Related Research Articles

The Hope Diamond is a 45.52 carats diamond that has been famed for its great size since the 18th century. Extracted in the 17th century from the Kollur Mine in Guntur, India, the Hope Diamond is a blue diamond. Its exceptional size has revealed new information about the formation of diamonds.

The Cullinan Diamond is the largest gem-quality rough diamond ever found, weighing 3,106 carats (621.20 g), discovered at the Premier No.2 mine in Cullinan, South Africa, on 26 January 1905. It was named after Thomas Cullinan, the owner of the mine. In April 1905, it was put on sale in London, but despite considerable interest, it was still unsold after two years. In 1907, the Transvaal Colony government bought the Cullinan and Prime Minister Louis Botha presented it to Edward VII, the British king who reigned over the territory. It was then cut by Joseph Asscher & Co. in Amsterdam.

The Argyle Diamond Mine was a diamond mine located in the East Kimberley region in the remote north of Western Australia. Argyle was at times the largest diamond producer in the world by volume, although the proportion of gem-quality diamonds was low. It was the only known significant source of pink and red diamonds, and additionally provided a large proportion of other naturally coloured diamonds, including champagne, cognac and rare blue diamonds.

The Orlov, also often considered to be the same diamond known as The Great Mughal Diamond, is a large diamond of Indian origin, currently displayed as a part of the Diamond Fund collection of Moscow's Kremlin Armoury. It is described as having the shape and proportions of half a chicken's egg. In 1774, it was encrusted into the Imperial Sceptre of Russian Empress Catherine the Great.
The Heart of Eternity is a diamond measuring 27.64 carats, rated in color as "Fancy Vivid Blue" by the Gemological Institute of America. The Heart of Eternity was cut by the Steinmetz Group, who owned the diamond before selling it to the De Beers Group.
The Ocean Dream is a diamond, measuring 5.51 carats, and rated in color as Fancy Deep Blue-Green by the Gemological Institute of America. The Ocean Dream is the first and one of the only natural diamonds known to the GIA to possess a blue-green hue, making it one of the rarest diamonds in the world. A blue-green colour is commonly seen in artificially enhanced diamonds, whose colour is imparted by various irradiation methods. The Ocean Dream originated in Central Africa, and is currently owned by the Cora Diamond Corporation.
The Pink Star, formerly known as the Steinmetz Pink, is a diamond weighing 59.60 carats, rated in color as Fancy Vivid Pink by the Gemological Institute of America. The Pink Star was mined by De Beers in 1999 in South Africa, and weighed 132.5 carats in the rough. The Pink Star is the largest known diamond having been rated Vivid Pink. As a result of this exceptional rarity, the Beny Steinmetz Group called Steinmetz Diamonds took a cautious 20 months to cut the Pink. It was unveiled in Monaco on 29 May 2003 in a public ceremony.

The Jubilee Diamond, originally known as the Reitz Diamond is a colourless, cushion-shaped diamond weighing 245.35 carats, making it the sixth largest diamond in the world. It was originally named after Francis William Reitz, the then president of the Orange Free State where the stone was discovered, before being renamed to honour the 60th anniversary of the coronation of Queen Victoria in 1897.

The Premier Mine is an underground diamond mine owned by Petra Diamonds in the town of Cullinan, 40 kilometres (25 mi) east of Pretoria, Gauteng Province, South Africa. Established in 1902, it was renamed the Cullinan Diamond Mine in November 2003 in celebration of its centenary. The mine is a carrot-shaped volcanic pipe and has a surface area of 32 hectares. The mine rose to prominence in 1905, when the Cullinan Diamond – the largest rough diamond of gem quality ever found – was discovered there.

Harry Winston was an American jeweler. He donated the Hope Diamond to the Smithsonian Institution in 1958 after owning it for a decade. He also traded the Portuguese Diamond to the Smithsonian in 1963 in exchange for 3,800 carats of small diamonds.
Shlomo Moussaieff was an Israeli jeweler, of Bukharan Jewish descent. He was the grandson of the gemstone trader Rabbi Moussaieff from Uzbekistan. Founder of Moussaieff Jewellers Ltd., he and his wife Alisa were ranked No. 315 on the Sunday Times Rich List 2011, with a fortune estimated at £220 million. In addition, he was regarded as one of the world's top private collectors of antiquities associated with the Bible and ancient Near East, with a collection of 60,000 artefacts.
The largest flawless diamond in the world is known as The Paragon, a D-color gem weighing 137.82 carats (27.564 g), and the tenth largest white diamond in the world. The gem was mined in Brazil and attracted attention for being an exceptional white, flawless stone of great size. The Mayfair-based jeweller Graff Diamonds acquired the stone in Antwerp, cut it into an unusual seven-sided kite shield configuration, and set it in a necklace which separates to both necklace and bracelet lengths. Apart from the main stone, this necklace also contains rare pink, blue, and yellow diamonds, making a total mass of 190.27 carats (38.054 g). The necklace has associations with the end of the millennium and was worn by model Naomi Campbell at a diamond gala held by De Beers and Versace at Syon House in 1999.

Diamond is a gemstone formed by cutting a raw diamond. Diamonds are one of the best-known and most sought-after gems, and they have been used as decorative items since ancient times.
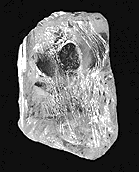
The 968.9-carat (193.78 g) Star of Sierra Leone diamond was discovered by miners on February 14, 1972, in the Diminco alluvial mines in the Koidu area of Sierra Leone. It ranks as the fourth-largest gem-quality diamond and the largest alluvial diamond ever discovered.

Brown diamonds are the most common color variety of natural diamonds. In most mines, brown diamonds account for 15% of production. The brown color makes them less attractive to some people as gemstones, and most are used for industrial purposes. However, improved marketing programs, especially in Australia and the United States, have resulted in brown diamonds becoming valued as gemstones and even referred to as chocolate diamonds.
Graff is a British multinational jeweller based in London. It was founded by British jeweller Laurence Graff in 1960. A vertically integrated company, Graff operations comprise the design, manufacture and retail distribution of jewellery and watches.

The Patiala Necklace was a necklace designed and made by Cartier in 1928. It was part of the largest ever single order to Cartier to date, made in 1925 by the Indian royal, the Maharaja of Patiala, for the Patiala Necklace and other jewelry worth ₹1,000 million.

The DeYoung Red Diamond is a 5.03-carat unmounted rare red diamond. It is the third-largest red diamond in the world, and the only one on public display. Sydney DeYoung obtained the diamond, which was mistaken for a garnet, at a flea market. The diamond was given to the Smithsonian Institution after DeYoung's death in 1986.

A red diamond is a diamond which displays red color and exhibits the same mineral properties as colorless diamonds. Red diamonds are commonly known as the most expensive and the rarest diamond color in the world, even more so than pink or blue diamonds, as very few red diamonds have been found. Red diamonds, just like pink diamonds, are greatly debated as to the source of their color, but the gemological community most commonly attributes both colors to gliding atoms in the diamond's structure as it undergoes enormous pressure during its formation.
References
- 1 2 3 "The Splendor of Diamonds". 2016-03-21. Archived from the original on 2016-03-21. Retrieved 2023-01-30.
- ↑ "Moussaieff Jewelers". GemSelect. 22 July 2008. Retrieved 29 April 2012.
- ↑ "A Man of Good Fortune". Haaretz . 10 October 2001. Retrieved 29 April 2012.
- ↑ "An Important Exhibition of Seven Rare Gem Diamonds | Gems & Gemology". 2014-02-27. Archived from the original on 2014-02-27. Retrieved 2023-01-30.