External links
- NEO CANDO
- The Center on Urban Poverty and Community Development
- CUPCD Blog
- National Neighborhood Indicators Project
- The Urban Institute
| Academics |
| |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Campus |
| |||||
| Athletics | ||||||
| People | ||||||
| Student life |
| |||||
An editor has nominated this article for deletion. You are welcome to participate in the deletion discussion , which will decide whether or not to retain it. |
| Type | Research and information center affiliated with Case Western Reserve University |
|---|---|
| Location | , , |
| Campus | Urban |
| Website | http://neocando.case.edu/cando/index.jsp |
Northeast Ohio Community and Neighborhood Data for Organizing (NEO CANDO) is an online database built and managed by the Center on Urban Poverty and Community Development, under the direction of Co-director Claudia Coulton at the Mandel School of Applied Social Sciences in Cleveland, Ohio. The database was started in 1988 as CANDO and now houses data for a 17-county region centering on the Greater Cleveland, and the Cuyahoga County area in Northeast Ohio. This data is varied in its completeness for geographies, but contains crime data for the City of Cleveland, food stamp and TANF usage counts, social indicators, economic indicators, and a restricted-use section for properties in the foreclosure, sheriff's sale and Real Estate Owned (REO) process. These data are used by neighborhood associations, Non-profit organizations, governmental agencies such as the Cuyahoga County Planning Commission, and Community Development Corporations such as Slavic Village Development, to plan activities, or to improve neighborhoods, or to propose social programing, and to combat the advance of urban decay accelerated by the 2010 United States foreclosure crisis.
Its use to combat the negative effects of the foreclosure crisis, has been noted and supported as a national model at conferences, such as the national Reclaiming Vacant Properties Conference and in several reports, such as Forefront, a publication of the Federal Reserve Bank of Cleveland, and REO & Vacant Properties: Strategies for Neighborhood Stabilization which is a joint publication of the Federal Reserve Banks of Boston and Cleveland and the Board of Governors.
The Center is a member of the National Neighborhood Indicators Partnership (NNIP), a nationwide partnership of 34 similar organizations, an initiative of the Urban Institute. The mission of the partnership is to democratize social, economic, and other indicator data down to the neighborhoods level for use by local governments and other agencies operating locally.
The Center on Urban Poverty and Community Development (CUPCD) is based in a university context as part of the Mandel School of Applied Social Sciences at Case Western Reserve University. The Mandel School strongly emphasizes direct work with local citywide and community institutions to address the opportunities and problems of poor neighborhoods. The CUPCD mission is "to create, communicate, and apply knowledge of value to a broad range of audiences and constituents concerned with the ultimate goal of reducing urban poverty and its consequences. . . . The Center serves as a pathway between the university, and the community, linking social science to social change."
CUPCD Director Claudia Coulton began assembling neighborhood-level data soon after the Center was founded. In 1990, the Center issued a full report on trends in Cleveland's neighborhoods over the preceding two decades-a report used as the primary basis for the formation of the [ Arthur Naparstek | Cleveland Foundation Commission on Poverty] which was the foundation for "The Cleveland Community-Building Initiative" report (c.f. History of Cleveland). That study became the foundation for the U.S. Department of Housing and Urban Development's Urban Revitalization Demonstration Act of 1993, known as HOPE VI. As this and other reports were more widely disseminated, the Center began to receive more requests for data assistance. In response to this demand, the staff developed the original CAN DO system.
In its current form, NEO CANDO contains neighborhood-level information from the 1990 census and from a variety of administrative data files (information, for the most part, for every year since 1980). Administrative data series go back to 1979 and are now updated annually. System data are made available through a user-friendly, menu-driven, online database network. The data can be accessed via the Internet through the Center's website at http://neocando.case.edu. It can also be mapped and downloaded for a user's additional analysis. Community groups can thus access and use the database directly. Center staff provide training and technical assistance to help them use it effectively in planning and program development.

Cleveland, officially the City of Cleveland, is a city in the U.S. state of Ohio and the county seat of Cuyahoga County. Located in Northeast Ohio along the southern shore of Lake Erie, it is situated across the U.S. maritime border with Canada and lies approximately 60 miles (97 km) west of Pennsylvania. Cleveland ranks as the most populous city on Lake Erie, the second-most populous city in Ohio, and the 54th-most populous city in the U.S. with a 2020 population of 372,624. The city anchors the Cleveland metropolitan area, the 33rd-largest in the U.S. at 2.18 million residents, as well as the larger Cleveland–Akron–Canton combined statistical area, the most populous in Ohio and the 17th-largest in the country with a population of 3.63 million in 2020.

Cuyahoga County is a large urban county located in the northeastern part of the U.S. state of Ohio. The county seat and largest city is Cleveland. As of the 2020 census, its population was 1,264,817, making it the second-most populous county in the state.

Kamm's Corners is a neighborhood on the West Side of Cleveland, Ohio. It is bounded by the streetcar suburb of Lakewood to the north, the Rocky River Reservation of the Cleveland Metroparks and the suburbs of Rocky River and Fairview Park to the west, the New York Central Railroad tracks to the east, and Puritas Road to the south. Kamm's Corners Plaza and Warren Village are the major retail centers of the neighborhood. According to the 2019 U.S. census estimate, the neighborhood has the highest concentration of Irish Americans in Cleveland and Cuyahoga County.

Broadway–Slavic Village is a neighborhood on the Southeast side of Cleveland, Ohio. One of the city's oldest neighborhoods, it originated as the township of Newburgh, first settled in 1799. Much of the area has historically served as home to Cleveland's original Czech and Polish immigrants. While demographics have shifted over the decades, the largest part of Broadway today, Slavic Village, is named for these earlier communities.
The Furman Center for Real Estate and Urban Policy is a joint center at New York University School of Law and the NYU Wagner School of Public Service. The Furman Center was established in 1995 to create a place where people interested in affordable housing and land use issues could turn to for factual, objective research and information. Since that time, the Furman Center has become an authority on such matters in New York City. The Furman Center has a three-part mission, including providing objective academic research about land use, real estate, housing and urban affairs, with a particular focus on New York City, promoting intense debate and productive discussion among elected, academic, and industry leaders, and presenting essential data and analysis about the state of New York City's housing and neighborhoods.

Joe Cimperman is an American politician who served as a member of the Cleveland City Council, representing near-west side neighborhoods from 1997 to 2016. A Democrat, he had previously been chairman of the Health and Human Services Committee and a member of the Community and Economic Development Committee, Legislation and Public Parks Committee and Property and Recreation Committee.

Brooklyn Centre is a neighborhood on the West Side of Cleveland, Ohio. It borders Old Brooklyn to the south, Stockyards, Clark–Fulton, and Tremont to the north, and the Cuyahoga Valley and the suburb of Cuyahoga Heights to the east.
The Jack, Joseph and Morton Mandel School of Applied Social Sciences is a school of social work, one of the six professional schools within the Case Western Reserve University system, located in the University Circle in Cleveland, OH. Established in 1915, it is one of the first schools of social work in the United States to be affiliated with a university.
Slavic Village Development (SVD) is a non-profit community development corporation serving the North and South Broadway neighborhoods of Cleveland, Ohio. Over a period of 22 years, SVD has invested $160 million in these neighborhoods through various housing projects.

The National Community Stabilization Trust is a Washington, D.C.-based non-profit organization that facilitates the transfer of foreclosed and abandoned properties from financial institutions nationwide to local housing organizations to promote property reuse and neighborhood stability. According to U.S. Banker, the Stabilization Trust was "created to act as a middleman between cities looking to acquire abandoned properties and the lenders looking to unload them."

Dr. Arthur J. Naparstek was a professor of social work and Dean of the Mandel School of Applied Social Sciences at Case Western Reserve University in Cleveland, Ohio. He was an expert on urban redevelopment and neighborhood revitalization whose community-building concepts served as the basis for local and national government programs in both the United States and Israel.
A bank walkaway is a decision by a mortgage lender to not foreclose on a defaulted mortgage, or to not complete foreclosure proceedings. These are sometimes referred to as abandoned foreclosures or stalled foreclosures, though this latter term is also used more broadly when the foreclosure process has stalled for other reasons.

Central, also known as Cedar–Central, is a neighborhood on the East Side of Cleveland, Ohio. Situated on the outskirts of downtown, Central is bounded roughly by East 71st Street on its east and Interstate 90 on its west, with Euclid Avenue on its north and Interstate 77 and the Penn Central Railroad to the south. The neighborhood is eponymously named for its onetime main thoroughfare, Central Avenue. It is home to several schools, including East Technical High School.

Cuyahoga Valley is a neighborhood on the Central and South Side of Cleveland, Ohio, located along the Cuyahoga River. Formerly known as Industrial Valley, the neighborhood was originally limited to only one section of the geographic Cuyahoga River Valley, but the city expanded it in 2012 to include the entire valley area. The present neighborhood includes the Flats and extends from the peninsula of Whiskey Island on Lake Erie in the north to the borders of the suburbs of Newburgh Heights and Cuyahoga Heights in the south. To the east, it borders Downtown Cleveland and the neighborhoods of Broadway–Slavic Village and Central. To the west, it borders the neighborhoods of Detroit–Shoreway, Ohio City, Tremont, and Brooklyn Centre.

Clark–Fulton is a neighborhood on the West Side of Cleveland, Ohio. It is bounded by Ohio City to the north, Tremont to the east, Brooklyn Centre to the south, and Stockyards on the west. The neighborhood, which covers about one square mile, is Cleveland's most densely populated community. In recent years, the neighborhood has begun calling itself La Villa Hispaña due to its large Hispanic population, Puerto Rican and otherwise. The community is focused on advancing and promoting Hispanic-owned businesses and cultural activities.
The Making Connections Survey is a neighborhood-based, longitudinal and cross-sectional survey funded by the Annie E. Casey Foundation. It serves as an evaluation of a larger initiative supported by the foundation and was designed to collect data measuring how neighborhood change affects the well-being of children. The Making Connections Survey was conducted by National Opinion Research Center at the University of Chicago between 2002 and 2011 with residents in ten low-income communities across the United States. The final survey dataset includes responses from roughly 28,000 interviews at three points in time.

The demographics of Cleveland have fluctuated throughout the city's history. From its founding in 1796, Cleveland's population grew to 261,353 by 1890, and to 796,841 by 1920, making it the fifth largest city in the United States at the time. By 1930, the population rose to 900,429 and, after World War II, it reached 914,808. Due to various historical factors including deindustrialization, suburbanization, and urban sprawl, Cleveland's population began decreasing in the 1960s. By 1970, the city's population was 750,903. By 1980, it was 573,822 and it had lost its position as one of the top 10 largest cities in the U.S. By 2020, the population had further fallen to 372,624. Beginning in 2018, the city's population began to flatten, after decades of decline. Additionally, between 2010 and 2020, several neighborhoods within Cleveland saw a significant population increase, most notably Downtown, but also University Circle and several West Side neighborhoods.

The Jewish community of the Greater Cleveland area comprises a significant ethnoreligious population of the U.S. State of Ohio. It began in 1839 by immigrants from Bavaria and its size has significantly grown in the decades since then. In the early 21st century, Ohio's census data reported over 150,000 Jews, with the Cleveland area being home to more than 50% of this population. As of 2018, Greater Cleveland is the 23rd largest Jewish community in the United States. As of 2023, the Cleveland Jewish Community is estimated to be about 100,000 people.
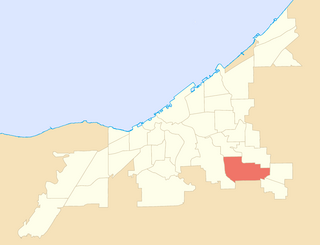
Union–Miles Park is a neighborhood on the Southeast side of Cleveland, Ohio, in the United States. The neighborhood draws its name from Union Avenue, and Miles Park in its far southwest corner.
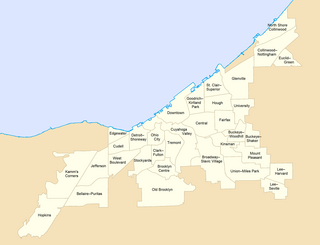
Neighborhoods in Cleveland refer to the 34 neighborhood communities of the city of Cleveland, Ohio, as defined by the Cleveland City Planning Commission. Based on historical definitions and census data, the neighborhoods serve as the basis for various urban planning initiatives on both the municipal and metropolitan levels. Technically known as Statistical Planning Areas (SPAs), they also provide a "framework for summarizing socio-economic and other statistics within the city." City neighborhood boundaries were last revised by the City Planning Commission in 2012.