
A sarcoma is a cancer that arises from transformed cells of mesenchymal origin. Connective tissue is a broad term that includes bone, cartilage, fat, vascular, or hematopoietic tissues, and sarcomas can arise in any of these types of tissues. As a result, there are many subtypes of sarcoma, which are classified based on the specific tissue and type of cell from which the tumor originates. It is important to note that sarcomas are primary connective tissue tumors, meaning that they arise in connective tissues. This is in contrast to secondary connective tissue tumors, which occur when a cancer from elsewhere in the body spreads to the connective tissue. The word sarcoma is derived from the Greek σάρξ sarx meaning "flesh".

A myxoma is a myxoid tumor of primitive connective tissue. It is most commonly found in the heart but can also occur in other locations.
Pituitary adenomas are tumors that occur in the pituitary gland. Pituitary adenomas are generally divided into three categories dependent upon their biological functioning: benign adenoma, invasive adenoma, and carcinomas. Most adenomas are benign, approximately 35% are invasive and just 0.1% to 0.2% are carcinomas. Pituitary adenomas represent from 10% to 25% of all intracranial neoplasms and the estimated prevalence rate in the general population is approximately 17%.
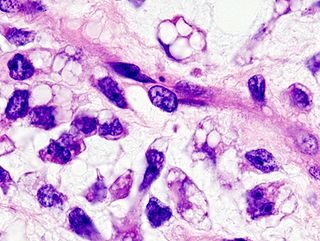
Liposarcoma is a cancer that arises in fat cells in soft tissue, such as that inside the thigh or in the retroperitoneum. It is a rare type of cancer that bears a resemblance to fat cells when examined under a microscope. It is typically a large, bulky tumor, and tends to have multiple smaller satellites that extend beyond the main confines of the tumor. Liposarcomas, like all sarcomas, are rare.
The International Classification of Diseases for Oncology (ICD-O) is a domain-specific extension of the International Statistical Classification of Diseases and Related Health Problems for tumor diseases. This classification is widely used by cancer registries.

A hemangiopericytoma is a type of soft-tissue sarcoma that originates in the pericytes in the walls of capillaries. When inside the nervous system, although not strictly a meningioma tumor, it is a meningeal tumor with a special aggressive behavior. It was first characterized in 1942.
Carney complex and its subsets LAMB syndrome and NAME syndrome are autosomal dominant conditions comprising myxomas of the heart and skin, hyperpigmentation of the skin (lentiginosis), and endocrine overactivity. It is distinct from Carney's triad. Approximately 7% of all cardiac myxomas are associated with Carney complex.
Primary tumors of the heart are extremely rare tumors that arise from the normal tissues that make up the heart. This is in contrast to secondary tumors of the heart, which are typically either metastatic from another part of the body, or infiltrate the heart via direct extension from the surrounding tissues.

A myxoma is a rare benign tumor of the heart. Myxomas are the most common primary cardiac tumor in adults, and are most commonly found within the left atrium. Myxomas may also develop in the other heart chambers. The tumor is derived from multipotent mesenchymal cells.
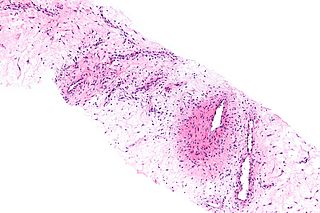
Angiomyxoma is a myxoid tumor involving the blood vessels.
Plexiform fibrohistiocytic tumor is a rare tumor that arises primarily on the upper extremities of children and young adults.

Neurothekeoma is a benign cutaneous tumor first described by Gallager and Helwig, who proposed the term in order to reflect the presumed origin of the lesion from nerve sheath. Microscopically, the lesions described closely resembled the tumor, "nerve sheath myxoma", an entity first described by Harkin and Reed. The latter had, through the years, been variously described as "Bizarre cutaneous neurofibroma", "Myxoma of nerve sheath", and "Pacinian neurofibroma".
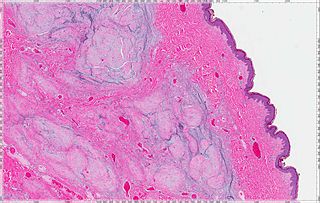
A cutaneous myxoma, or superficial angiomyxoma, consists of a multilobulated myxoid mass containing stellate or spindled fibroblasts with pools of mucin forming cleft-like spaces. There is often a proliferation of blood vessels and an inflammatory infiltrate. Staining is positive for vimentin, negative for cytokeratin and desmin, and variable for CD34, Factor VIIIa, SMA, MSA and S-100.
Extraskeletal myxoid chondrosarcoma (EMC) is a rare low-grade malignant mesenchymal neoplasm of the soft tissues, that differs from other sarcomas by unique histology and characteristic chromosomal translocation. There is an uncertain differentiation and neuroendocrine differentiation is even possible.

Endometrial stromal sarcoma is a malignant subtype of endometrial stromal tumor arising from the stroma of the endometrium rather than the glands. There are three grades for endometrial stromal tumors, as follows. It was previously known as endolymphatic stromal myosis because of diffuse infiltration of myometrial tissue or the invasion of lymphatic channels.
Carney triad (CT) is characterized by the coexistence of three types of neoplasms, mainly in young women, including gastric gastrointestinal stromal tumor, pulmonary chondroma, and extra-adrenal paraganglioma. The underlying genetic defect remains elusive. CT is distinct from Carney complex, and the Carney-Stratakis syndrome.
Ectomesenchymal chondromyxoid tumor (ECT) is a benign intraoral tumor with presumed origin from undifferentiated (ecto)mesenchymal cells. There are some who think it is a myoepithelial tumor type.
Plexiform angiomyxoid myofibroblastic tumor (PAMT), also called plexiform angiomyxoma, plexiform angiomyxoid tumor, or myxofibroma, is an extremely rare benign mesenchymal myxoid tumor along the gastrointestinal tract. Most of PAMTs occur in the gastric antral region, but they can be situated anywhere in the stomach. There is one recorded case of PAMT located in duodenum.
Acral myxoinflammatory fibroblastic sarcoma is a rare low-grade sarcoma. It is most commonly found in the extremities but has been reported elsewhere in the body.








