DNA glycosylases are a family of enzymes involved in base excision repair, classified under EC number EC 3.2.2. Base excision repair is the mechanism by which damaged bases in DNA are removed and replaced. DNA glycosylases catalyze the first step of this process. They remove the damaged nitrogenous base while leaving the sugar-phosphate backbone intact, creating an apurinic/apyrimidinic site, commonly referred to as an AP site. This is accomplished by flipping the damaged base out of the double helix followed by cleavage of the N-glycosidic bond.
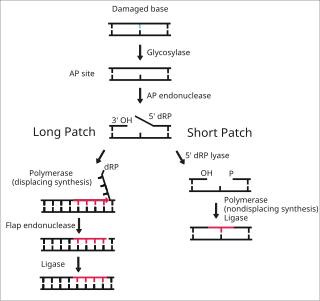
Base excision repair (BER) is a cellular mechanism, studied in the fields of biochemistry and genetics, that repairs damaged DNA throughout the cell cycle. It is responsible primarily for removing small, non-helix-distorting base lesions from the genome. The related nucleotide excision repair pathway repairs bulky helix-distorting lesions. BER is important for removing damaged bases that could otherwise cause mutations by mispairing or lead to breaks in DNA during replication. BER is initiated by DNA glycosylases, which recognize and remove specific damaged or inappropriate bases, forming AP sites. These are then cleaved by an AP endonuclease. The resulting single-strand break can then be processed by either short-patch or long-patch BER.

Werner syndrome ATP-dependent helicase, also known as DNA helicase, RecQ-like type 3, is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the WRN gene. WRN is a member of the RecQ Helicase family. Helicase enzymes generally unwind and separate double-stranded DNA. These activities are necessary before DNA can be copied in preparation for cell division. Helicase enzymes are also critical for making a blueprint of a gene for protein production, a process called transcription. Further evidence suggests that Werner protein plays a critical role in repairing DNA. Overall, this protein helps maintain the structure and integrity of a person's DNA.

8-Oxoguanine glycosylase, also known as OGG1, is a DNA glycosylase enzyme that, in humans, is encoded by the OGG1 gene. It is involved in base excision repair. It is found in bacterial, archaeal and eukaryotic species.

G/T mismatch-specific thymine DNA glycosylase is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the TDG gene. Several bacterial proteins have strong sequence homology with this protein.

Exonuclease 1 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the EXO1 gene.
Centrin-2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CETN2 gene. It belongs to the centrin family of proteins.

Endonuclease III-like protein 1 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the NTHL1 gene.

Chloride intracellular channel 4, also known as CLIC4,p644H1,HuH1, is a eukaryotic gene.
Endonuclease VIII-like 1 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the NEIL1 gene.

GPI transamidase component PIG-T is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the PIGT gene.

Trafficking kinesin-binding protein 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the TRAK1 gene.

BAG family molecular chaperone regulator 2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the BAG2 gene.

REX2, RNA exonuclease 2 homolog , also known as REXO2, is an enzyme which in humans is encoded by the REXO2 gene.

Galactosylgalactosylxylosylprotein 3-beta-glucuronosyltransferase 3 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the B3GAT3 gene.

Zinc transporter ZIP2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SLC39A2 gene.

Chondroitin sulfate proteoglycan 5 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CSPG5 gene.

The FPG IleRS zinc finger domain represents a zinc finger domain found at the C-terminal in both DNA glycosylase/AP lyase enzymes and in isoleucyl tRNA synthetase. In these two types of enzymes, the C-terminal domain forms a zinc finger.

In molecular biology, the H2TH domain is a DNA-binding domain found in DNA glycosylase/AP lyase enzymes, which are involved in base excision repair of DNA damaged by oxidation or by mutagenic agents. Most damage to bases in DNA is repaired by the base excision repair pathway. These enzymes are primarily from bacteria, and have both DNA glycosylase activity EC 3.2.2.- and AP lyase activity EC 4.2.99.18. Examples include formamidopyrimidine-DNA glycosylases and endonuclease VIII (Nei).

Nei endonuclease VIII-like 3 is a protein in humans that is encoded by the NEIL3 gene.


















