Southern Company is an American gas and electric utility holding company based in the southern United States. It is headquartered in Atlanta, Georgia, with executive offices also located in Birmingham, Alabama. The company is currently the second largest utility company in the U.S. in terms of customer base. Through its subsidiaries it serves 9 million gas and electric utility customers in 6 states. Southern Company's regulated regional electric utilities serve a 120,000-square-mile (310,000 km2) territory with 27,000 miles (43,000 km) of distribution lines.

The Pacific Gas and Electric Company (PG&E) is an American investor-owned utility (IOU) with publicly traded stock. The company is headquartered in the Pacific Gas & Electric Building, in San Francisco, California, United States. PG&E provides natural gas and electricity to most of the northern two-thirds of California, from Bakersfield and the north side of Santa Barbara County, to near the state line with Oregon and Nevada, which represents 5.2 million households.

Southern California Edison, the largest subsidiary of Edison International, is the primary electricity supply company for much of Southern California. It provides 15 million people with electricity across a service territory of approximately 50,000 square miles. However, the Los Angeles Department of Water and Power, San Diego Gas & Electric (SDG&E), Imperial Irrigation District, and some smaller municipal utilities serve substantial portions of the southern California territory. The northern part of the state is generally served by the Pacific Gas & Electric Company of San Francisco. Other investor-owned utilities (IOUs) in California include SDG&E, PacifiCorp, Bear Valley Electric, and Liberty Utilities.
Puget Sound Energy (PSE) is an energy utility based in the U.S. state of Washington, providing the Puget Sound region with electrical power and natural gas. The utility serves electricity to more than 1.1 million customers in Island, King, Kitsap, Kittitas, Pierce, Skagit, Thurston, and Whatcom counties, and provides natural gas to 750,000 customers in King, Kittitas, Lewis, Pierce, Snohomish and Thurston counties. The company's electric and natural gas service area spans 6,000 square miles (16,000 km2).

Solar Energy Generating Systems (SEGS) is a concentrated solar power plant in California, United States. With the combined capacity from three separate locations at 354 megawatt (MW), it is the world's second largest solar thermal energy generating facility, after the commissioning of the even larger Ivanpah facility in 2014. It consists of nine solar power plants in California's Mojave Desert, where insolation is among the best available in the United States. SEGS I–II (44 MW) are located at Daggett, SEGS III–VII (150 MW) are installed at Kramer Junction, and SEGS VIII–IX (160 MW) are placed at Harper Lake. NextEra Energy Resources operates and partially owns the plants located at Kramer Junction. On January 26, 2018, the SEGS VIII and IX at Harper Lake were sold to renewable energy company Terra-Gen, LLC. A tenth plant had been in construction and SEGS XI and SEGS XII had been planned by Luz Industries, but the developer filed for bankruptcy in 1992, because it was unable to secure construction financing.
GenOn Energy Holdings, formerly Mirant Corporation, was a subsidiary of GenOn Energy, and is now a part of NRG Energy.

FirstEnergy Corp is an electric utility headquartered in Akron, Ohio. Its subsidiaries and affiliates are involved in the distribution, transmission, and generation of electricity, as well as energy management and other energy-related services. Its ten electric utility operating companies comprise one of the United States' largest investor-owned utilities, based on serving 6 million customers within a 65,000-square-mile (170,000 km2) area of Ohio, Pennsylvania, West Virginia, Virginia, Maryland, New Jersey and New York. Its generation subsidiaries control more than 16,000 megawatts of capacity, and its distribution lines span over 194,000 miles. In 2018, FirstEnergy ranked 219 on the Fortune 500 list of the largest public corporations in the United States by revenue.

NRG Energy, Inc. is a large American energy company, dual-headquartered in Princeton, New Jersey and Houston, Texas. It was formerly the wholesale arm of Northern States Power Company (NSP), which became Xcel Energy, but became independent in 2000. NRG Energy is involved in energy generation and retail electricity. Their portfolio includes nuclear generation, coal generation, wind generation, utility scale generation, distributed solar generation, and oil generation. NRG serves 2.9 million retail customers in Texas, Connecticut, Delaware, Illinois, Maryland, Massachusetts, New Jersey, New York, Pennsylvania, Ohio, and the District of Columbia.

The Moss Landing Power Plant is a natural gas powered electricity generation plant located in Moss Landing, California, United States, at the midpoint of Monterey Bay. Its large stacks are landmarks, visible throughout the Monterey Bay Area. The plant is owned and operated by Houston-based Dynegy and currently has a generation capacity of 1020 MW (net) from its two combined cycle generation units. It was once the largest power plant in the state of California, with a generation capacity of 2560 MW, before its two large supercritical steam units were taken offline.
Silicon Valley Power (SVP) is a not-for-profit municipal electric utility owned and operated by the City of Santa Clara, California, USA. SVP provides electricity service to approximately 52,000 residential and business customers, including large corporations such as Intel, Yahoo!, Applied Materials, Owens Corning and NVIDIA. SVP also owns and maintains a dark fiber network named SVP Fiber Enterprise, and provides citywide free outdoor Wi-Fi access as part of its installed wireless network communications system that supports SVP MeterConnect, SVP’s Advanced Metering Infrastructure program.
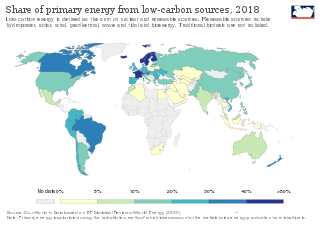
Low-carbon power comes from processes or technologies that produce power with substantially lower amounts of carbon dioxide emissions than is emitted from conventional fossil fuel power generation. It includes low carbon power generation sources such as wind power, solar power, hydropower and nuclear power. The term largely excludes conventional fossil fuel plant sources, and is only used to describe a particular subset of operating fossil fuel power systems, specifically, those that are successfully coupled with a flue gas carbon capture and storage (CCS) system. Globally, 36.4% of electricity generation comes from low-carbon sources. As of 2018 the largest low-carbon energy sources globally were hydropower and nuclear power, with the latter providing over 50% of low-carbon power alone in United States and European Union.

Spalding Power Station is a 860 MW gas-fired power station one mile north of Spalding on West Marsh Road close to the River Welland. The current site provides enough electricity for one million households.
The Charles P. Crane Generating Station was a 400 megawatt (MW) coal power plant located on the Carroll Island Road in Bowleys Quarters, Maryland, 14 miles (23 km) east of Baltimore. The power plant was operated by C.P. Crane, LLC, a subsidiary of Avenue Capital Group. The station had two coal-fired generating units, rated at 190 and 209 MW nominal capacity, and powered by cyclone steam boilers. It also had a 16 MW oil-fired combustion turbine. The Crane station occupies 157 acres (64 ha) on the Middle River Neck Peninsula adjacent to the Seneca Creek tributary of the Gunpowder River, and is on the rural side of the Baltimore County Urban Rural Demarcation Line. The plant was closed in June 2018.

Luminant is a Texas-based electric utility. It is a wholly owned subsidiary of Energy Future Holdings Corporation. Luminant's operations include electricity generation and wholesaling, mining, construction, and development. The company has capacity for the generation of 18,300 megawatts (MW) of electricity in 20 power plants spread across Texas, of which 2,300 MW come from nuclear power generated at the company's Comanche Peak Nuclear Power Plant, 5,800 MW from coal-fired power plants, and the remainder from natural gas-fired plants. Luminant is also a major purchaser of wind power.

Danskammer Generating Station is located on the shore of the Hudson River in the Town of Newburgh, New York, United States, 0.5 miles (0.8 km) upstream of the larger oil-fired Roseton Generating Station. Danskammer 'units 1 and 2 burn natural gas as a primary fuel, and oil as a backup fuel, whereas units 3 and 4 are exclusively fired with natural gas.
Measurement of life-cycle greenhouse gas emissions involves calculating the global-warming potential of energy sources through life-cycle assessment. These are usually sources of only electrical energy but sometimes sources of heat are evaluated. The findings are presented in units of global warming potential per unit of electrical energy generated by that source. The scale uses the global warming potential unit, the carbon dioxide equivalent, and the unit of electrical energy, the kilowatt hour (kWh). The goal of such assessments is to cover the full life of the source, from material and fuel mining through construction to operation and waste management.
The Blythe Mesa Solar Power Project, also known as the Blythe Solar Energy Center, is a 235 megawatt (MWAC) photovoltaic power plant near the city of Blythe in Riverside County, California. It occupies about 2,000 acres of public land managed by the Bureau of Land Management in the Mojave Desert. The construction uses CdTe thin film panels from the U.S. firm First Solar, and the majority of the output is being sold to Kaiser Permanente and Southern California Edison under 20-year power purchase agreements.

The Crescent Dunes Solar Energy Project is a currently non-producing solar thermal power project with an installed capacity of 110 megawatt (MW) and 1.1 gigawatt-hours of energy storage located near Tonopah, about 190 miles (310 km) northwest of Las Vegas. Crescent Dunes was the first concentrated solar power (CSP) plant with a central receiver tower and advanced molten salt energy storage technology.

Gateway Generating Station (GGS), formerly Contra Costa Unit 8 Power Project, is a combined-cycle natural gas-fired power station in Contra Costa County, California, north of Antioch.












