
An oil well is a drillhole boring in Earth that is designed to bring petroleum oil hydrocarbons to the surface. Usually some natural gas is released as associated petroleum gas along with the oil. A well that is designed to produce only gas may be termed a gas well. Wells are created by drilling down into an oil or gas reserve and if necessary equipped with extraction devices such as pumpjacks. Creating the wells can be an expensive process, costing at least hundreds of thousands of dollars, and costing much more when in difficult-to-access locations, e.g., offshore. The process of modern drilling for wells first started in the 19th century but was made more efficient with advances to oil drilling rigs and technology during the 20th century.

A drilling rig is an integrated system that drills wells, such as oil or water wells, or holes for piling and other construction purposes, into the earth's subsurface. Drilling rigs can be massive structures housing equipment used to drill water wells, oil wells, or natural gas extraction wells, or they can be small enough to be moved manually by one person and such are called augers. Drilling rigs can sample subsurface mineral deposits, test rock, soil and groundwater physical properties, and also can be used to install sub-surface fabrications, such as underground utilities, instrumentation, tunnels or wells. Drilling rigs can be mobile equipment mounted on trucks, tracks or trailers, or more permanent land or marine-based structures. The term "rig" therefore generally refers to the complex equipment that is used to penetrate the surface of the Earth's crust.
A mud engineer works on an oil well or gas well drilling rig, and is responsible for ensuring the properties of the drilling fluid, also known as drilling mud, are within designed specifications.

A chemical plant is an industrial process plant that manufactures chemicals, usually on a large scale. The general objective of a chemical plant is to create new material wealth via the chemical or biological transformation and or separation of materials. Chemical plants use specialized equipment, units, and technology in the manufacturing process. Other kinds of plants, such as polymer, pharmaceutical, food, and some beverage production facilities, power plants, oil refineries or other refineries, natural gas processing and biochemical plants, water and wastewater treatment, and pollution control equipment use many technologies that have similarities to chemical plant technology such as fluid systems and chemical reactor systems. Some would consider an oil refinery or a pharmaceutical or polymer manufacturer to be effectively a chemical plant.
Transformer oil or insulating oil is an oil that is stable at high temperatures and has excellent electrical insulating properties. It is used in oil-filled wet transformers, some types of high-voltage capacitors, fluorescent lamp ballasts, and some types of high-voltage switches and circuit breakers. Its functions are to insulate, suppress corona discharge and arcing, and to serve as a coolant.

In geotechnical engineering, drilling fluid, also known as drilling mud, is used to aid the drilling of boreholes into the earth. Used while drilling oil and natural gas wells and on exploration drilling rigs, drilling fluids are also used for much simpler boreholes, such as water wells.

A blowout is the uncontrolled release of crude oil and/or natural gas from an oil well or gas well after pressure control systems have failed. Modern wells have blowout preventers intended to prevent such an occurrence. An accidental spark during a blowout can lead to a catastrophic oil or gas fire.

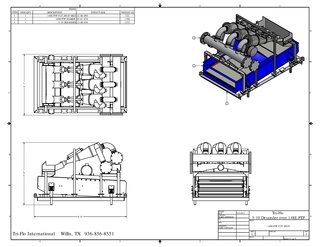
Shale shakers are components of drilling equipment used in many industries, such as coal cleaning, mining, oil and gas drilling.They are the first phase of a solids control system on a drilling rig, and are used to remove large solids (cuttings) from the drilling fluid ("mud").

Drill cuttings are broken bits of solid material removed from a borehole drilled by rotary, percussion, or auger methods and brought to the surface in the drilling mud. Boreholes drilled in this way include oil or gas wells, water wells, and holes drilled for geotechnical investigations or mineral exploration.
A well kill is the operation of placing a column of special fluids of the required density into a well bore in order to prevent the flow of reservoir fluids without the need for pressure control equipment at the surface. It works on the principle that the hydrostatic head of the "kill fluid" or "kill mud" will be enough to suppress the pressure of the formation fluids. Well kills may be planned in the case of advanced interventions such as workovers, or be contingency operations. The situation calling for a well kill will dictate the method taken.
An oil production plant is a facility which processes production fluids from oil wells in order to separate out key components and prepare them for export. Typical oil well production fluids are a mixture of oil, gas and produced water. An oil production plant is distinct from an oil depot, which does not have processing facilities.

A mud tank is an open-top container, typically made of square steel tube and steel plate, to store drilling fluid on a drilling rig. They are also called mud pits, as they were once simple pits in the earth.
Desanders and desilters are solid control equipment with a set of hydrocyclones that separate sand and silt from the drilling fluids in drilling rigs. Desanders are installed on top of the mud tank following the shale shaker and the degasser, but before the desilter. The desander removes the abrasive solids from the drilling fluids which cannot be removed by shakers. Normally, the solid diameters for desanders to separate would be 45~74μm, and 15~44μm for desilters.

Mud Gas Separator is commonly called a gas-buster or poor boy degasser. It captures and separates the large volumes of free gas within the drilling fluid. If there is a "kick" situation, this vessel separates the mud and the gas by allowing it to flow over baffle plates. The gas then is forced to flow through a line, venting to a flare. A "kick" situation happens when the annular hydrostatic pressure in a drilling well temporarily falls below that of the formation, or pore, pressure in a permeable section downhole, and before control of the situation is lost.
A degasser is a device used in the upstream oil industry to remove dissolved and entrained gases from a liquid. In drilling it is used to remove gasses from drilling fluid which could otherwise form bubbles. In a produced water treatment plant it is part of the process to clean produced water prior to disposal.

Offshore oil spill prevention and response is the study and practice of reducing the number of offshore incidents that release oil or hazardous substances into the environment and limiting the amount released during those incidents.

Oil well control is the management of the dangerous effects caused by the unexpected release of formation fluid, such as natural gas and/or crude oil, upon surface equipment of oil or gas drilling rigs and escaping into the atmosphere. Technically, oil well control involves preventing the formation gas or fluid (hydrocarbons), usually referred to as kick, from entering into the wellbore during drilling or well interventions.












