
HyperCard is a software application and development kit for Apple Macintosh and Apple IIGS computers. It is among the first successful hypermedia systems predating the World Wide Web.

An integrated development environment (IDE) is a software application that provides comprehensive facilities to computer programmers for software development. An IDE normally consists of at least a source code editor, build automation tools, and a debugger. Some IDEs, such as NetBeans and Eclipse, contain the necessary compiler, interpreter, or both; others, such as SharpDevelop and Lazarus, do not.

Microsoft Word is a word processor developed by Microsoft. It was first released on October 25, 1983 under the name Multi-Tool Word for Xenix systems. Subsequent versions were later written for several other platforms including IBM PCs running DOS (1983), Apple Macintosh running the Classic Mac OS (1985), AT&T Unix PC (1985), Atari ST (1988), OS/2 (1989), Microsoft Windows (1989), SCO Unix (1994), and macOS.

Qt is a free and open-source widget toolkit for creating graphical user interfaces as well as cross-platform applications that run on various software and hardware platforms such as Linux, Windows, macOS, Android or embedded systems with little or no change in the underlying codebase while still being a native application with native capabilities and speed. Qt is currently being developed by The Qt Company, a publicly listed company, and the Qt Project under open-source governance, involving individual developers and organizations working to advance Qt. Qt is available under both commercial licenses and open source GPL 2.0, GPL 3.0, and LGPL 3.0 licenses.

System 6 is a graphical user interface-based operating system for Macintosh computers. It was released in 1988 by Apple Computer, Inc. and is part of the classic Mac OS series of operating systems. System 6 was included with all new Macintosh computers until it was succeeded by System 7 in 1991. The boxed version of System 6 cost $49 when introduced. System 6 is classed as a monolithic operating system. It features an improved MultiFinder, which allows for co-operative multitasking.

Shake is a discontinued image compositing package used in the post-production industry developed by Nothing Real for Windows and later acquired by Apple Inc. Shake was widely used in visual effects and digital compositing for film, video and commercials. Shake exposed its node graph architecture graphically. It enabled complex image processing sequences to be designed through the connection of effects "nodes" in a graphical workflow interface. This type of compositing interface allowed great flexibility, including the ability to modify the parameters of an earlier image processing step "in context". Many other compositing packages, such as Blender, Blackmagic Fusion, Nuke and Cineon, also used a similar node-based approach.

Microsoft XNA is a freeware set of tools with a managed runtime environment provided by Microsoft that facilitates video game development and management. XNA is based on the .NET Framework, with versions that run on Windows NT, Windows Phone and the Xbox 360. XNA content is built with the XNA Game Studio, and played using the XNA Framework, or published as native executables.
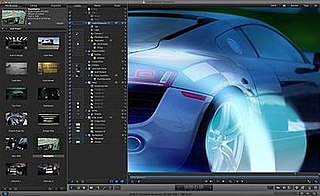
Motion is a software application produced by Apple Inc. for their macOS operating system. It is used to create and edit motion graphics, titling for video production and film production, and 2D and 3D compositing for visual effects.

BBEdit is a proprietary text editor made by Bare Bones Software, originally developed for Macintosh System Software 6, and currently supporting macOS.

Lazarus is a free cross-platform visual integrated development environment (IDE) for rapid application development (RAD) using the Free Pascal compiler.
Geovisualization or geovisualisation, refers to a set of tools and techniques supporting the analysis of geospatial data through the use of interactive visualization.
Microsoft Visual SourceSafe (VSS) is a discontinued source control program, oriented towards small software development projects. Like most source control systems, SourceSafe creates a virtual library of computer files. While most commonly used for source code, SourceSafe can handle any type of file in its database, but older versions were shown to be unstable when used to store large amounts of non-textual data such as images, and compiled executables.
The Apple Developer Tools are a suite of software tools from Apple to aid in making software dynamic titles for the macOS and iOS platforms. The developer tools were formerly included on macOS install media, but are now exclusively distributed over the Internet. As of macOS 10.12, Xcode is available as a free download from the Mac App Store.

Microsoft Visual Studio is an integrated development environment (IDE) from Microsoft. It is used to develop computer programs, as well as websites, web apps, web services and mobile apps. Visual Studio uses Microsoft software development platforms such as Windows API, Windows Forms, Windows Presentation Foundation, Windows Store and Microsoft Silverlight. It can produce both native code and managed code.

The KDE Software Compilation was an umbrella term for the desktop environment plus a range of included applications produced by KDE. From its 1.0 release in July 1998 until the release of version 4.4 in February 2010, the Software Compilation was simply known as KDE, which stood for K Desktop Environment until the rebrand. The then called KDE SC was used for all releases from 4.4 onward until the final release 4.14 in July 2014. It consisted of the KDE Plasma 4 desktop and those KDE applications, whose development teams chose to follow the Software Compilation's release schedule. After that, the KDE SC was split into three separate product entities: KDE Plasma, KDE Frameworks and KDE Applications, each with their own independent release schedules.
ArKaos is an application for live visual performance, conceived as a visual sampler for video loops that can be triggered from the computer, or through a hardware interface. The application is available in two versions: ArKaos VJ MIDI, conceived as a live video performance instrument, often used in conjunction with a MIDI keyboard, and ArKaos VJ DMX, which can be controlled with a DMX console.
Harmony is a Java-based software for creating high-definition music videos with 2D and 3D animations. The application was developed by Digital Chaotics, a company based in San Jose, California and established in 2010 by Ken and Leanna Scott.

The Xojo programming environment and programming language is developed and commercially marketed by Xojo, Inc. of Austin, Texas for software development targeting macOS, Microsoft Windows, Linux, iOS, the Web and Raspberry Pi. Xojo uses a proprietary object-oriented BASIC dialect, formerly known as REALbasic, but now known as Xojo.

DIPS is a set of plug-in objects that handle real-time digital image processing in Max/MSP programming environment. Combining with the built-in objects of the environment, DIPS enables to program the interaction between audio and visual events with ease, and supports the realization of interactive multimedia art as well as interactive computer music.














