The history of the Central African Republic is roughly composed of four distinct periods. The earliest period of settlement began around 10,000 years ago when nomadic people first began to settle, farm and fish in the region. The next period began around 1,000 to 3,000 years ago when several non-indigenous groups began to migrate into the region from other parts of the continent. The third period involved the colonial conquest and rule of the country by France and Germany which spanned from the late 1800s until 1960 when the Central African Republic became an independent state. The final period has been the era during which the Central African Republic has been an independent state.

Bangui is the capital and largest city of the Central African Republic. As of 2012 it had an estimated population of 734,350. It was established as a French outpost in 1889 and named after its location on the northern bank of the Ubangi River ; the Ubangi itself was named from the Bobangi word for the "rapids" located beside the settlement, which marked the end of navigable water north from Brazzaville. The majority of the population of the Central African Republic lives in the western parts of the country, in Bangui and the surrounding area.

Équateur was one of the eleven provinces of the Democratic Republic of the Congo between 1966 and 2015, when it was split into the new, smaller Équateur province, as well as the Tshuapa, Mongala, Nord-Ubangi and Sud-Ubangi provinces.

Ubangi-Shari was a French colony in central Africa, a part of French Equatorial Africa.

Gbadolite or Gbado-Lite is the capital of Nord-Ubangi Province in the Democratic Republic of the Congo. The town is located 12 kilometres (7.5 mi) south of the Ubangi River at the border to the Central African Republic and 1,150 kilometres (710 mi) northeast of the national capital Kinshasa. Gbadolite was the ancestral home and residence of Joseph-Désiré Mobutu, later self-styled as Mobutu Sese Seko where airport, colleges, malls, supermarkets and libraries were built by the President in a program of modernization.

Ubangi-Shari was a French colony in central Africa which later became the independent country of the Central African Republic on August 13, 1960. It followed the establishment of the Bangui outpost in 1889, and was named in 1894.
Articles related to the Democratic Republic of the Congo include:

Bosobolo is a small town in Nord-Ubangi Province of northern Democratic Republic of the Congo. As of 2009 it had an estimated population of 16,397. It is the administrative center of Bosobolo Sector.

Synodontis multimaculatus, known as the dotted synodontis, is a species of upside-down catfish that is native to the Democratic Republic of the Congo where it is found in the Ubangi River. It was first described by British-Belgian zoologist George Albert Boulenger in 1902, from a specimen collected in the Ubangi River in Mobayi-Mbongo, the Democratic Republic of the Congo. The species name multimaculatus is derived from the word multi, meaning many, and the Latin word maculatus, meaning spots, referring to the many spots on the fish.

Kungu is a town and capital of one of the four territories of Sud-Ubangi Province, Democratic Republic of the Congo. The Ubangi River forms the western boundary of Kungu Territory, separating it from the Republic of the Congo. The Ngiri River, which flows southward through the Ngiri Reserve, originates near the town of Kungu.
Bondo Territory is a territory in the Bas-Uele Province of the Democratic Republic of the Congo. The administrative capital is the town of Bondo.
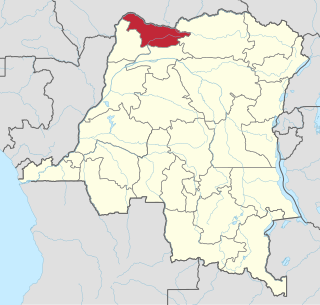
Nord-Ubangi is one of the 26 provinces of the Democratic Republic of the Congo. It is located in the northwestern part of the country on the Ubangi River. Its capital is the city of Gbadolite.

Tumba-Ngiri-Maindombe is the largest Wetland of International Importance in the world as recognized by the Ramsar Convention. The site covers an area of 65,696 square kilometres (25,365 sq mi) in the region around Lake Tumba in the western Congo Basin in the Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC). This is more than twice the size of Belgium or Maryland.
The Ngiri Reserve is a protected area of the Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC). It is located in western Équateur province, in the Bomongo, Bikoro and Makanza territories, and covers a total area of 1,000 square kilometres (390 sq mi). It extends northward from the confluence of the Congo River and the Ubangi River. According to the World Wide Fund for Nature (WWF) the reserve will conserve biodiversity and the ecosystem in the Ngiri triangle.
The Ngiri River is a tributary of the Ubangi River that flows southward through the Sud-Ubangi District of Équateur province, Democratic Republic of the Congo.

Bomongo is a town in the Équateur Province of the Democratic Republic of the Congo, the headquarters of Bomongo Territory. It lies on the west bank of the Ngiri River. Bomongo is the only town in the Ngiri Reserve, a sparsely populated region of swamp forest between the Ubangi and Congo rivers.

Yakoma is a town in the Nord-Ubangi province of the Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC), the headquarters of the Yakoma Territory.
Mbongo is the common ancestor of the Sawa peoples of Cameroon according to their oral traditions.