
Northeast India (officially the North Eastern Region(NER)) is the easternmost region of India representing both a geographic and political administrative division of the country. It comprises eight states—Arunachal Pradesh, Assam, Manipur, Meghalaya, Mizoram, Nagaland and Tripura (commonly known as the "Seven Sisters"), and the "brother" state Sikkim.
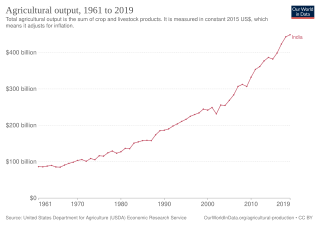
The history of agriculture in India dates back to the neolithic. India ranks second worldwide in farm outputs. As per Indian economic survey 2018, agriculture employed more than 50% of the Indian work force and contributed 17–18% to country's GDP.
The Ministry of Development of North Eastern Region is a Government of India ministry, established in September 2001, which functions as the nodal Department of the Central Government to deal with matters related to the socio-economic development of the eight States of Northeast India: Arunachal Pradesh, Assam, Manipur, Meghalaya, Mizoram, Nagaland, Tripura and Sikkim. It acts as a facilitator between the Central Ministries/ Departments and the State Governments of the North Eastern Region in the economic development including removal of infrastructural bottlenecks, provision of basic minimum services, creating an environment for private investment and to remove impediments to lasting peace and security in the North Eastern Region.

Bhupesh Baghel is an Indian politician serving as the 3rd and current Chief Minister of Chhattisgarh since 2018. He was president of Chhattisgarh Pradesh Congress from 2014 to 2019. He represents the Patan constituency in the Chhattisgarh Legislative Assembly since 2013 and from 2003 to 2008. He had been cabinet minister of Transportation in undivided Madhya Pradesh in Digvijaya Singh government from 1999 to 2003. He was first Minister for Revenue, Public Health Engineering and Relief Work of Chhattisgarh.

Singngat is one of the sub-divisional headquarters of Churachandpur district in the Indian state of Manipur and is a key administrative centre in the southwestern border of the state. The Manipur Government officially recorded the name as Singhat, that's because the Meiteis find it difficult to pronounce the original name.

Sashastra Seema Bal is a border guarding force of India deployed along its borders with Nepal and Bhutan. It is one of the seven Central Armed Police Forces under the administrative control of the Ministry of Home Affairs (MHA).
The 2009 Union budget of India was presented by the finance minister, Pranab Mukherjee, on 6 July 2009.

Kinema is a fermented soybean food, prepared by the Nepali communities of the Eastern Himalayas region: Eastern Nepal, and Darjeeling, Kalimpong and Sikkim regions of India. Kinema is a traditional food of the Limbu people.

Indian Gorkhas also known as Nepali Indians, are Nepali language-speaking Indians. The modern term "Indian Gorkha" is used to differentiate the ethnic Gorkhas from Nepalis.

Common Service Centres (CSC) are physical facilities for delivering Government of India e-Services to rural and remote locations where availability of computers and Internet was negligible or mostly absent. They are multiple-services-single-point model for providing facilities for multiple transactions at a single geographical location.

Agriculture in India is highly susceptible to risks like droughts and floods. It is necessary to protect the farmers from natural calamities and ensure their credit eligibility for the next season. For this purpose, the Government of India introduced many agricultural schemes throughout the country.

Northeast India consists of the eight states Arunachal Pradesh, Assam, Manipur, Meghalaya, Mizoram, Nagaland, Sikkim and Tripura. Tourism in this area is based around the unique Himalayan landscape and culture distinct from the rest of India.

National Agriculture Market or eNAM is an online trading platform for agricultural commodities in India. The market facilitates farmers, traders and buyers with online trading in commodities.

Rice production or Paddy production is one of the main productions and staple foods in Sri Lanka. Rice is the staple food of 21.8 million Sri Lankans and is the livelihood of more than 1.8 million farmers. More than 30 percent of the total labour force is directly or indirectly involved in the rice sector. The annual per capita consumption of rice was around 92 kg (203 lb) in 1998 and is dependent on the paddy production in the country and the price of imported wheat flour. In 1998 total production was 2.69 million MT of rough rice (paddy), which is about 96 percent of the national requirement. With the present population growth rate of 1.2 percent, slightly increasing per capita consumption, requirements for seed, and for wastage in handling, Sri Lanka needs about 3.1 million MT of paddy by the year 2005. Hence, it is projected that the national average yield should increase to 4.1 t/ha to feed the population of Sri Lanka in 2005. It cultivates in all districts of Sri Lanka during two monsoon seasons. It is estimated that about 708,000 ha of land uses for paddy. The seasons are called Maha season and Yala season. Maha Season starts by September and ends by March during North-east monsoon, and Yala season starts by May and ends by August.
Operation Greens is a project approved by the Ministry of Food Processing Industries with the target to stabilise the supply of tomato, onion and potato crops in India, as well as to ensure their availability around the country, year-round without price volatility. It was first introduced in the 2018-2019 Union budget of India, and has been allocated Rs 500 crores to promote farmer producers' organisations (FPOs), agri-logistics, processing facilities and professional management.

The hill tribes of Northeast India are hill people, mostly classified as Scheduled Tribes (STs), who live in the Northeast India region. This region has the largest proportion of scheduled tribes in the country.
Pradhan Mantri Garib Kalyan Anna Yojana is a food security welfare scheme announced by the Government of India on March 26 2020, during the COVID-19 pandemic in India. The program is operated by the Department of Food and Public Distribution under the Ministry of Consumer Affairs, Food and Public Distribution. But the nodal ministry is Ministry of Finance.
Punjab Agri Export Corporation Limited (PAGREXCO) is a government enterprise established by the Government of Punjab in the year 1997 as the nodal agency for agricultural export from the state of Punjab, India. The company works for export of fresh and processed agricultural produce, infrastructural development and policy implementation in the state. It is a subsidiary of Punjab Agro Industries Corporation. The company has been awarded Sustainable Development Goals Action Award by the Punjab Planning Department for Sustainable Organic Production and Innovative Marketing System. It has also received Leadership award in Agriculture Marketing.
Bar Council of Assam, Nagaland, Meghalaya, Manipur, Tripura, Mizoram, Arunachal Pradesh and Sikkim is the regulatory and statutorily representative body for lawyers practicing law in the states of Assam, Nagaland, Meghalaya, Manipur, Tripura, Mizoram, Arunachal Pradesh and Sikkim. It was constituted as per the mandatory requirement as per Advocates Act, 1961 and Bar Council of India. In March 1953, S. R. Das as head of the 'All India Bar Committee', proposed the creation of the apex body as an All-India Bar Council and Bar council at state levels and submitted a report to the Central Government of India. Members of the Bar Council are elected from among members enrolled and practicing as lawyers practicing law in the states of Assam, Nagaland, Meghalaya, Manipur, Tripura, Mizoram, Arunachal Pradesh and Sikkim and they represent the state in Bar Council of India meetings. Bar Council of a place designs standards of professional conduct to be followed by members, and designs etiquettes and has the power to enforce disciplinary guidelines over the members of bar council.














