Double-clutching is a method of shifting gears used primarily for vehicles with an unsynchronized manual transmission, such as commercial trucks and specialty vehicles. While double clutching is not necessary in a vehicle that has a synchronized manual transmission, the technique can be advantageous for smoothly upshifting in order to accelerate and, when done correctly, it prevents wear on the synchronizers which normally equalize transmission input and output speeds to allow downshifting.
Heel-and-toe shifting is an advanced driving technique used mostly in performance driving with a manual gearbox, although some drivers use it on the road in everyday conditions in the interest of effectiveness. It involves operating the throttle and brake pedals simultaneously with the right foot, while facilitating normal activation of the clutch with the left foot. It is used when braking and downshifting simultaneously, and allows the driver to "blip" the throttle to raise the engine speed and smoothly engage the lower gear.

An automatic transmission is a multi-speed transmission used in internal combustion engine-based motor vehicles that does not require any driver input to change forward gears under normal driving conditions. It typically includes a transmission, axle, and differential in one integrated assembly, thus technically becoming a transaxle.

A manual transmission (MT), also known as manual gearbox, standard transmission, or stick shift, is a multi-speed motor vehicle transmission system, where gear changes require the driver to manually select the gears by operating a gear stick and clutch.

In mechanical or automotive engineering, a freewheel or overrunning clutch is a device in a transmission that disengages the driveshaft from the driven shaft when the driven shaft rotates faster than the driveshaft. An overdrive is sometimes mistakenly called a freewheel, but is otherwise unrelated.
A semi-automatic transmission is a multiple-speed transmission where part of its operation is automated, but the driver's input is still required to launch the vehicle from a standstill and to manually change gears. Most semi-automatic transmissions used in cars and motorcycles are based on conventional manual transmissions or sequential manual transmissions, but use an automatic clutch system. However, some semi-automatic transmissions have also been based on standard hydraulic automatic transmissions with torque converters and planetary gearsets.
Engine braking occurs when the retarding forces within an engine are used to slow down a motor vehicle, as opposed to using additional external braking mechanisms such as friction brakes or magnetic brakes.
The modern usage of the automotive term manumatic denotes an automatic transmission that allows the driver to select a specific gear, typically using paddle-shifters, steering wheel-mounted push-buttons, or "+" and "-" controls on the gear selector.

A direct-shift gearbox is an electronically-controlled, dual-clutch, multiple-shaft, automatic gearbox, in either a transaxle or traditional transmission layout, with automated clutch operation, and with fully-automatic or semi-manual gear selection. The first dual-clutch transmissions were derived from Porsche in-house development for the Porsche 962 in the 1980s.

A preselector gearbox is a type of manual transmission mostly used on passenger cars and racing cars in the 1930s, in buses from 1940-1960 and in armoured vehicles from the 1930s to the 1970s. The defining characteristic of a preselector gearbox is that the gear shift lever allowed the driver to "pre-select" the next gear, usually with the transmission remaining in the current gear until the driver pressed the "gear change pedal" at the desired time.

The automated manual transmission (AMT) is a type of transmission for motor vehicles. It is essentially a conventional manual transmission but uses automatic actuation to operate the clutch and/or shift between gears.
A transmission control unit (TCU), also known as a transmission control module (TCM), or a gearbox control unit (GCU), is a type of automotive ECU that is used to control electronic automatic transmissions. Similar systems are used in conjunction with various semi-automatic transmissions, purely for clutch automation and actuation. A TCU in a modern automatic transmission generally uses sensors from the vehicle, as well as data provided by the engine control unit (ECU), to calculate how and when to change gears in the vehicle for optimum performance, fuel economy and shift quality.
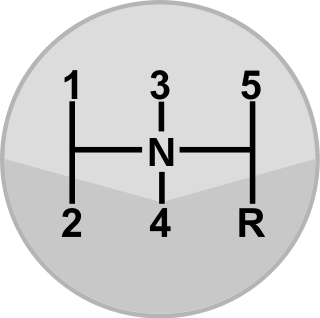
A gear stick, gear lever, gearshift or shifter, more formally known as a transmission lever, is a metal lever attached to the transmission of an automobile. The term gear stick mostly refers to the shift lever of a manual transmission, while in an automatic transmission, a similar lever is known as a gear selector. A gear stick will normally be used to change gear whilst depressing the clutch pedal with the left foot to disengage the engine from the drivetrain and wheels. Automatic transmission vehicles, including hydraulic automatic transmissions, automated manual and older semi-automatic transmissions, like VW Autostick, and those with continuously variable transmissions, do not require a physical clutch pedal.
The name Autostick has been used for a Volkswagen semi-automatic transmission, which is a vacuum-operated automatic clutch system, coupled with a conventional 3-speed manual transmission. The "AutoStick" system designed by Chrysler allows for manual selection of gears with a standard hydraulic automatic transmission, also known as a manumatic.
Clutch control refers to the act of controlling the speed of a vehicle with a manual transmission by partially engaging the clutch plate, using the clutch pedal instead of the accelerator pedal. The purpose of a clutch is in part to allow such control; in particular, a clutch provides transfer of torque between shafts spinning at different speeds. In the extreme, clutch control is used in performance driving, such as starting from a dead stop with the engine producing maximum torque at high RPM.
Synchronized downshift rev-matching system is a technology invented by Nissan for use on the Nissan 370Z. In combination with the Engine Control Unit (ECU) and various sensors, the engine electronically blips the throttle for the driver during both downshifts and upshifts to allow for better and smoother shifting, and improved handling.

A motorcycle transmission is a transmission created specifically for motorcycle applications. They may also be found in use on other light vehicles such as motor tricycles and quadbikes, go-karts, offroad buggies, auto rickshaws, mowers, and other utility vehicles, microcars, and even some superlight racing cars.
9G-Tronic is Mercedes-Benz's trademark name for its nine-speed automatic transmission, starting off with the W9A 700 as core model.

Car controls are the components in automobiles and other powered road vehicles, such as trucks and buses, used for driving and parking.
The Dacia Easy-R is an automated manual transmission used by Renault and Dacia that uses electro-mechanical actuation to automate the gear shifts. The Easy-R uses a traditional manual gearbox with a computer-controlled, electronic clutch; the gear shifts are automatic, and the need for a clutch pedal is eliminated.








