
The Cooper Creek is a river in the Australian states of Queensland and South Australia. It was the site of the death of the explorers Burke and Wills in 1861. It is sometimes known as the Barcoo River from one of its tributaries and is one of three major Queensland river systems that flow into the Lake Eyre basin. The flow of the creek depends on monsoonal rains falling months earlier and many hundreds of kilometres away in eastern Queensland. It is 1,300 kilometres (810 mi) in length.

John McDouall Stuart, often referred to as simply "McDouall Stuart", was a Scottish explorer and one of the most accomplished of all Australia's inland explorers.

Edward John Eyre was an English land explorer of the Australian continent, colonial administrator, Lieutenant-Governor of New Zealand's New Munster province, and Governor of Jamaica.

The Flinders Ranges are the largest mountain ranges in South Australia, which starts about 200 km (125 mi) north of Adelaide. The ranges stretch for over 430 km (265 mi) from Port Pirie to Lake Callabonna.

The Eyre Peninsula is a triangular peninsula in South Australia. It is bounded by the Spencer Gulf on the east, the Great Australian Bight on the west, and the Gawler Ranges to the north.

The Vulkathunha-Gammon Ranges National Park is a protected area in the Flinders Ranges of South Australia, immediately south-west of and adjacent to the Arkaroola Protection Area. They encompass some of the most rugged and spectacular country in South Australia.

The Flinders River is the longest river in Queensland, Australia, at approximately 1,004 kilometres (624 mi). It was named in honour of the explorer Matthew Flinders. The catchment is sparsely populated and mostly undeveloped. The Flinders rises on the western slopes of the Great Dividing Range in North West Queensland and flows generally north-west through the Gulf Country, across a large, flat clay pan, before entering the Gulf of Carpentaria.

Robert O'Hara Burke was an Irish soldier and police officer who achieved fame as an Australian explorer. He was the leader of the ill-fated Burke and Wills expedition, which was the first expedition to cross Australia from south to north, finding a route across the continent from the settled areas of Victoria to the Gulf of Carpentaria. The expedition party was well equipped, but Burke was not experienced in bushcraft. A Commission of Inquiry held by the Government of Victoria to investigate the failure of the expedition was a censure of Burke's judgement.

William John Wills was a British surveyor who also trained as a surgeon. He was the second-in-command of the Burke and Wills expedition, which was the first expedition to cross Australia from south to north, finding a route across the continent from the settled areas of Victoria to the Gulf of Carpentaria. He and the expedition leader Robert O'Hara Burke both died of exhaustion on the expedition's return journey.

Lake Frome / Munda is a large endorheic lake in the Australian state of South Australia to the east of the Northern Flinders Ranges. It is a large, shallow, unvegetated salt pan, 100 kilometres (62 mi) long and 40 kilometres (25 mi) wide, lying mostly below sea level and having a total surface area of 259,615 hectares. It only rarely fills with brackish water flowing down usually dry creeks in the Northern Flinders Ranges from the west, or exceptional flows down the Strzelecki Creek from the north.

Innamincka, formerly Hopetoun, is a township and locality in north-east South Australia. By air it is 820 kilometres north-east of the state capital, Adelaide, and 365 kilometres north-east of the closest town, Lyndhurst. It is 66 kilometres north-east of the Moomba Gas Refinery. The town lies within the Innamincka Regional Reserve and is surrounded by the Strzelecki Desert to the south and the Sturt Stony Desert to the north. It is linked by road to Lyndhurst via the Strzelecki Track, to the Birdsville Developmental Road via Cordillo Downs Road and Arrabury Road, and the Walkers Crossing Track to the Birdsville Track. The Walkers Crossing Track is closed in summer and only traversable in dry weather. The township is situated along the Cooper Creek, a part of the Lake Eyre basin.

The Strzelecki Desert is located in the Far North Region of South Australia, South West Queensland and western New South Wales. It is positioned in the northeast of the Lake Eyre Basin, and north of the Flinders Ranges. Two other deserts occupy the Lake Eyre Basin—the Tirari Desert and the Simpson Desert.
Edward John Eyre made two expeditions into the interior of South Australia in 1839. At the time nobody had been any further than the head of Spencer Gulf. The first expedition, in May, set out from Adelaide. It is not exactly clear how far north he reached before turning back, but somewhere in the Flinders Ranges. The second expedition, in August, sailed to Port Lincoln, and struck out west following the coast to Streaky Bay. Forced back again by inhospitable conditions, he went east and then further north than the previous attempt, eventually finding the lake that is now called Lake Torrens.
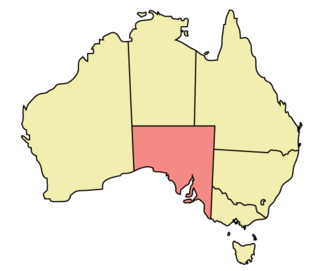
The geography of South Australia incorporates the south central part of the continent of Australia. It is one of the six states of Australia. South Australia is bordered on the west by Western Australia, to the north by the Northern Territory, Queensland to the northeast, and both New South Wales and Victoria to the east. South Australia's south coast is flanked by the Great Australian Bight and the Southern Ocean.

Robert Cock was one of the first European explorers of the Adelaide region of South Australia following the establishment of the colony in December 1836.

South Australia is an Australian state, situated in the southern central part of the country, and featuring some low-lying mountain ranges, the most significant being the Mount Lofty Ranges, which extend into the state's capital city, Adelaide, which comprises most of the state's population. Adelaide is situated on the eastern shores of Gulf St Vincent, on the Adelaide Plains, north of the Fleurieu Peninsula, between Gulf St Vincent and the low-lying Mount Lofty Ranges. The state of South Australia, which stretches along the coast of the continent and has boundaries with every other state in Australia, with the exception of the Australian Capital Territory and Tasmania. The Western Australia border has a history with South Australia, involving the South Australian Government Astronomer, Dodwell and the Western Australian Government Astronomer, Curlewis in the 1920s to mark the border on the ground.

Mount Hill is a prominent peak in the Australian state of South Australia on the eastern side of southern Eyre Peninsula. It is located within the locality of Butler.

Edward Bate Scott was a pioneering colonist of South Australia who accompanied Edward John Eyre on several journeys and had a later career with the South Australian Police Force.
Blanchewater Station is a pastoral lease that operates as a cattle station in the far north of South Australia.
The Yandruwandha, alternatively known as Jandruwanta, are an Aboriginal Australian people living in the Lakes area of South Australia, south of Cooper Creek and west of the Wangkumara people.

















