A cairn is a human-made pile of stones raised for a purpose, usually as a marker or as a burial mound. The word cairn comes from the Scottish Gaelic: càrn.

The Isle of Man had become physically separated from Great Britain and Ireland by 6500 BC. It appears that colonisation took place by sea sometime during the Mesolithic era. The island has been visited by various raiders and trading peoples over the years. After being settled by people from Ireland in the first millennium AD, the Isle of Man was converted to Christianity and then suffered raids by Vikings from Norway. After becoming subject to Norwegian suzerainty as part of the Kingdom of Mann and the Isles, the Isle of Man later became a possession of the Scottish and then the English crowns.

Stonehenge is a prehistoric megalithic structure on Salisbury Plain in Wiltshire, England, two miles (3 km) west of Amesbury. It consists of an outer ring of vertical sarsen standing stones, each around 13 feet (4.0 m) high, seven feet (2.1 m) wide, and weighing around 25 tons, topped by connecting horizontal lintel stones, held in place with mortise and tenon joints, a feature unique among contemporary monuments. Inside is a ring of smaller bluestones. Inside these are free-standing trilithons, two bulkier vertical sarsens joined by one lintel. The whole monument, now ruinous, is aligned towards the sunrise on the summer solstice and sunset on the winter solstice. The stones are set within earthworks in the middle of the densest complex of Neolithic and Bronze Age monuments in England, including several hundred tumuli.

A megalith is a large stone that has been used to construct a prehistoric structure or monument, either alone or together with other stones. There are over 35,000 structures or arrangements in Europe alone, located widely from Sweden to the Mediterranean sea.

Avebury is a Neolithic henge monument containing three stone circles, around the village of Avebury in Wiltshire, in south-west England. One of the best-known prehistoric sites in Britain, it contains the largest megalithic stone circle in the world. It is both a tourist attraction and a place of religious importance to contemporary pagans.
Gerhard Bersu was a German archaeologist who excavated widely across Europe. He was forced into exile from Germany in 1937 due to anti-Semitic laws in pre-war Nazi Germany. He was interned on the Isle of Man during World War II where he made several significant archaeological discoveries such as the Viking boat burial at Balladoole.

Spiro Mounds is an Indigenous archaeological site located in present-day eastern Oklahoma. The site was built by people from the Arkansas Valley Caddoan culture. that remains from an American Indian culture that was part of the major northern Caddoan Mississippian culture. The 80-acre site is located within a floodplain on the southern side of the Arkansas River. The modern town of Spiro developed approximately seven miles to the south.

The dolmens of Jersey are Neolithic sites, including dolmens, in Jersey. They range over a wide period, from around 4800 BC to 2250 BC, these dates covering the periods roughly designated as Neolithic, or “new stone age”, to Chalcolithic, or “copper age”.

Philip Moore Callow Kermode, was a Manx antiquarian, historian and naturalist.

Dartmoor kistvaens are burial tombs or cists from the late Neolithic and early Bronze Age, i.e. from c. 2500 BC to c. 1500 BC. Kistvaens have been found in many places, including Dartmoor, a 954 km2 area of moorland in south Devon, England. The box-like stone tombs were created when the ancient people of the area lived in hut circles. Cists are often to be found in the centre of a cairn circle although some appear solitary which could be the result of the loss of an original slight mound. There are over 180 known cists on Dartmoor although there could be up to 100 that remain buried underneath unexplored cairns. In the South West there are no cists to be found on the Quantock Hills, only 2 to be found on Exmoor and 58 to be found on Bodmin Moor. The Dartmoor cists are unique in that about 94% have the longer axis of the tomb orientated in a NW/SE direction It appears that Dartmoor cists were positioned in such a way that the deceased were facing the Sun.
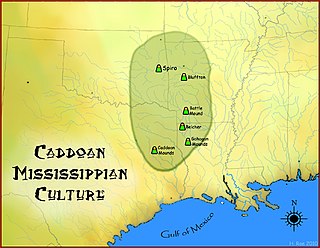
The Gahagan Mounds Site (16RR1) is an Early Caddoan Mississippian culture archaeological site in Red River Parish, Louisiana. It is located in the Red River Valley. The site is famous for the three shaft burials and exotic grave goods excavated there in the early twentieth century.

Five Wells is a Neolithic chambered tomb between the villages of Chelmorton and Taddington on Taddington Moor in the Derbyshire Peak District in England.
The Ronaldsway Culture was the way of life of a Stone Age people on the Isle of Man. Sometimes referred to as Manx Ronaldsway, it dates from the later Neolithic and from the third millennium BC, but more precise dating is a matter of debate.
This page is a glossary of archaeology, the study of the human past from material remains.

King Orry's Grave is the largest megalithic tomb on the Isle of Man. It is situated in Minorca, in the northern part of the village of Laxey, partly in a private cottage garden. It is some 4000 to 5000 years old; however the reference to King Orry is to the 11th century local ruler Godred Crovan, who has a number of supposed burial places. The modern name likely dates to the early 19th century.

Umm Al Maa is an archaeological site in northwest Qatar located in the municipality of Al Khor, near the border with Al Shamal. It is most notable for its ancient cemetery, which is thought to date to the Bronze Age.

Chapel Hill, Balladoole is a significant historical and archaeological site in Arbory on the Isle of Man. The site is a short distance from Castletown in the south of the Island. It is located on a small hilltop overlooking the coast. Balladoole has undergone extensive archaeological excavations in the 20th century, most notably in 1944-1945 by German archaeologist Gerhard Bersu who was interned on the Isle of Man during World War II.

Knock y Doonee is a significant historical and archaeological site in the parish of Andreas on the northern coast of the Isle of Man. The site has been in ritual use for centuries. Archaeological excavations have uncovered a Christian keeill with a bilingual ogham stone and a Christian carved stone cross; and on a nearby hilltop a Viking Age boat burial.

Cashtal yn Ard(Castle of the Heights) is a Neolithic chambered tomb in Cornaa, in the parish of Maughold in the Isle of Man. It is situated on a low hill overlooking much of the surrounding parish of Maughold and across to the Lake District in England. The cairn was excavated in the 1930s and again in 1999. It is one of the most significant megalithic tombs on both the Isle of Man and Britain.

The Knowes of Trotty is a Bronze Age cemetery located in Mainland, Orkney in Scotland. The ancient site consists of a group of twelve surviving burial mounds, dating to 2030–1770 BC. Along with cremated human remains, four gold discs and a number of amber beads and pendants were discovered in the largest mound in 1858. Knowes of Trotty is one of the earliest group of burial mounds in Orkney and one of the largest Bronze Age cemeteries in the United Kingdom.