A sabre or (American English)saber is a type of backsword with a curved blade associated with the light cavalry of the early modern and Napoleonic periods. Originally associated with Central European cavalry such as the hussars, the sabre became widespread in Western Europe during the Thirty Years' War. Lighter sabres also became popular with infantry of the early 17th century. In the 19th century, models with less curving blades became common and were also used by heavy cavalry.

During the American Civil War, the United States Army, the land force that fought to preserve the collective Union of the states, was often referred to as the Union army, the federal army, or the northern army. It proved essential to the restoration and preservation of the United States as a working, viable republic.
In the United States Navy, officers have various ranks. Equivalency between services is by pay grade. United States Navy commissioned officer ranks have two distinct sets of rank insignia: On dress uniform a series of stripes similar to Commonwealth naval ranks are worn; on service khaki, working uniforms, and special uniform situations, the rank insignia are identical to the equivalent rank in the US Marine Corps.
The chart below shows the current enlisted rank insignia of the United States Army, with seniority, and pay grade, increasing from right to left. The enlisted ranks of corporal (E-4) and higher are considered non-commissioned officers (NCOs). The rank of specialist is also in pay grade E-4, but does not hold non-commissioned officer status; it is common that a soldier may never hold the rank of corporal, and instead be promoted from specialist to sergeant, attaining junior NCO status at that time.

"Other ranks" (ORs) is the term used to refer to all ranks below officers in the British Army and the Royal Marines. It includes warrant officers, non-commissioned officers ("NCOs") and ordinary soldiers with the rank of private or regimental equivalent. Officers may, in speaking, distinguish themselves from those "in the ranks".

The Field Artillery Branch is the field artillery branch of the United States Army. This branch, alongside the infantry and cavalry branches, was formerly considered to be one of the "classic" combat arms branches, but is today included within the "Maneuver, Fires and Effects" (MFE) classification, in accordance with current U.S. Army organizational doctrine.

Field artillery in the American Civil War refers to the artillery weapons, equipment, and practices used by the artillery branch to support infantry and cavalry forces in the field. It does not include siege artillery, use of artillery in fixed fortifications, coastal or naval artillery. It also does not include smaller, specialized artillery pieces classified as infantry guns.

A brigade major was the chief of staff of a brigade in the British Army. They most commonly held the rank of major, although the appointment was also held by captains, and was head of the brigade's "G - Operations and Intelligence" section directly, and oversaw the two other branches, "A – Administration" and "Q – Quartermaster". Intentionally ranked lower than the lieutenant colonels commanding the brigade's combat battalions, his role was to expand on, detail and execute the intentions of the commanding brigadier.
The ranks and insignia of the Confederate States were a rank insignia system devised for the military of the Confederate States of America during the American Civil War.
United States Army commissioned officers rank insignia in use today.

The Marine Corps noncommissioned officer's sword is a sword worn by noncommissioned officers (NCOs) and staff noncommissioned officers (SNCOs) of the United States Marine Corps. The NCO sword was adopted in 1859 and is patterned after the United States Army's foot officers' sword of 1850. The M1859 NCO sword continues service today as the Marine Corps drill and ceremonial sword. The sword's use is restricted by regulation to ceremonial occasions by an NCO or Staff NCO in charge of troops under arms or at weddings and wedding receptions where at least one of those being married is in uniform and has the rank of Corporal or higher.

The Model 1860 Light Cavalry Saber is a long sword made of steel and brass, used by US cavalry from the American Civil War until the end of the Indian wars; some were still in use during the Spanish–American War. It was 41 inches (104 cm) long with a 35 by 1 in blade and weighed 2 lb 4 oz (1.0 kg) alone or 3 lb 10 oz (1.6 kg) with iron scabbard.

The Model 1840 noncommissioned officers' sword was adopted by the United States military in 1840. Based primarily on a sword used by the French Army, the model 1840 NCO proved somewhat heavy hilted and ill balanced. For over 70 years, it was widely used by the Army; today its usage is restricted to ceremonial occasions. The sword had a 31-inch blade, a cast brass hilt resembling the more expensive wire-wrapped leather grips, and a leather scabbard rather than the steel used by cavalry troopers and officers, although some makers, such as Emerson and Silver, issued a steel scabbard rather than leather to protect from wear. Leather scabbards were phased out beginning in 1868.

The West Point Cadets' Sword is issued to cadet officers of the United States Military Academy at West Point, New York for wear when the uniform is designated as "under arms," to include formal functions, drill, parades, inspections and graduation. The swords are issued to cadets in their First Class (4th) year, and are returned to the Academy upon separation, although Cadets have the option of buying their saber or purchasing a newly made one. Despite its straight blade and lack of a knuckle guard, it is referred to by USMA staff and cadets as a "saber," likely because the commands for its manual of arms utilize that term as the command of execution

The general officers of the Confederate States Army (CSA) were the senior military leaders of the Confederate States of America during the American Civil War of 1861–1865. They were often former officers from the United States Army before the Civil War, while others were given the rank based on merit or when necessity demanded. Most Confederate generals needed confirmation from the Confederate States Congress, much like prospective generals in the modern U.S. armed forces.
The military uniforms of the Union Army in the American Civil War were widely varied and, due to limitations on supply of wool and other materials, based on availability and cost of materials. The ideal uniform was prescribed as a dark blue coat with lighter pants, with a black hat. Officer's ranks were denoted with increasing levels of golden decoration. Specific jobs, companies, and units had markedly different styles at times, often following European customs such as that of the Zouaves. Officers uniforms tended to be highly customized and would stray from Army standard. Ironically, several main pieces of gear had been created by order of the U.S. War Secretary Jefferson Davis before the war; he later became Confederate President.
Each branch of the Confederate States armed forces had its own service dress and fatigue uniforms and regulations regarding them during the American Civil War, which lasted from April 12, 1861, until May 1865.
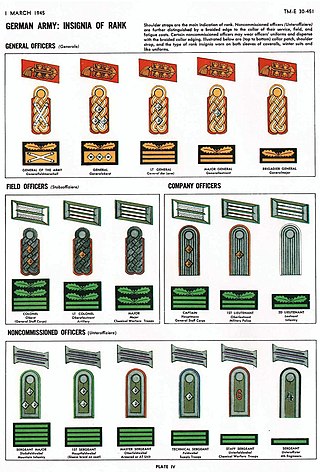
The Heer as the German army and part of the Wehrmacht inherited its uniforms and rank structure from the Reichsheer of the Weimar Republic (1921–1935). There were few alterations and adjustments made as the army grew from a limited peacetime defense force of 100,000 men to a war-fighting force of several million men.

The Model 1902 Army Officers' Saber is the current sword used by officers of the United States Army and United States Air Force. The official nomenclature for the current regulation U.S. Army saber is “saber for all officers, Model 1902”. It was adopted on July 17, 1902, by authority of General Order No. 81. The M1902 saber was authorized for all officers, both infantry and cavalry, with the exception of Chaplains. The lightly curved blade measures between 30 and 34 inches long with weights initially specified by the U.S. Army to be between 20.2 and 22.8 ounces and a point of balance of 3.25 inches from the hilt as specified for infantry sabers.











