
Computer-aided manufacturing (CAM) also known as computer-aided modeling or computer-aided machining is the use of software to control machine tools in the manufacturing of work pieces. This is not the only definition for CAM, but it is the most common. It may also refer to the use of a computer to assist in all operations of a manufacturing plant, including planning, management, transportation and storage. Its primary purpose is to create a faster production process and components and tooling with more precise dimensions and material consistency, which in some cases, uses only the required amount of raw material, while simultaneously reducing energy consumption. CAM is now a system used in schools and lower educational purposes. CAM is a subsequent computer-aided process after computer-aided design (CAD) and sometimes computer-aided engineering (CAE), as the model generated in CAD and verified in CAE can be input into CAM software, which then controls the machine tool. CAM is used in many schools alongside CAD to create objects.
Autodesk, Inc. is an American multinational software corporation that makes software products and services for the architecture, engineering, construction, manufacturing, media, education, and entertainment industries. Autodesk is headquartered in San Francisco, California, and has offices worldwide. Its U.S. offices are located in the states of California, Oregon, Colorado, Texas, Michigan, New Hampshire and Massachusetts. Its Canada offices are located in the provinces of Ontario, Quebec, and Alberta.
Mastercam is a suite of computer-aided manufacturing (CAM) and CAD/CAM software applications developed by CNC Software, LLC. Founded in Massachusetts in 1983, CNC Software are headquartered in Tolland, Connecticut.
Creo Parametric, formerly known, together with Creo Elements/Pro, as Pro/Engineer and Wildfire, is a solid modeling or CAD, CAM, CAE, and associative 3D modeling application, running on Microsoft Windows.

In machining, numerical control, also called computer numerical control (CNC), is the automated control of tools by means of a computer. It is used to operate tools such as drills, lathes, mills, grinders, routers and 3D printers. CNC transforms a piece of material into a specified shape by following coded programmed instructions and without a manual operator directly controlling the machining operation.

CAD/CAM refers to the integration of computer-aided design (CAD) and computer-aided manufacturing (CAM). Both of these require powerful computers. CAD software helps designers and draftsmen; CAM "reduces manpower costs" in the manufacturing process.

Tebis is a CAD/CAM software provided by Tebis AG, with headquarters in Martinsried near Munich/Germany. Development locations: Martinsried and Norderstedt, Germany International locations: China, Spain, France, Italy, Portugal, Sweden, United Kingdom, USA.

A Tool and Cutter Grinder is used to sharpen milling cutters and tool bits along with a host of other cutting tools.
Delcam is a supplier of advanced CAD/CAM software for the manufacturing industry. The company has grown steadily since being founded formally in 1977, after initial development work at Cambridge University, UK. It is now a global developer of product design and manufacturing software, with subsidiaries and joint ventures in North America, South America, Europe and Asia with a total staff of over 800 people and local support provided from over 300 re-seller offices worldwide. It was listed on the London Stock Exchange until 6 February 2014, when it was acquired by Autodesk. It now operates as a wholly owned, independently operated subsidiary of Autodesk.

Vero Software is a company based in Cheltenham, England, that specialises in CAD CAM.
Surfware, Inc. is a Camarillo, CA-based company involved in the development of CAD/CAM software.

STEP-NC is a machine tool control language that extends the ISO 10303 STEP standards with the machining model in ISO 14649, adding geometric dimension and tolerance data for inspection, and the STEP PDM model for integration into the wider enterprise. The combined result has been standardized as ISO 10303-238.
Cimatron is an Israeli software company that produces CAD/CAM software for manufacturing, toolmaking and CNC programming applications.

A computer numerical control (CNC) router is a computer-controlled cutting machine which typically mounts a hand-held router as a spindle which is used for cutting various materials, such as wood, composites, metals, plastics, glass, and foams. CNC routers can perform the tasks of many carpentry shop machines such as the panel saw, the spindle moulder, and the boring machine. They can also cut joinery such as mortises and tenons.

Multiaxis machining is a manufacturing process that involves tools that move in 4 or more directions and are used to manufacture parts out of metal or other materials by milling away excess material, by water jet cutting or by laser cutting. This type of machining was originally performed mechanically on large complex machines. These machines operated on 4, 5, 6, and even 12 axes which were controlled individually via levers that rested on cam plates. The cam plates offered the ability to control the tooling device, the table in which the part is secured, as well as rotating the tooling or part within the machine. Due to the machines size and complexity it took extensive amounts of time to set them up for production. Once computer numerically controlled machining was introduced it provided a faster, more efficient method for machining complex parts.

WorkNC is a Computer aided manufacturing (CAM) software developed by Sescoi for multi-axis machining.
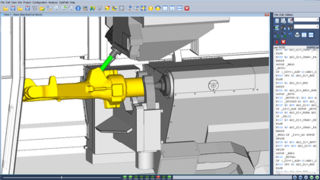
Vericut, is a software program used for simulating CNC machining. It is used to simulate tool motion and the material removal process, detecting errors or areas of inefficiency in NC programs. It was developed by CGTech Inc. and first released in 1988.

In manufacturing, freeform surface machining refers to the machining of complex surfaces that are not uniformly planar. The industries which most often manufactures free-form surfaces are basically aerospace, automotive, die mold industries, biomedical and power sector for turbine blades manufacturing. Generally 3- or 5-axis CNC milling machines are used for this purpose. The manufacturing process of freeform surfaces is not an easy job, as the tool path generation in present CAM technology is generally based on geometric computation so tool path are not optimum. The geometry can also be not described explicitly so errors and discontinuities occurrence in the solid structure cannot be avoided. Free-form surfaces are machined with the help of different tool path generation method like adaptive iso-planar tool path generation, constant scallop tool path generation, adaptive iso-parametric method, iso-curvature, isophote and by other methods. The different methods are chosen based on the parameters which is needed to be optimized.
Digital manufacturing is an integrated approach to manufacturing that is centered around a computer system. The transition to digital manufacturing has become more popular with the rise in the quantity and quality of computer systems in manufacturing plants. As more automated tools have become used in manufacturing plants it has become necessary to model, simulate, and analyze all of the machines, tooling, and input materials in order to optimize the manufacturing process. Overall, digital manufacturing can be seen sharing the same goals as computer-integrated manufacturing (CIM), flexible manufacturing, lean manufacturing, and design for manufacturability (DFM). The main difference is that digital manufacturing was evolved for use in the computerized world.

Fusion is a commercial computer-aided design (CAD), computer-aided manufacturing (CAM), computer-aided engineering (CAE) and printed circuit board (PCB) design software application, developed by Autodesk. It is available for Windows, macOS and web browser, with simplified applications available for Android and iOS. Fusion is licensed as a paid subscription, with a free limited home-based, non-commercial personal edition available.














