Related Research Articles
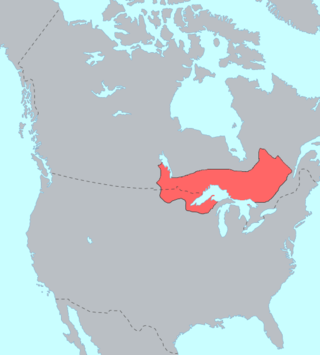
The Ojibwe are an Anishinaabe people whose homeland covers much of the Great Lakes region and the northern plains, extending into the subarctic and throughout the northeastern woodlands. The Ojibwe, being Indigenous peoples of the Northeastern Woodlands and of the subarctic, are known by several names, including Ojibway or Chippewa. As a large ethnic group, several distinct nations also consider themselves Ojibwe, including the Saulteaux, Nipissings, and Oji-Cree.

The St. Croix River is a tributary of the Mississippi River, about 169 mi (272 km) long, in the U.S. states of Wisconsin and Minnesota. The lower 125 mi (201 km) of the river form the border between Wisconsin and Minnesota. The river is a National Scenic Riverway under the protection of the National Park Service. A hydroelectric plant at the Saint Croix Falls Dam supplies power to the Minneapolis–Saint Paul metropolitan area.

Hayward is a city in Sawyer County, Wisconsin, United States, next to the Namekagon River. Its population was 2,533 at the 2020 census. It is the county seat of Sawyer County. The city is surrounded by the Town of Hayward. The City of Hayward was formally organized in 1883.
Chippewa is an alternate term for the Ojibwe tribe of North America.
The St. Croix Chippewa Indians are a historical Band of Ojibwe located along the St. Croix River, which forms the boundary between the U.S. states of Wisconsin and Minnesota. The majority of the St. Croix Band are divided into two groups: the federally recognized St. Croix Chippewa Indians of Wisconsin, and the St. Croix Chippewa Indians of Minnesota, who are one of four constituent members forming the federally recognized Mille Lacs Band of Ojibwe. The latter is one of six bands in the federally recognized Minnesota Chippewa Tribe.

The Lac Courte Oreilles Tribe is one of six federally recognized bands of Ojibwe people located in present-day Wisconsin. It had 7,275 enrolled members as of 2010. The band is based at the Lac Courte Oreilles Indian Reservation in northwestern Wisconsin, which surrounds Lac Courte Oreilles. The main reservation's land is in west-central Sawyer County, but two small plots of off-reservation trust land are located in Rusk, Burnett, and Washburn counties. The reservation was established in 1854 by the second Treaty of La Pointe.

The Treaty of La Pointe may refer to either of two treaties made and signed in La Pointe, Wisconsin between the United States and the Ojibwe (Chippewa) Native American peoples. In addition, the Isle Royale Agreement, an adhesion to the first Treaty of La Pointe, was made at La Pointe.

The Snake River is a 104-mile-long (167 km) tributary of the St. Croix River in east-central Minnesota in the United States. It is one of three streams in Minnesota with this name. Its name is a translation from the Ojibwa Ginebigo-ziibi, after the Dakota peoples who made their homes along this river. Kanabec County's name is derived from the Ojibwe word for this river.
Pillager Band of Chippewa Indians are a historical band of Chippewa (Ojibwe) who settled at the headwaters of the Mississippi River in present-day Minnesota. Their name "Pillagers" is a translation of Makandwewininiwag, which literally means "Pillaging Men". The French called them Pilleurs, also a translation of their name. The French and Americans adopted their autonym for their military activities as the advance guard of the Ojibwe in the invasion of the Dakota country.

The Namekagon River is a tributary of the St. Croix River. It is 101 miles (163 km) long and is located in northwestern Wisconsin in the United States. Its course is protected as part of the St. Croix National Scenic Riverway.

Chief Buffalo was a major Ojibwa leader, born at La Pointe in Lake Superior's Apostle Islands, in what is now northern Wisconsin, USA.

The Sandy Lake Tragedy was the culmination in 1850 of a series of events centered in Big Sandy Lake, Minnesota that resulted in the deaths of several hundred Lake Superior Chippewa. Officials of the Zachary Taylor Administration and Minnesota Territory sought to relocate several bands of the tribe to areas west of the Mississippi River. By changing the location for fall annuity payments, the officials intended the Chippewa to stay at the new site for the winter, hoping to lower their resistance to relocation. Due to delayed and inadequate payments of annuities and lack of promised supplies, about 400 Ojibwe, mostly men and 12% of the tribe, died of disease, starvation and cold. The outrage increased Ojibwe resistance to removal. The bands effectively gained widespread public support to achieve permanent reservations in their traditional territories.
The Lake Superior Chippewa are a large number of Ojibwe (Anishinaabe) bands living around Lake Superior; this territory is considered part of northern Michigan, Wisconsin, and Minnesota in the United States. They migrated into the area by the seventeenth century, encroaching on the Eastern Dakota people who had historically occupied the area. The Ojibwe defeated the Eastern Dakota, who migrated west into the Great Plains after the final battle in 1745. While they share a common culture including the Anishinaabe language, this highly decentralized group of Ojibwe includes at least twelve independent bands in the region.
Lake Lena is an unincorporated community and Native American village in Ogema Township, Pine County, Minnesota, United States, located along the Lower Tamarack River. It currently is the administrative center for the Mille Lacs Indian Reservation, District III.
Lac Courte Oreilles is a large freshwater lake located in northwest Wisconsin in Sawyer County in townships 39 and 40 north, ranges 8 and 9 west. It is irregular in shape, having numerous peninsulas and bays, and is approximately six miles long in a southwest to northeast direction and with a maximum width of about two miles (3 km). Lac Courte Oreilles is 5,039 acres (20.39 km2) in size with a maximum depth of 90 feet (27 m) and a shoreline of 25.4 miles (40.9 km). The lake has a small inlet stream that enters on the northeast shore of the lake and flows from Grindstone Lake, a short distance away to the north. An outlet on the southeast shore of the lake leads through a very short passage to Little Lac Courte Oreilles, then via the Couderay River to the Chippewa River, and ultimately to the Mississippi River at Lake Pepin.

Chief Beautifying Bird or Dressing Bird, was a principal chief of the Prairie Rice Lake Band of the Lake Superior Chippewa, originally located near Rice Lake, Wisconsin. He served as the principal chief about the middle of the 19th century.
Anishinaabe tribal political organizations are political consortiums of Anishinaabe nations that advocate for the political interests of their constituencies. Anishinaabe people of Canada are considered as First Nations, and of the United States as Native Americans.
Windigo Lake is a freshwater lake located in north central Wisconsin in the Town of Bass Lake, Sawyer County, United States, in township 40 north, range 9 west. The lake is irregular in shape, with numerous peninsulas and bays, and is approximately one mile in diameter. Windigo Lake is 529.6 acres (2.143 km2) in size with a maximum depth of 51 feet (16 m) and a shoreline of 9 miles (14 km). The lake does not have an obvious inflow or outflow stream and is classified as a seepage lake, i.e., a lake without an inlet or an outlet.
Namekagon Transit is the primary provider of mass transportation in Hayward, Wisconsin and the Lac Courte Oreilles Reservation with three routes serving the region. The name "Namekagon" in the Ojibwe language means "place of the sturgeon". As of 2021, the system provided 58,404 rides over 32,795 annual vehicle revenue hours with 16 vehicles.
References
- ↑ See, for example, Journals of Jonathan Carver; ed. John Parker; Minnesota Historical Society Press; St. Paul; 1976 at page 126 where the party made a decision to use the Chippewa River rather than the St. Croix River for this reason.
- ↑ Journals of Jonathan Carver; ed. John Parker; Minnesota Historical Society Press; St. Paul; 1976 (pages 129 and 167).
- ↑ Schoolcraft's Expedition to Lake Itasca; ed. Philip P. Mason; Michigan State University Press; East Lansing; 1958 (page 6).
- ↑ However, in this opinion the Wisconsin Attorney General states that this portage has now been abandoned and replaced by other transportation methods.