Related Research Articles

Rhys ap Gruffydd or ap Gruffudd was the ruler of the kingdom of Deheubarth in south Wales from 1155 to 1197. Today, he is commonly known as The Lord Rhys, in Welsh Yr Arglwydd Rhys, although this title may have not been used in his lifetime. He usually used the title "Proprietary Prince of Deheubarth" or "Prince of South Wales", but two documents have been discovered in which he uses the title "Prince of Wales" or "Prince of the Welsh". Rhys was one of the most successful and powerful Welsh princes, and, after the death of Owain Gwynedd of Gwynedd in 1170, the dominant power in Wales.

The Kingdom of Powys was a Welsh successor state, petty kingdom and principality that emerged during the Middle Ages following the end of Roman rule in Britain. It very roughly covered the northern two-thirds of the modern county of Powys and part of today's English West Midlands. More precisely, and based on the Romano-British tribal lands of the Ordovices in the west and the Cornovii in the east, its boundaries originally extended from the Cambrian Mountains in the west to include the modern West Midlands region of England in the east. The fertile river valleys of the Severn and Tern are found here, and this region is referred to in later Welsh literature as "the Paradise of Powys".
Richard fitz Gilbert de Clare 3rd feudal baron of Clare in Suffolk, was an Anglo-Norman nobleman. A marcher lord in Wales, he was also the founder of Tonbridge Priory in Kent.
Gwenllian ferch Gruffydd was Princess consort of Deheubarth in Wales, and married to Gruffydd ap Rhys, Prince of Deheubarth. Gwenllian was the daughter of Gruffudd ap Cynan (1055–1137), Prince of Gwynedd and Angharad ferch Owain, and a member of the princely Aberffraw family of Gwynedd. Gwenllian's "patriotic revolt" and subsequent death in battle at Kidwelly Castle contributed to the Great Revolt of 1136.

Bleddyn ap Cynfyn, sometimes spelled Blethyn, was an 11th-century Welsh king. King Harold Godwinson and Tostig Godwinson installed him and his brother, Rhiwallon, as the co-rulers of Gwynedd on his father's death in 1063, during their destruction of the kingdom of their half-brother, king Gruffydd ap Llywelyn. Bleddyn became king of Powys and co-ruler of the Kingdom of Gwynedd with his brother Rhiwallon from 1063 to 1075. His descendants continued to rule Powys as the House of Mathrafal.
Ifor Bach also known as Ifor ap Meurig and in anglicised form Ivor Bach, Lord of Senghenydd, was a twelfth-century resident in and a leader of the Welsh in south Wales.
Caradog ap Gruffydd was a Prince of Gwent in south-east Wales in the time of Gruffydd ap Llywelyn and the Norman conquest, who reunified his family's inheritance of Morgannwg and made repeated attempts to reunite southern Wales by claiming the inheritance of the Kingdom of Deheubarth.
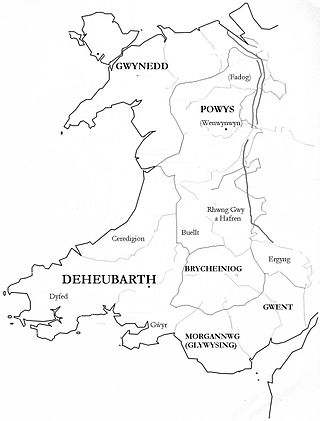
Gwent was a medieval Welsh kingdom, lying between the Rivers Wye and Usk. It existed from the end of Roman rule in Britain in about the 5th century until the Norman invasion of Wales in the 11th century. Along with its neighbour Glywyssing, it seems to have had a great deal of cultural continuity with the earlier Silures, keeping their own courts and diocese separate from the rest of Wales until their conquest by Gruffydd ap Llywelyn. Although it recovered its independence after his death in 1063, Gwent was the first of the Welsh kingdoms to be overrun following the Norman conquest.

Glywysing was, from the sub-Roman period to the Early Middle Ages, a petty kingdom in south-east Wales. Its people were descended from the Iron Age tribe of the Silures, and frequently in union with Gwent, merging to form Morgannwg.
Morgannwg was a medieval Welsh kingdom formed via the merger of the kingdoms of Glywysing and Gwent.
Seisyll ap Dyfnwal was a 12th-century Welsh Lord of Gwent Uwchcoed.
This article is about the particular significance of the century 1101–1200 to Wales and its people.
This article is about the particular significance of the century 1001–1100 to Wales and its people.

Wales in the High Middle Ages covers the 11th to 13th centuries in Welsh history. Beginning shortly before the Norman invasion of the 1060s and ending with the Conquest of Wales by Edward I between 1278 and 1283, it was a period of significant political, cultural and social change for the country.

The history of Gwynedd in the High Middle Ages is a period in the History of Wales spanning the 11th through the 13th centuries. Gwynedd, located in the north of Wales, eventually became the most dominant of Welsh polities during this period. Contact with continental courts allowed for Gwynedd to transition from a petty kingdom into an increasingly sophisticated principality of seasoned courtiers capable of high level deplomacy and representation; not only with the Angevine kings, but also the king of France and the Papal See. Distinctive achievements in Gwynedd include further development of Medieval Welsh literature, particularly poets known as the Beirdd y Tywysogion associated with the court of Gwynedd; the reformation of bardic schools; and the continued development of Cyfraith Hywel. All three of these further contributed to the development of a Welsh national identity in the face of Anglo-Norman encroachment of Wales.
Morgan ap Hywel was Lord of Gwynllwg in Wales from about 1215 until his death in 1245, and for many years laid claim to the lordship of Caerleon, which had been seized by the Earl of Pembroke. For most of his life he was at peace with the English, at a time when there were periodic revolts by Welsh leaders against their rule. He may have participated in a crusade between 1227 and 1231.
Owain ap Caradog, known as Owain ‘Wan’ was the son and heir of King Caradog ap Gruffydd of Morgannwg, who contested the Kingdom of Deheubarth and was killed in the Battle of Mynydd Carn in 1081. Owain contented himself by ruling the former sub-kingdom and later Lordship of Gwynllwg, while the title of King of Morgannwg went to his relative Iestyn ap Gwrgant, who was subsequently deposed c. 1090 as part of the Norman conquest of Wales. In spite of this Owain continued to hold onto territories between the Rhymney and Usk, and may, probably with some struggle, have held onto some or all of Caerleon, where in 1086 the Domesday book records that a small colony of eight carucates of land was held by Turstin FitzRolf, standard bearer to William the Conqueror at Hastings, under the overlordship of William d'Ecouis, a magnate with lands in Herefordshire, Norfolk and other counties. Also listed on the manor were three Welshmen with as many ploughs and carucates, who continued their Welsh customs.
Iorwerth ab Owain was a Welsh prince of Gwynllŵg and Lord of Caerleon.

Hywel ab Iorwerth was a Welsh lord of Caerleon.
References
- ↑ "Welsh Gentry 2". Archived from the original on 11 December 2013. Retrieved 4 December 2013.
- ↑ "Robert Trett: A history of Caerleon Castle".
- ↑ "David Crouch: Roger (Roger fitz Miles), earl of Hereford (Oxford DNB)".
- ↑ David Crouch: The march and the welsh Kings. In: Edmund King: The Anarchy of King Stephen's Reign. Oxford Univ. Press, Oxford 1994, ISBN 978-0-19-820364-3, p. 277
- ↑ "David Crouch: Iorwerth ab Owain (Oxford DNB)".