band of Chippewa Indians, is a federally recognized American Indian tribe in east-central Minnesota. The Band has 4,302 members as of 2012. Its homeland is the Mille Lacs Indian Reservation, consisting of District I, District II, District IIa, and District III.
The Mille Lacs Indians, also known as the Mille Lacs and Snake River Band of Chippewa, are a Band of Indians formed from the unification of the Mille Lacs Band of Mississippi Chippewa (Ojibwe) with the Mille Lacs Band of Mdewakanton Sioux (Dakota). Today, their successor apparent Mille Lacs Band of Ojibwe consider themselves as being Ojibwe, but many on their main reservation have the ma'iingan (wolf) as their chief doodem (clan), which is an indicator of Dakota origins.
Mississippi River Band of Chippewa Indians or simply the Mississippi Chippewa, are a historical Ojibwa Band inhabiting the headwaters of the Mississippi River and its tributaries in present-day Minnesota.

The Snake River is a 104-mile-long (167 km) tributary of the St. Croix River in east-central Minnesota in the United States. It is one of three streams in Minnesota with this name. Its name is a translation from the Ojibwa Ginebigo-ziibi, after the Dakota peoples who made their homes along this river. Kanabec County's name is derived from the Ojibwe word for this river.

Mille Lacs Kathio State Park, also known as Kathio Site, is a Minnesota state park on Mille Lacs Lake. The park preserves habitation sites and mound groups, believed to date between 3000 BC and 1750 AD, that document Dakota Indian culture and Ojibwe-Dakota relationships. The park contains 19 identified archaeological sites, making it one of the most significant archaeological collections in Minnesota. The earliest site dates to the Archaic period and shows evidence of copper tool manufacture. The Dakota lived in this area roughly until the 18th century, when many bands of them were moving southward into the prairies and river areas of southern Minnesota. At the same time, Ojibwe (Anishinaabe) were moving in from the east. Ojibwe oral tradition, published by William Whipple Warren, suggests that there was a battle in which they successfully took control of the area from the Lakota.
Maude Kegg was an Ojibwa writer, folk artist, and cultural interpreter. She was a member of the Mille Lacs Band of Ojibwe, located in east-central Minnesota.

The Sandy Lake Tragedy was the culmination in 1850 of a series of events centered in Big Sandy Lake, Minnesota that resulted in the deaths of several hundred Lake Superior Chippewa. Officials of the Zachary Taylor Administration and Minnesota Territory sought to relocate several bands of the tribe to areas west of the Mississippi River. By changing the location for fall annuity payments, the officials intended the Chippewa to stay at the new site for the winter, hoping to lower their resistance to relocation. Due to delayed and inadequate payments of annuities and lack of promised supplies, about 400 Ojibwe, mostly men and 12% of the tribe, died of disease, starvation and cold. The outrage increased Ojibwe resistance to removal. The bands effectively gained widespread public support to achieve permanent reservations in their traditional territories.
The Lake Superior Chippewa are a large number of Ojibwe (Anishinaabe) bands living around Lake Superior; this territory is considered part of northern Michigan, Wisconsin, and Minnesota in the United States. They migrated into the area by the seventeenth century, encroaching on the Eastern Dakota people who had historically occupied the area. The Ojibwe defeated the Eastern Dakota, who migrated west into the Great Plains after the final battle in 1745. While they share a common culture including the Anishinaabe language, this highly decentralized group of Ojibwe includes at least twelve independent bands in the region.
Lake Lena is an unincorporated community and Native American village in Ogema Township, Pine County, Minnesota, United States, located along the Lower Tamarack River. It currently is the administrative center for the Mille Lacs Indian Reservation, District III.

The St. Croix Chippewa Indians of Wisconsin are a federally recognized tribe of Ojibwe people located in Northwest Wisconsin, along the St. Croix River valley and watershed. The band had 1,054 members as of 2010.
Sandy Lake is an unincorporated community Native American village located in Turner Township, Aitkin County, Minnesota, United States. Its name in the Ojibwe language is Gaa-mitaawangaagamaag, meaning "Place of the Sandy-shored Lake". The village is administrative center for the Sandy Lake Band of Mississippi Chippewa, though the administration of the Mille Lacs Indian Reservation, District II, is located in the nearby East Lake.

The Snake River Trading Post is a reconstructed fur trade post on the Snake River west of Pine City, Minnesota, United States of America. The post was established in the fall of 1804 by John Sayer, a partner in the North West Company, and built by his crew of voyageurs. The site operated for several years, although its exact period of operation is unknown. It was later destroyed by fire.

Fort Ripley was a United States Army outpost on the upper Mississippi River, in mid-central Minnesota from 1848 to 1877. It was situated a few miles from the Indian agencies for the Ho-Chunk and Ojibwe in Iowa Territory and then the Minnesota Territory. Its presence spurred immigration into the area and the pioneer settlement of Crow Wing developed approximately 6.75 miles (10.86 km) north of the fort. The post was initially named Fort Marcy. It then was renamed Fort Gaines and in 1850 was renamed again for distinguished Brigadier General Eleazer Wheelock Ripley of the War of 1812. It was the second major military reservation established in what would become Minnesota.
Patrick William Kruse, also known as Pat Kruse, is a Native American culture teacher and artist that specializes in birchbark art and quillwork. He works alongside his son Gage to create birch bark paintings.

Margaret Bonga Fahlstrom was a mixed-race woman of African and Ojibwe descent who came from a fur trading family in the Great Lakes region. In 1823, she married Jacob Fahlstrom, the first Swedish settler in Minnesota, and lived with him on a small farm at Coldwater Spring near Fort Snelling. Margaret was one of the few free Black women living in the area around the time that enslaved women such as Harriet Robinson Scott were struggling to find a path to freedom. In 1838, the Fahlstroms became the first converts to the Methodist faith in Minnesota, and moved to a farm in Washington County in 1840. Jacob became well known as the Methodist lay preacher "Father Jacob". His success as a traveling Christian missionary was often attributed to his fluency in the Ojibwe language, as well as his marriage. Margaret and her daughters were also known for their involvement in early church meetings in Minnesota, and their hospitality toward Methodist circuit riders.













