
The Great Hanshin Earthquake occurred on January 17, 1995, at 05:46:53 JST in the southern part of Hyōgo Prefecture, Japan, including the region known as Hanshin. It measured 6.9 on the moment magnitude scale and had a maximum intensity of 7 on the JMA Seismic Intensity Scale. The tremors lasted for approximately 20 seconds. The focus of the earthquake was located 17 km beneath its epicenter, on the northern end of Awaji Island, 20 km away from the center of the city of Kobe.
Minato is Japanese for 'harbor', and may refer to:

The Steel Bridge is a through truss, double-deck vertical-lift bridge across the Willamette River in Portland, Oregon, United States, opened in 1912. Its lower deck carries railroad and bicycle/pedestrian traffic, while the upper deck carries road traffic, and light rail (MAX), making the bridge one of the most multimodal in the world. It is the only double-deck bridge with independent lifts in the world and the second oldest vertical-lift bridge in North America, after the nearby Hawthorne Bridge. The bridge links the Rose Quarter and Lloyd District in the east to Old Town Chinatown neighborhood in the west.

The Champlain Bridge was a steel truss cantilever bridge with approach viaducts constructed of prestressed concrete beams supporting a prestressed concrete deck paved with asphalt. Opened in 1962, the bridge crossed the Saint Lawrence River, connecting the Island of Montreal to its South Shore suburbs.

The Rainbow Bridge is a suspension bridge crossing northern Tokyo Bay between Shibaura Pier and the Odaiba waterfront development in Minato, Tokyo, Japan.

A cantilever bridge is a bridge built using structures that project horizontally into space, supported on only one end. For small footbridges, the cantilevers may be simple beams; however, large cantilever bridges designed to handle road or rail traffic use trusses built from structural steel, or box girders built from prestressed concrete.

A truss bridge is a bridge whose load-bearing superstructure is composed of a truss, a structure of connected elements, usually forming triangular units. The connected elements, typically straight, may be stressed from tension, compression, or sometimes both in response to dynamic loads. There are several types of truss bridges, including some with simple designs that were among the first bridges designed in the 19th and early 20th centuries. A truss bridge is economical to construct primarily because it uses materials efficiently.

The Ross Island Bridge is a cantilever truss bridge that spans the Willamette River in Portland, Oregon. It carries U.S. Route 26 across the river between southwest and southeast Portland. The bridge opened in 1926 and was designed by Gustav Lindenthal and honors Oregon pioneer Sherry Ross. It is named for its proximity to Ross Island. Although it looks like a deck arch bridge, it is a cantilever deck truss bridge, a rare type in Oregon.
The Isaiah David Hart Bridge is a truss bridge that spans the St. Johns River in Jacksonville, Florida. It carries U.S. Route 1 Alternate and State Road 228 (SR 228). It is named after Isaiah Hart, the founder of Jacksonville and is often referred to as the Hart Bridge. It was designed by Sverdrup & Parcel. The Hart Bridge is one of the longest truss bridges in the world, and has the world's third longest main span of any truss bridge.

The High Bridge is a railroad bridge crossing the Kentucky River Palisades, in Kentucky. The bridge, about 275 feet over the river below, connects Jessamine and Mercer counties. It was formally dedicated in 1879, and is the first cantilever bridge built in the United States. It has a three-span continuous under-deck truss, which is used by Norfolk Southern Railway to carry trains between Lexington and Danville. The High Bridge is a National Historic Civil Engineering Landmark.

The Glenwood Bridge is a cantilever bridge in Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania, which carries Pennsylvania Route 885 over the Monongahela River. It started construction on June 3, 1958. It was completed in 1966 to replace an old, decayed, unsafe iron bridge built in 1894, which carried Pittsburgh Railways streetcar tracks and vehicle traffic on a wooden deck.
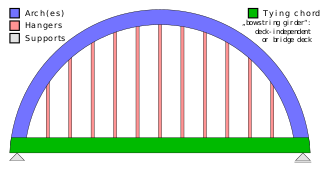
A tied-arch bridge is an arch bridge in which the outward-directed horizontal forces of the arch(es) are borne as tension by a chord tying the arch ends rather than by the ground or the bridge foundations. This strengthened chord may be the deck structure itself or consist of separate, independent tie-rods.

The Miami Bridge, also known as the McDaniel Memorial Bridge, is a new concrete girder bridge that was built to replace a cantilever through truss bridge over the Missouri River at Miami, Missouri between Saline County, Missouri and Carroll County, Missouri. The Miami Bridge carries Route 41. The Miami Bridge was built in 1939, and its deck was replaced in 1983 as part of a rehabilitation project. The old bridge's main cantilever span was 474.7 feet, while the two anchor spans were each 415 feet in length, resulting in a total cantilever truss length of 1304.7 feet. There were 11 approach spans, including four Warren deck truss spans, three on the northern approach and one on the southern approach. All remaining approach spans were steel stringer (multi-beam/girder) spans. Total bridge length including approach spans is 2,071.9 feet. The bridge's deck width is 23.0 feet and it has vertical clearance of 16.5 feet.

The Kettle Falls Bridges is the collective name for a pair of steel cantilever bridges carrying State Route 20/U.S. Route 395 and the Kettle Falls International Railway across the Columbia River at Kettle Falls, Washington. The south bridge carries motor vehicle traffic while the similar northern span is used for rail.

The Jefferson Street Viaduct is a historic structure located in Ottumwa, Iowa, United States. The riveted Warren deck truss bridge was completed in 1936. It was listed on the National Register of Historic Places in 1998 as a part of the Highway Bridges of Iowa MPS.

The AJX Bridge is a historic Pratt truss bridge in southwestern Johnson County, Wyoming. The bridge was built in 1931 across the South Fork of the Powder River near Kaycee, Wyoming. AJX Bridge was built to provide a river crossing for U.S. Route 87. It was placed on the National Register of Historic Places in 1985 as part of a Multiple Property Submission devoted to historic bridges in Wyoming.

The South Street Bridge is a historic Pratt truss bridge, carrying Vermont Route 31 across the Poultney River just south of the village center of Poultney, Vermont. Built in 1923, it is one of a small number of surviving Pratt through trusses in the state, and one of just three that survives from the period before the state's devastating 1927 floods. It was listed on the National Register of Historic Places in 2009 as Bridge 4.

The Quechee Gorge Bridge is a historic bridge, carrying U.S. Route 4 (US 4) across Quechee Gorge, near the Quechee village of Hartford, Vermont. Built in 1911, it is Vermont's oldest surviving steel arch bridge. It was listed on the National Register of Historic Places in 1990.

The Jeffersonville Bridge is a steel girder bridge carrying Vermont Route 108 across the Lamoille River, just north of the village of Jeffersonville, Vermont. It was built in 2014, replacing a Parker through truss bridge built in 1931; the latter bridge was listed on the National Register of Historic Places in 1991.


















