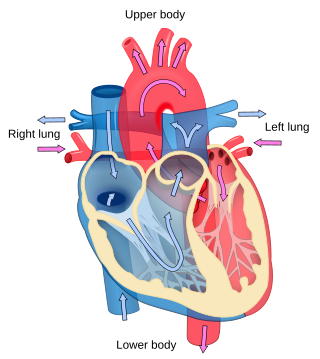
Cardiology is the study of the heart. Cardiology is a branch of medicine that deals with disorders of the heart and the cardiovascular system. The field includes medical diagnosis and treatment of congenital heart defects, coronary artery disease, heart failure, valvular heart disease, and electrophysiology. Physicians who specialize in this field of medicine are called cardiologists, a sub-specialty of internal medicine. Pediatric cardiologists are pediatricians who specialize in cardiology. Physicians who specialize in cardiac surgery are called cardiothoracic surgeons or cardiac surgeons, a specialty of general surgery.

Cardiothoracic surgery is the field of medicine involved in surgical treatment of organs inside the thoracic cavity — generally treatment of conditions of the heart, lungs, and other pleural or mediastinal structures.

dextro-Transposition of the great arteries is a potentially life-threatening birth defect in the large arteries of the heart. The primary arteries are transposed.

Interventional cardiology is a branch of cardiology that deals specifically with the catheter based treatment of structural heart diseases. Andreas Gruentzig is considered the father of interventional cardiology after the development of angioplasty by interventional radiologist Charles Dotter.

The University of Ottawa Heart Institute (UOHI) (French: Institut de cardiologie de l'Université d'Ottawa ) is Canada's largest cardiovascular health centre. It is located in Ottawa, Ontario, Canada. It began as a department in The Ottawa Hospital, and since has evolved into a complete cardiac centre, encompassing prevention, diagnosis, treatment, rehabilitation, research, and education.

A cardiovascular perfusionist, clinical perfusionist or perfusiologist, and occasionally a cardiopulmonary bypass doctor or clinical perfusion scientist, is a healthcare professional who operates the cardiopulmonary bypass machine during cardiac surgery and other surgeries that require cardiopulmonary bypass to manage the patient's physiological status. As a member of the cardiovascular surgical team, the perfusionist also known as the clinical perfusionist helps maintain blood flow to the body's tissues as well as regulate levels of oxygen and carbon dioxide in the blood, using a heart–lung machine.

Cardiac catheterization is the insertion of a catheter into a chamber or vessel of the heart. This is done both for diagnostic and interventional purposes.
The Rastelli procedure is an open heart surgical procedure developed by Italian physician and cardiac surgery researcher, Giancarlo Rastelli, in 1967 at the Mayo Clinic, and involves using a pulmonary or aortic homograft conduit to relieve pulmonary obstruction in double outlet right ventricle with pulmonary stenosis.
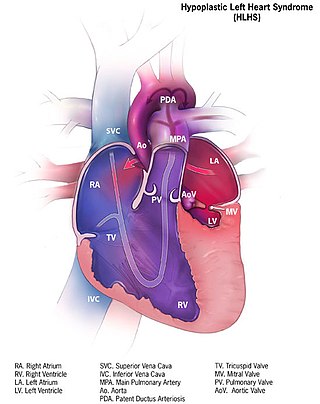
Hypoplastic left heart syndrome (HLHS) is a rare congenital heart defect in which the left side of the heart is severely underdeveloped and incapable of supporting the systemic circulation. It is estimated to account for 2-3% of all congenital heart disease. Early signs and symptoms include poor feeding, cyanosis, and diminished pulse in the extremities. The etiology is believed to be multifactorial resulting from a combination of genetic mutations and defects resulting in altered blood flow in the heart. Several structures can be affected including the left ventricle, aorta, aortic valve, or mitral valve all resulting in decreased systemic blood flow.

The Riley Hospital for Children at Indiana University Health is a nationally ranked freestanding 456-bed, pediatric acute care children's hospital in Indianapolis, Indiana, United States. It is affiliated with the Indiana University School of Medicine. Riley Hospital for Children is a member of the Indiana University Health system, the only children's hospital in the network. The hospital provides comprehensive pediatric specialties and subspecialties to infants, children, teens, and young adults aged 0–21 throughout Indiana and features an ACS verified level I pediatric trauma center. Its regional pediatric intensive-care unit and neonatal intensive care units serve the entire Midwest region. In addition, Riley has two helipads for rapid transport of emergent pediatric care. Riley Hospital for Children is named for James Whitcomb Riley, a writer and poet who lived in Indianapolis.

Devi Prasad Shetty is an Indian cardiac surgeon who is the chairman and founder of Narayana Health, a chain of 24 medical centers in India. He has performed more than 100,000 heart operations. In 2004 he was awarded the Padma Shri, the fourth highest civilian award, followed by the Padma Bhushan in 2012, the third highest civilian award by the Government of India for his contribution to the field of affordable healthcare.

Royal Papworth Hospital is a specialist heart and lung hospital, located on the Cambridge Biomedical Campus in Cambridgeshire, England. The Hospital is run by Royal Papworth Hospital NHS Foundation Trust.
Sri Jayadeva Institute of Cardiovascular Sciences and Research (SJICR) is a tertiary care autonomous healthcare institute run by the Government of Karnataka, in Bengaluru, with additional centers in Mysuru and Kalaburagi. At the Bengaluru campus, it presently has 1150 in-patient beds for cardiology, cardiothoracic surgery and pediatric cardiology, spread over two twin eight story buildings and is considered one of the largest dedicated heart hospitals in Asia. This new building which was opened in 2001 and was built at a cost of US$17 million.

MedStar Washington Hospital Center is the largest private hospital in Washington, D.C. A member of MedStar Health, the not-for-profit Hospital Center is licensed for 926 beds. Health services in primary, secondary and tertiary care are offered to adult and neonatal patients. It also serves as a teaching hospital for Georgetown University School of Medicine.

Atrial septostomy is a surgical procedure in which a small hole is created between the upper two chambers of the heart, the atria. This procedure is primarily used to palliate dextro-Transposition of the great arteries or d-TGA, a life-threatening cyanotic congenital heart defect seen in infants. It is performed prior to an arterial switch operation. Atrial septostomy has also seen limited use as a surgical treatment for pulmonary hypertension. The first atrial septostomy was developed by Vivien Thomas in a canine model and performed in humans by Alfred Blalock. The Rashkind balloon procedure, a common atrial septostomy technique, was developed in 1966 by American cardiologist William Rashkind at the Children's Hospital of Philadelphia.
Cardiothoracic anesthesiology is a subspeciality of the medical practice of anesthesiology, devoted to the preoperative, intraoperative, and postoperative care of adult and pediatric patients undergoing cardiothoracic surgery and related invasive procedures.

Narayana Health is an Indian for-profit private hospital network headquartered in Bangalore. It was founded by Dr. Devi Shetty in the year 2000.

Narayana Multispeciality Hospital, Jaipur is a tertiary care hospital of the Narayana Health Group in Jaipur, Rajasthan, India. It treats patients from Rajasthan and other neighbouring states. The hospital is accredited by the Joint Commission (JCI) and is the first hospital in Rajasthan to obtain this accreditation. It was commissioned in 2011 in Sanganer, with cardiology, neurosciences, orthopaedics and nephrology its main specialities.

Narayana Multispecialty Hospital, HSR Layout is a hospital in Bangalore, India and is part of the Narayana Health Group of Hospitals. The main specialties of the hospital are Cardiology, Orthopedics, General Medicine, day care surgeries, gastroenterology, obstetrics and genecology and emergency services. The hospital is NABH accredited, and has three operating theaters and a catheterisation laboratory. The hospital services the residential communities residing in and around HSR Layout.
Transcatheter pulmonary valve replacement (TPVR), also known as percutaneous pulmonary valve implantation (PPVI), is the replacement of the pulmonary valve via catheterization through a vein. It is a significantly less invasive procedure in comparison to open heart surgery and is commonly used to treat conditions such as pulmonary atresia.

















