The Global 200 is the list of ecoregions identified by the World Wide Fund for Nature (WWF), the global conservation organization, as priorities for conservation. According to WWF, an ecoregion is defined as a "relatively large unit of land or water containing a characteristic set of natural communities that share a large majority of their species dynamics, and environmental conditions". For example, based on their levels of endemism, Madagascar gets multiple listings, ancient Lake Baikal gets one, and the North American Great Lakes get none.

The Western Guinean lowland forests ecoregion is a tropical moist broadleaf forest ecoregion of West Africa. It is centered on Liberia, with portions in surrounding countries. It is the westernmost tropical rainforest in Africa, and has high levels of species endemism, with over 200 species of endemic plants.

The Northeastern Brazil restingas are an ecoregion of northeastern Brazil. Restingas are coastal forests which form along coastal sand dunes in Brazil. The soils are typically sandy, acidic, and nutrient-poor, and are characterized by medium-sized trees and shrubs adapted to local conditions. Restingas have aspects of mangroves, caatingas, wetlands, and moist forests, often forming along wind-driven sand dunes. The Northeast Brazil restingas are the most northerly of the forest type in Brazil.
The Central America bioregion is a biogeographic region comprising southern Mexico and Central America.

The Isthmian–Atlantic moist forests (NT0129) are a Central American tropical moist broadleaf forest ecoregion located on the lowland slopes on the caribbean sea side of Nicaragua and Costa Rica and the Gulf and Pacific Ocean sides of Panama. The forest species are a mix of North American and South American, as this region only became a land bridge in the past 3 million years.

The Belizean pine forests is an ecoregion that represents an example of lowland and premontane pine forests in the Neotropical realm, where the dominant tree species is Caribbean pine. The vegetation here is generally adapted to the xeric, acidic and nutrient-poor conditions along the Belizean near coastal zone of the Caribbean versant.

The Hainan Island monsoon rain forests ecoregion covers mountainous interior of Hainan Island in China. The tropical forests receive over 1,000 mm/year of rain, heavily concentrated in the summer rainy season. The island has high levels of biodiversity, with over 4,200 plant species, 630 of which are endemic to the island. The region is under ecological pressure from deforestation for agriculture and timber extraction.

The Luang Prabang montane rain forests ecoregion covers elevations over 800 meters in the Luang Prabang mountains that straddle the border between northern Thailand and north-central Laos, and the highlands that stretch eastward across north-central Laos. While much of the forest cover has been degraded, there are still large areas of relatively untouched forest.

The Southern Annamites montane rain forests ecoregion covers a region of high biodiversity in the central and southern mountains of the Annamite Range in Vietnam. Terrain ranges from wet lowland forest to evergreen hardwood and conifer montane rain forest. There is a short dry season centered on January–February, but fog and dew are common throughout the year and support a lush forest character.

The Tonle Sap-Mekong peat swamp forests ecoregion covers a patchwork of areas permanently inundated with fresh water along the Tonle Sap River and Mekong River floodplains in Cambodia and Vietnam. The terrain is mostly flat, with extensive agricultural fields, reed beds, and degraded shrub forest. Less than 10% of the region is in its original state, and less than 1% is protected. Habitat in the region is distinguished from the Tonle Sap freshwater swamp forests ecoregion that runs through the middle, as that ecoregion is only seasonally flooded.

The Northern Khorat Plateau moist deciduous forests ecoregion covers a small area on the border between northeastern Thailand and Laos, in the transition zone between the drier Khorat Plateau to the south and the wetter Annamite Range and Luang Prabang Range mountains to the north. Much of the ecoregion has been converted to agriculture along the floodplain of the middle course of the Mekong River.

The Eastern Java-Bali rain forests ecoregion covers the lowland areas of the eastern half of the island of Java, and the island of Bali, in Indonesia. This ecoregion is distinct from the Eastern Java-Bali montane rain forests, which exists at higher elevations where mountain forest habitat dominates. Very little of the natural lowland rainforest remains in its pre-human settlement state.

The Central American Atlantic moist forests ecoregion covers the lowland coastal forests of Honduras, southeast Guatemala, and the eastern forests of Nicaragua. Half of the ecoregion is closed-canopy tropical broadleaf evergreen forest, with tree heights reaching 50 meters. This ecoregion has the largest single fragment of natural forest in Central America, with a size of 14,629 square kilometres (5,648 sq mi). The total area is 89,979 square kilometres (34,741 sq mi).

The Costa Rican seasonal moist forests ecoregion covers the Pacific Slope of the volcanic mountain range of northwestern Costa Rica and the extreme south of Nicaragua. The area has a distinct dry season during which the characteristic deciduous trees drop their leaves. The forests themselves have been highly degraded in the past by human conversion to agriculture and settlement. The Costa Rican capital city of San Jose is in the middle of this ecoregion.

The Isthmian–Pacific moist forests ecoregion covers the lowland tropical evergreen forests on the Pacific side of the central mountains of southern Costa Rica and western Panama. As the meeting zone between North and South American floral communities, the area is one of very high biodiversity. Much of the rainforest has, however, been cleared for subsistence agriculture and cattle grazing.

The Panamanian dry forests ecoregion covers low-lying dry forests around the coast of the Gulf of Panama on the Pacific Ocean side of Panama. It is one of the most heavily degraded ecoregions in Central America, having been heavily converted to agriculture. However, it is also important for its high biodiversity, high rates of endemic species, and its importance as a biological corridor between the moist forests inland and the mangroves on the coast.

The Mesoamerican Gulf-Caribbean mangroves ecoregion covers the series of disconnected mangrove habitats along the eastern coast of Central America. These salt-water wetlands are found in river deltas, lagoons, and low-lying areas facing the Gulf of Mexico and Caribbean Sea, from Tampico, Mexico to central Panama. The mangroves are areas of high biodiversity and endemism. Many of the sites are protected as national parks or nature reserves.
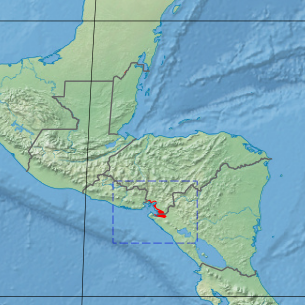
The Gulf of Fonseca mangroves ecoregion covers the brackish mangrove forests around the Gulf of Fonseca on the Pacific Ocean. The Gulf is the meeting point El Salvador, Honduras, and Nicaragua. The Gulf is one of the two primary nesting sites of the critically endangered Hawksbill turtle in the eastern Pacific. In the Honduras portion, there are seven nature reserves that collectively make up a RAMSAR wetland of international importance, providing protection for migratory birds, sea turtle, and fish.

The Cayos Miskitos-San Andrés & Providencia moist forests ecoregion cover the forested areas of four islands in the western Caribbean Sea - Cayos Miskitos and the Corn Islands off the east coast of Nicaragua, and San Andrés and Providencia Islands farther east and belonging to the nation of Colombia. The forests on San Adres and Providencia have been heavily degraded by agriculture - coconuts on San Andres, oranges on Providencia. A significant feature of the ecoregion is the surrounding corals reefs, which are large and well preserved. While not technically a part of this terrestrial ecoregion, they are related to the islands.

The Trinidad and Tobago moist forests ecoregion covers most of Trinidad Island and Tobago Island near the coast of South America where the southeastern Caribbean Sea meets the Atlantic Ocean. Small portions of the islands around river estuaries and coastal lowlands are mangroves or dry forests. Species diversity is very high, in particular for plants and birds. Tobago, being much smaller, has fewer species.



















