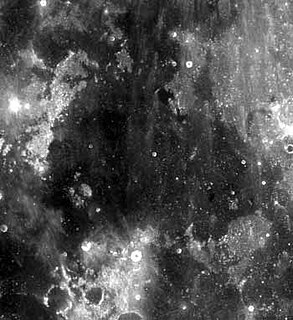
Mare Cognitum is a lunar mare located in a basin or large crater which sits in the second ring of Oceanus Procellarum. To the northwest of the mare is the Montes Riphaeus mountain range, part of the rim of the buried crater or basin containing the mare. Previously unnamed, the mare received its name in 1964 in reference to its selection as the target for the successful impact probe Ranger 7, the first American spacecraft to return closeup images of the Moon's surface.

Mare Serenitatis is a lunar mare located to the east of Mare Imbrium on the Moon. Its diameter is 674 km (419 mi).

Montes Haemus is a mountain range that forms the southwestern edge of the Mare Serenitatis basin on the Moon. They form a less prominent mirror image of the Montes Apenninus range to the west, and curve up to nearly join at the northern end. The eastern edge terminates with the Promontorium Archerusia, to the northwest of the crater Plinius. This end reaches a gap where the Mare Serenitatis to the north joins the Mare Tranquillitatis to the south.
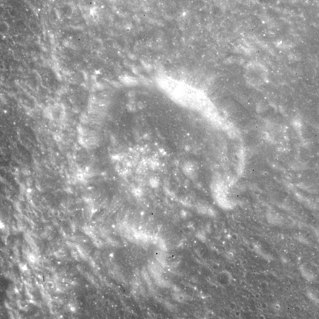
Secchi is a small lunar impact crater formation on the northwest edge of Mare Fecunditatis. It was named after the 19th-century Italian astronomer Angelo Secchi. To the northeast is the crater Taruntius. The western rim is joined with a section of the minor Montes Secchi range. The rim of this crater has been opened in the northern and southern ends, leaving two curved ridges facing each other across the crater floor. To the south is a pair of rilles designated the Rimae Secchi. These lie near the edge of the mare, and have a combined length of about 40 kilometers.

Apianus is a lunar impact crater that is located on the rugged south-central highlands of the Moon. It is named after 16th century German mathematician and astronomer Petrus Apianus. It is located to the northeast of the crater Aliacensis, and to the northwest of Poisson. The worn crater Krusenstern is attached to the west-northwestern rim.

Apollo is an enormous impact crater located in the southern hemisphere on the far side of the Moon. This formation dwarfs the large crater Oppenheimer that is located next to the western rim. The crater Barringer lies across the northern wall. To the southeast is the crater Anders, and Kleymenov is just to the east of the rim.
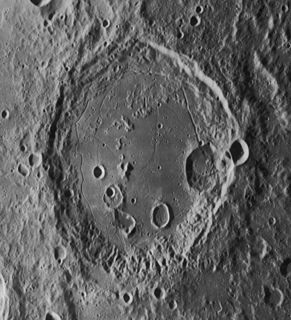
Gauss is a large lunar impact crater, named after Carl Friedrich Gauss, that is located near the northeastern limb of the Moon's near side. It belongs to a category of lunar formations called a walled plain, meaning that it has a diameter of at least 110 kilometers, with a somewhat sunken floor and little or no central massif. Due to its location, this crater appears considerably foreshortened when viewed from the Earth, and its visibility is affected by libration.

Montes Jura is a mountain range in the northwest part of the near side of the Moon. The selenographic coordinates of this range are 47.1° N 34.0° W. It has a diameter of 422 km, with mountains rising to approximately 3800m above the level of Sinus Iridum. They were named after the Jura Mountains in eastern France / western Switzerland.

Montes Archimedes is a mountain range on the Moon. It is named after the nearby crater Archimedes, which in turn is named after the ancient Greek mathematician Archimedes.

Santos-Dumont is a small lunar impact crater that lies in the northern end of the Montes Apenninus range at the eastern edge of the Mare Imbrium. It is located about 30 kilometers to the northeast of Mons Hadley, a mountain massif.

Mons Hadley is a massif in the northern portion of the Montes Apenninus, a range in the northern hemisphere of the Moon. It has a height of 4.2 km (14,000 ft) above the adjacent plain and a maximum diameter of 25 km at the base.

Montes Harbinger is an isolated cluster of lunar mountains at the western edge of the Mare Imbrium basin.

Mons Vitruvius is a mountain on the Moon that is located in the Montes Taurus region just to the north of Mare Tranquillitatis and to the southeast of Mare Serenitatis. This massif is located at selenographic coordinates of 19.4° N, 30.8° E, and it has a diameter across the base of 15 km. It rises to a maximum height of about 2.3 km near the northeastern end. This mountain was named after the nearby crater Vitruvius, located to the south-southeast. The eponym for this crater is ancient Roman engineer and architect Marcus Vitruvius Pollio.

Mons Hadley Delta (δ) is a massif in the northern portion of the Montes Apenninus, a range in the northern hemisphere of the Moon adjacent to Mare Imbrium. It has a height of 3.6 km above the plains to the north and west.

Sinus Aestuum forms a northeastern extension to Mare Insularum. It is centered at selenographic coordinates 12.1° N, 8.3° W, and it lies within a diameter of about 320 km.

Palus Putredinis is a small lunar mare in the basin of Mare Imbrium. It stretches from the crater Archimedes southeast toward the rugged Montes Apenninus range located on the southeastern edge of Mare Imbrium. This region is a nearly level, lava-flooded plain bounded by the crater Autolycus and nearby highlands to the northeast and the foothills of the Montes Archimedes to the southwest. The selenographic coordinates are 27.4° N, 0.0° E, and it lies within a diameter of 180 km.

Lacus Bonitatis is a small lunar mare that lies to the northwest of the prominent crater Macrobius. Further to the north of Lacus Bonitatis is the Montes Taurus mountain range.

Montes Caucasus is a rugged range of mountains in the northeastern part of the Moon. It begins at a gap of level surface that joins the Mare Imbrium to the west with the Mare Serenitatis to the east, and extends in an irregular band to the north-northeast to the western side of the prominent crater Eudoxus. The range forms the northwestern boundary of the Mare Serenitatis. It forms a continuation of the Montes Apenninus range to the southwest.

Mount Marilyn is a lunar mountain within the Montes Secchi, which separate Mare Fecunditatis to the east from Mare Tranquillitatis to the west. It was named at about the time of the Apollo 8 mission to the Moon in 1968 by astronaut Jim Lovell for his wife, Marilyn. The name was informal until July 26, 2017, when it was officially recognized by the IAU. Its approximate position is 40 degrees E, 1.1 degrees N.
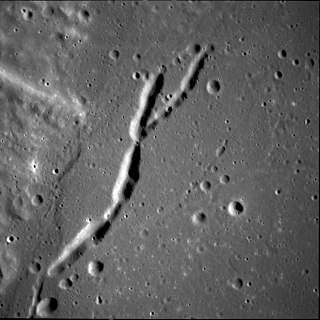
Rimae Secchi is a system of rilles on the Moon, in northwestern Mare Fecunditatis. They are approximately 40 km long and run along the shore of the mare.






















