
Flow cytometry (FC) is a technique used to detect and measure the physical and chemical characteristics of a population of cells or particles.

In biochemistry, immunostaining is any use of an antibody-based method to detect a specific protein in a sample. The term "immunostaining" was originally used to refer to the immunohistochemical staining of tissue sections, as first described by Albert Coons in 1941. However, immunostaining now encompasses a broad range of techniques used in histology, cell biology, and molecular biology that use antibody-based staining methods.
The National Institute of Arthritis and Musculoskeletal and Skin Diseases (NIAMS) is one of the institutes and centers that make up the National Institutes of Health, an agency of the United States Department of Health and Human Services (HHS).
Invitrogen is one of several brands under the Thermo Fisher Scientific corporation. The product line includes various subbrands of biotechnology products, such as machines and consumables for polymerase chain reaction, reverse transcription, cloning, culturing, stem cell production, cell therapy, regenerative medicine, immunotherapy, transfection, DNA/RNA purification, diagnostic tests, antibodies, and immunoassays.

Cellomics is the discipline of quantitative cell analysis using bioimaging methods and informatics with a workflow involving three major components: image acquisition, image analysis, and data visualization and management. These processes are generally automated. All three of these components depend on sophisticated software to acquire qualitative data, quantitative data, and the management of both images and data, respectively. Cellomics is also a trademarked term, which is often used interchangeably with high-content analysis (HCA) or high-content screening (HCS), but cellomics extends beyond HCA/HCS by incorporating sophisticated informatics tools.
Immunomagnetic separation (IMS) is a laboratory tool that can efficiently isolate cells out of body fluid or cultured cells. It can also be used as a method of quantifying the pathogenicity of food, blood or feces. DNA analysis have supported the combined use of both this technique and Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR). Another laboratory separation tool is the affinity magnetic separation (AMS), which is more suitable for the isolation of prokaryotic cells.
Sigma-Aldrich is an American chemical, life science, and biotechnology company owned by the multinational chemical conglomerate Merck Group
High-content screening (HCS), also known as high-content analysis (HCA) or cellomics, is a method that is used in biological research and drug discovery to identify substances such as small molecules, peptides, or RNAi that alter the phenotype of a cell in a desired manner. Hence high content screening is a type of phenotypic screen conducted in cells involving the analysis of whole cells or components of cells with simultaneous readout of several parameters. HCS is related to high-throughput screening (HTS), in which thousands of compounds are tested in parallel for their activity in one or more biological assays, but involves assays of more complex cellular phenotypes as outputs. Phenotypic changes may include increases or decreases in the production of cellular products such as proteins and/or changes in the morphology of the cell. Hence HCA typically involves automated microscopy and image analysis. Unlike high-content analysis, high-content screening implies a level of throughput which is why the term "screening" differentiates HCS from HCA, which may be high in content but low in throughput.

Sartorius AG is an international pharmaceutical and laboratory equipment supplier, covering the segments of Bioprocess Solutions and Lab Products & Services. In September 2021, Sartorius has been admitted to the DAX, Germany's largest stock market index. As a leading partner to the biopharmaceutical research and industry, Sartorius supports its customers in the development and production of biotech drugs and vaccines - from the initial idea in the laboratory to commercial production. Sartorius conducts its operating business in the two divisions Bioprocess Solutions and Lab Products&Services. The divisions bundle their respective businesses according to the same application areas and customer groups. The divisions share some of the infrastructure and central services.
Cell sorting is the process through which a particular cell type is separated from others contained in a sample on the basis of its physical or biological properties, such as size, morphological parameters, viability and both extracellular and intracellular protein expression. The homogeneous cell population obtained after sorting can be used for a variety of applications including research, diagnosis, and therapy.

Cytometry is the measurement of number and characteristics of cells. Variables that can be measured by cytometric methods include cell size, cell count, cell morphology, cell cycle phase, DNA content, and the existence or absence of specific proteins on the cell surface or in the cytoplasm. Cytometry is used to characterize and count blood cells in common blood tests such as the complete blood count. In a similar fashion, cytometry is also used in cell biology research and in medical diagnostics to characterize cells in a wide range of applications associated with diseases such as cancer and AIDS.
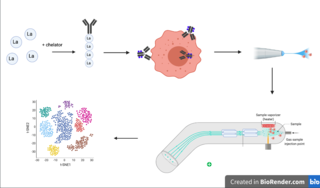
Cytometry by time of flight, or CyTOF, is an application of mass cytometry used to quantify labeled targets on the surface and interior of single cells. CyTOF allows the quantification of multiple cellular components simultaneously using an ICP-MS detector.
Eurogentec is a biotechnology supplier, based in Belgium, that specializes in genomics and proteomics kits, reagents, and certain biologics. It was founded in 1985 as a spin-off from the University of Liège. Eurogentec operates two licensed contract manufacturing organization facilities in Belgium which produce custom biologic and oligonucleotide products mainly for European pharmaceutical companies, but also holds a license from the U.S. FDA to export a commercial protein product to the U.S.. These products are used to diagnose and treat various conditions.
Immudex is a Danish Reagents and Diagnostics company established in 2009. The company is operating from offices located in Copenhagen, Denmark, and in Fairfax, Virginia. Immudex specializes in the production of MHC Dextramers. MHC Dextramers are chemical reagents that are designed to detect antigen-specific T cells.

Mass cytometry is a mass spectrometry technique based on inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry and time of flight mass spectrometry used for the determination of the properties of cells (cytometry). In this approach, antibodies are conjugated with isotopically pure elements, and these antibodies are used to label cellular proteins. Cells are nebulized and sent through an argon plasma, which ionizes the metal-conjugated antibodies. The metal signals are then analyzed by a time-of-flight mass spectrometer. The approach overcomes limitations of spectral overlap in flow cytometry by utilizing discrete isotopes as a reporter system instead of traditional fluorophores which have broad emission spectra.

Standard BioTools Inc., previously known as Fluidigm Corp., offers analytical mass cytometry systems for flow cytometry and tissue imaging, along with associated assays and reagents, as well as an automated genomic analysis instrument and a variety of microfluidic arrays, or integrated fluidic circuits (IFCs), and consumables with fully kitted reagents. Custom assays and services are available with all systems and applications.
Complement-dependent cytotoxicity (CDC) is an effector function of IgG and IgM antibodies. When they are bound to surface antigen on target cell, the classical complement pathway is triggered by bonding protein C1q to these antibodies, resulting in formation of a membrane attack complex (MAC) and target cell lysis.
Tissue image cytometry or tissue cytometry is a method of digital histopathology and combines classical digital pathology and computational pathology into one integrated approach with solutions for all kinds of diseases, tissue and cell types as well as molecular markers and corresponding staining methods to visualize these markers. Tissue cytometry uses virtual slides as they can be generated by multiple, commercially available slide scanners, as well as dedicated image analysis software – preferentially including machine and deep learning algorithms. Tissue cytometry enables cellular analysis within thick tissues, retaining morphological and contextual information, including spatial information on defined cellular subpopulations.

SCTbio is global contract development and manufacturing organization (CDMO) providing cGMP services of Advanced Therapy Medicinal Products (ATMPs). It operates in Europe and North America. The company has strong expertise in the development of autologous cell-based products, cell banking and all needle-to-needle GMP operations, including a validated apheresis collection sites network, product manufacturing, QC, GMP storage, QA/QP release, and worldwide drug products supply for clinical and commercial scale.

Olga Ornatsky is a Soviet born, Canadian scientist. Ornatsky co-founded DVS Sciences in 2004 along with Dmitry Bandura, Vladimir Baranov and Scott D. Tanner.










