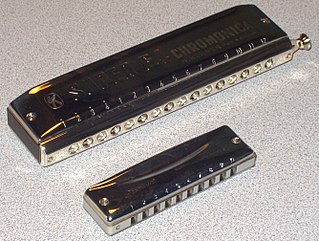
The harmonica, also known as a French harp or mouth organ, is a free reed wind instrument used worldwide in many musical genres, notably in blues, American folk music, classical music, jazz, country, and rock. The many types of harmonica include diatonic, chromatic, tremolo, octave, orchestral, and bass versions. A harmonica is played by using the mouth to direct air into or out of one holes along a mouthpiece. Behind each hole is a chamber containing at least one reed. The most common is the diatonic Richter-tuned with ten air passages and twenty reeds, often called the blues harp. A harmonica reed is a flat, elongated spring typically made of brass, stainless steel, or bronze, which is secured at one end over a slot that serves as an airway. When the free end is made to vibrate by the player's air, it alternately blocks and unblocks the airway to produce sound.

The melodica is a handheld free-reed instrument similar to a pump organ or harmonica. It features a musical keyboard on top, and is played by blowing air through a mouthpiece that fits into a hole in the side of the instrument. The keyboard usually covers two or three octaves. Melodicas are small, lightweight, and portable, and many are designed for children to play. They are popular in music education programs, especially in Asia. The modern form of the instrument was invented by Hohner in the late 1950s, though similar instruments have been known in Italy since the 19th century.

An aerophone is a musical instrument that produces sound primarily by causing a body of air to vibrate, without the use of strings or membranes, and without the vibration of the instrument itself adding considerably to the sound.

The sheng is a Chinese mouth-blown polyphonic free reed instrument consisting of vertical pipes.

The khene is a Lao mouth organ whose pipes, which are usually made of bamboo, are connected with a small, hollowed-out hardwood reservoir into which air is blown. The khene is the national instrument of Laos. The khene music is an integral part of Lao life that promotes family and social cohesion and it was inscribed in 2017 on the UNESCO Representative List of the Intangible Cultural Heritage of Humanity. Although it is associated with the Lao people of Laos and Isan nowadays, other similar instruments date back to the Bronze Age. In Cambodia, it is used among the ethnic Lao population of the province of Stung Treng and is used in lakhon ken, a Cambodian dance drama genre that features the khene as the main instrument In Vietnam, this instrument is used among the Tai peoples and the Muong people.

A free reed aerophone is a musical instrument that produces sound as air flows past a vibrating reed in a frame. Air pressure is typically generated by breath or with a bellows. In the Hornbostel–Sachs system, it is number: 412.13. Free reed instruments are contrasted with non-free or enclosed reed instruments, where the timbre is fully or partially dependent on the shape of the instrument body, Hornbostel–Sachs number: 42.

Hohner Musikinstrumente GmbH & Co. KG is a German manufacturer of musical instruments, founded in 1857 by Matthias Hohner (1833–1902). The roots of the Hohner firm are in Trossingen, Baden-Württemberg. Since its foundation, and though known for its harmonicas, Hohner has manufactured a wide range of instruments, such as kazoos, accordions, recorder flutes, melodicas, banjos, electric, acoustic, resonator and classical guitars, basses, mandolins and ukuleles

The bawu is a Chinese wind instrument. Although shaped like a flute, it is actually a free reed instrument, with a single metal reed. It is played in a transverse (horizontal) manner. It has a pure, clarinet-like timbre and its playing technique incorporates the use of much ornamentation, particularly bending tones.

The saenghwang is a Korean wind instrument. It is a free reed mouth organ derived from the Chinese sheng, though its tuning is different.
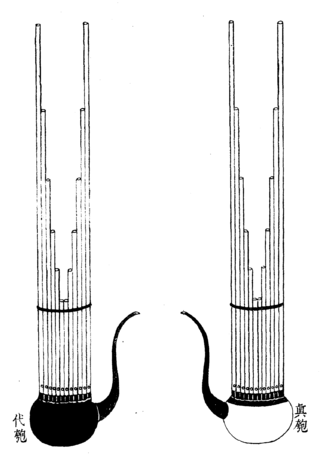
The Yu is a free reed wind instrument used in ancient China. It is similar to the sheng, with multiple bamboo pipes fixed in a wind chest which may be made out of bamboo, wood, or a gourd. Each pipe contains a free reed, which is also made of bamboo. Whereas the sheng is used to provide simultaneous tones in harmony, the yu is played in single lines melodically. The instrument was used, often in large numbers, in court orchestras of ancient China but is no longer used.

The lusheng is a Hmong musical instrument. It has a long history of 3000 years in China, traced back to the Tang Dynasty. It is a mouth organ with multiple bamboo pipes, each fitted with a free reed, which are fitted into a long blowing tube made of hardwood. It most often has five or six pipes of different pitches and is thus a polyphonic instrument. Its construction includes six parts. It comes in sizes ranging from very small to several meters in length.

The hulusi, also known as the cucurbit flute and the gourd flute is a free reed wind instrument from China, Vietnam and the Shan State and by the indigenous people of Assam. It is held vertically and has three bamboo pipes that pass through a Calabash gourd wind chest; the center pipe has finger holes and the outer two are typically drone pipes. It is not uncommon for a hulusi to have only one drone pipe while the second outer pipe is merely ornamental. The drone pipe has a finger hole which allows it to be stopped. Advanced configurations have keyed finger holes similar to a clarinet or oboe, which can greatly extend the range of the hulusi to several octaves.
The mangtong is a Chinese end-blown free reed wind instrument. It is used primarily by the Miao and Dong ethnic groups of the southern Chinese provinces of Guizhou and Guangxi, although it is sometimes used in contemporary Chinese compositions for the traditional instrument orchestra.

A tremolo harmonica is a type of diatonic harmonica, distinct by having two reeds per note. In a tremolo harmonica, the two reeds are tuned slightly off a reference pitch, one slightly sharp and the other slightly flat. This gives a unique wavering or warbling sound created by the two reeds being not exactly in tune with each other and difference in their subsequent waveforms acting against one another. The degree of beating can be varied depending on the desired effect. Instruments where the beating is faster due to the reeds being farther apart from the reference pitch are called "wet", whereas those where the beating is slower and less noticeable due to the reeds being more closely in tune are called "dry".

The gourd mouth organ is a free reed mouth organ played across East and Southeast Asia. It consists of a gourd wind chest with several bamboo or bronze pipes inserted on top of it, the numbers of pipes differing from region to region.
Hmong music is an important part of the culture of the Hmong people, an ethnic group from southeast Asia. Because the Hmong language is tonal, there is a close connection between Hmong music and the spoken language. Music is an important part of Hmong life, played for entertainment, for welcoming guests, and at weddings and funerals. Hmong musical instruments includes flutes such as the dra, leaves also called nblaw, 2-string violin, and the qeej or gaeng, a type of mouth organ.

Bamboo's natural hollow form makes it an obvious choice for many musical instruments.

The Hohner Harmonetta is a mouth-blown free-reed instrument which was introduced by Hohner in the 1950s. It has an approximately 3-octave range, from C3 to B5.

The ploy is a Cambodian wind instrument. It is constructed of a gourd body with 5 to 7 bamboo tubes protruding from the body, and a bamboo pipe set at a right angle to the gourd. Musicians blow air in through the bamboo tube, which fills the gourd "wind chest" and exits through the other bamboo tubes. Each of the bamboo sound-tubes has a metal rod inside, that vibrate in the air passing through the tube.






























