Related Research Articles

NGC 281, IC 11 or Sh2-184 is a bright emission nebula and part of an H II region in the northern constellation of Cassiopeia and is part of the Milky Way's Perseus Spiral Arm. This 20×30 arcmin sized nebulosity is also associated with open cluster IC 1590, several Bok globules and the multiple star, B 1. It collectively forms Sh2-184, spanning over a larger area of 40 arcmin. A recent distance from radio parallaxes of water masers at 22 GHz made during 2014 is estimated it lies 2.82±0.20 kpc. from us. Colloquially, NGC 281 is also known as the Pacman Nebula for its resemblance to the video game character.

The Lagoon Nebula is a giant interstellar cloud in the constellation Sagittarius. It is classified as an emission nebula and as an H II region.

The Omega Nebula, also known as the Swan Nebula, Checkmark Nebula, Lobster Nebula, and the Horseshoe Nebula is an H II region in the constellation Sagittarius. It was discovered by Philippe Loys de Chéseaux in 1745. Charles Messier catalogued it in 1764. It is by some of the richest starfields of the Milky Way, figuring in the northern two-thirds of Sagittarius.

The Cone Nebula is an H II region in the constellation of Monoceros. It was discovered by William Herschel on December 26, 1785, at which time he designated it H V.27. The nebula is located about 830 parsecs or 2,700 light-years away from Earth. The Cone Nebula forms part of the nebulosity surrounding the Christmas Tree Cluster. The designation of NGC 2264 in the New General Catalogue refers to both objects and not the nebula alone.

Sh2-279 is an HII region and bright nebulae that includes a reflection nebula located in the constellation Orion. It is the northernmost part of the asterism known as Orion's Sword, lying 0.6° north of the Orion Nebula. The reflection nebula embedded in Sh2-279 is popularly known as the Running Man Nebula.

NGC 1514 is a planetary nebula in the zodiac constellation of Taurus, positioned to the north of the star Psi Tauri along the constellation border with Perseus. Distance to the nebula is 466 pc, according to GAIA DR2 data.

NGC 6751, also known as the Glowing Eye Nebula, is a planetary nebula in the constellation Aquila. It is estimated to be about 6,500 light-years away.

NGC 7635, also known as the Bubble Nebula, Sharpless 162, or Caldwell 11, is an H II region emission nebula in the constellation Cassiopeia. It lies close to the open cluster Messier 52. The "bubble" is created by the stellar wind from a massive hot, 8.7 magnitude young central star, SAO 20575 (BD+60°2522). The nebula is near a giant molecular cloud which contains the expansion of the bubble nebula while itself being excited by the hot central star, causing it to glow. It was discovered in November 1787 by William Herschel. The star BD+60°2522 is thought to have a mass of about 44 M☉.

NGC 6210 is a planetary nebula located in the constellation Hercules, approximately 5.4 ± 1.3 kly from the Sun. It is positioned about 38° above the galactic plane at a vertical distance of about 3.3 kilolight-years (1 kpc) and thus has little extinction from intervening interstellar dust. This object was first recorded as a star-like feature by Joseph Lalande on March 22, 1799. However, credit for the discovery of a nebula goes to Wilhelm Struve in 1825. John L. E. Dreyer described it as, "a planetary nebula, very bright, very small, round, disc and border".
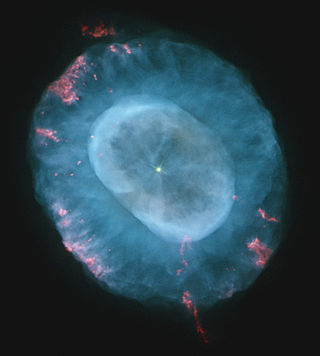
NGC 7662 is a planetary nebula located in the northern constellation Andromeda. It is known as the Blue Snowball Nebula, Snowball Nebula, and Caldwell 22. This nebula was discovered October 6, 1784 by the German-born English astronomer William Herschel. In the New General Catalogue it is described as a "magnificent planetary or annular nebula, very bright, pretty small in angular size, round, blue, variable nucleus". The object has an apparent visual magnitude of 8.3 and spans an angular size of 32″ × 28″. Parallax measurements give a distance estimate of 5,730 ± 340 ly (1,757 ± 103 pc).

NGC 6820 is a small reflection nebula near the open cluster NGC 6823 in Vulpecula. The reflection nebula and cluster are embedded in a large faint emission nebula called Sh 2-86. The whole area of nebulosity is often referred to as NGC 6820.

NGC 2626 is a reflection nebula, emission nebula, and absorption nebula in the constellation Vela. It is mostly illuminated by B1 star CD-40 4432 and ionized by the O8 quadruple star system HD 73882, together with other stars.

NGC 1222 is an early-type lenticular galaxy located in the constellation of Eridanus. The galaxy was discovered on 5 December 1883 by the French astronomer Édouard Stephan. John Louis Emil Dreyer, the compiler of the New General Catalogue, described it as a "pretty faint, small, round nebula" and noted the presence of a "very faint star" superposed on the galaxy.

NGC 422 is an open cluster located in the constellation Tucana. It was discovered on September 21, 1835, by John Herschel. It was described by John Louis Emil Dreyer as "very faint ", with Nubecular Minor being the Small Magellanic Cloud. It was also described by DeLisle Stewart as "only 3 extremely faint stars, close together, not a nebula."

NGC 456 is a nebula with an open cluster located in the constellation Tucana. It was discovered on August 1, 1826 by James Dunlop. It was described by Dreyer as "pretty faint, pretty large, irregularly round, mottled but not resolved, 1st of several."

NGC 460 is an open cluster with nebula located in the constellation Tucana. It was possibly observed on August 1, 1826, by James Dunlop, although it was officially discovered on April 11, 1834, by John Herschel. It was described by Dreyer as "very faint .", with Nubecular Minor being the Small Magellanic Cloud. It was also described by DeLisle Stewart as "faint, pretty large, irregularly round, gradually brighter middle, mottled but not resolved, 2nd of several."

NGC 1936 is an emission nebula which is part of the larger LMC-N44 nebula located in the Dorado constellation in the Large Magellanic Cloud. It was discovered by John Herschel in 1834 and added to the Catalogue of Nebulae and Clusters of Stars as NGC 1936. It was later observed by John Dunlop on September 27, 1936 and Williamina Fleming in 1901 and added to the Index Catalogue as IC 2127. Its apparent magnitude is 11.60.

NGC 1624, also known as Sh2-212 in the Sharpless catalog, is a very young open cluster in the constellation Perseus inside an emission nebula. It was discovered by German-British astronomer William Herschel in 1790. NGC 1624 is about 20,000 ly from Earth, and latest estimates give it an age of less than 4 million years. Its apparent magnitude is 11.8, and apparent diameter is about 3.0 arc minutes. Its celestial location is right ascension (α) 04h 40m 36.0s and declination (δ) +50° 27′ 42″. It is potentially an area of massive star formation.

NGC 522, also occasionally referred to as PGC 5218 or UGC 970, is a spiral galaxy located approximately 122 million light-years from the Solar System in the constellation Pisces. It was discovered on 25 September 1862 by astronomer Heinrich Louis d'Arrest.

NGC 6337, the Ghostly Cheerio or Cheerio Nebula, is a toroidal planetary nebula in the constellation Scorpius. It appears as a ring-shaped (annular) transparent nebula resembling a piece of the breakfast cereal Cheerios, hence the name. Filament and knots, and a faint shell surround the ring. Its magnitude is 11.90; its position in Scorpius is right ascension 17h 22m15.67s, declination -38° 29' 01.73". The Ghostly Cheerio has a redshift value of -0.000236.
References
- 1 2 "NED results for object NGC 7522". National Aeronautics and Space Administration / Infrared Processing and Analysis Center . Retrieved 16 August 2017.
- ↑ "NGC 7522". SIMBAD . Centre de données astronomiques de Strasbourg . Retrieved 16 August 2017.