
Epilepsy is a group of non-communicable neurological disorders characterized by recurrent epileptic seizures. Epileptic seizures can vary from brief and nearly undetectable periods to long periods of vigorous shaking due to abnormal electrical activity in the brain. These episodes can result in physical injuries, either directly such as broken bones or through causing accidents. In epilepsy, seizures tend to recur and may have no immediate underlying cause. Isolated seizures that are provoked by a specific cause such as poisoning are not deemed to represent epilepsy. People with epilepsy may be treated differently in various areas of the world and experience varying degrees of social stigma due to the scary nature of their symptoms.

An epileptic seizure, informally known as a seizure, is a period of symptoms due to abnormally excessive or synchronous neuronal activity in the brain. Outward effects vary from uncontrolled shaking movements involving much of the body with loss of consciousness, to shaking movements involving only part of the body with variable levels of consciousness, to a subtle momentary loss of awareness. Most of the time these episodes last less than two minutes and it takes some time to return to normal. Loss of bladder control may occur.

Myoclonus is a brief, involuntary, irregular twitching of a muscle or a group of muscles, different from clonus, which is rhythmic or regular. Myoclonus describes a medical sign and, generally, is not a diagnosis of a disease. These myoclonic twitches, jerks, or seizures are usually caused by sudden muscle contractions or brief lapses of contraction. The most common circumstance under which they occur is while falling asleep. Myoclonic jerks occur in healthy people and are experienced occasionally by everyone. However, when they appear with more persistence and become more widespread they can be a sign of various neurological disorders. Hiccups are a kind of myoclonic jerk specifically affecting the diaphragm. When a spasm is caused by another person it is known as a provoked spasm. Shuddering attacks in babies fall in this category.

Pyridoxine, is a form of vitamin B6 found commonly in food and used as a dietary supplement. As a supplement it is used to treat and prevent pyridoxine deficiency, sideroblastic anaemia, pyridoxine-dependent epilepsy, certain metabolic disorders, side effects or complications of isoniazid use, and certain types of mushroom poisoning. It is used by mouth or by injection.
Epilepsia partialis continua is a rare type of brain disorder in which a patient experiences recurrent motor epileptic seizures that are focal, and recur every few seconds or minutes for extended periods. It is sometimes called Kozhevnikov's epilepsia named after Russian psychiatrist Aleksei Yakovlevich Kozhevnikov who first described this type of epilepsy.

Clobazam, sold under the brand names Frisium, Onfi and others, is a benzodiazepine class medication that was patented in 1968. Clobazam was first synthesized in 1966 and first published in 1969. Clobazam was originally marketed as an anxioselective anxiolytic since 1970, and an anticonvulsant since 1984. The primary drug-development goal was to provide greater anxiolytic, anti-obsessive efficacy with fewer benzodiazepine-related side effects.

Valnoctamide has been used in France as a sedative-hypnotic since 1964. It is a structural isomer of valpromide, a valproic acid prodrug; unlike valpromide, however, valnoctamide is not transformed into its homologous acid, valnoctic acid, in vivo.
In medicine and medical anthropology, a culture-bound syndrome, culture-specific syndrome, or folk illness is a combination of psychiatric and somatic symptoms that are considered to be a recognizable disease only within a specific society or culture. There are no objective biochemical or structural alterations of body organs or functions, and the disease is not recognized in other cultures. The term culture-bound syndrome was included in the fourth version of the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders which also includes a list of the most common culture-bound conditions. Counterpart within the framework of ICD-10 are the culture-specific disorders defined in Annex 2 of the Diagnostic criteria for research.
Neurosteroids, also known as neuroactive steroids, are endogenous or exogenous steroids that rapidly alter neuronal excitability through interaction with ligand-gated ion channels and other cell surface receptors. The term neurosteroid was coined by the French physiologist Étienne-Émile Baulieu and refers to steroids synthesized in the brain. The term, neuroactive steroid refers to steroids that can be synthesized in the brain, or are synthesized by an endocrine gland, that then reach the brain through the bloodstream and have effects on brain function. The term neuroactive steroids was first coined in 1992 by Steven Paul and Robert Purdy. In addition to their actions on neuronal membrane receptors, some of these steroids may also exert effects on gene expression via nuclear steroid hormone receptors. Neurosteroids have a wide range of potential clinical applications from sedation to treatment of epilepsy and traumatic brain injury. Ganaxolone, a synthetic analog of the endogenous neurosteroid allopregnanolone, is under investigation for the treatment of epilepsy.
Epilepsy in animals is a group of neurological disorders characterized by seizures, caused by abnormal bursts of electrical activity in the brain. They can start and stop very abruptly and last any amount of time from a few seconds to a few minutes. Canine epilepsy is often genetic but epilepsy in cats and other pets is rarer, likely because there is no hereditary component to epilepsy in these animals.
Myoclonic epilepsy refers to a family of epilepsies that present with myoclonus. When myoclonic jerks are occasionally associated with abnormal brain wave activity, it can be categorized as myoclonic seizure. If the abnormal brain wave activity is persistent and results from ongoing seizures, then a diagnosis of myoclonic epilepsy may be considered.

According to Hindu mythology, Apasmāra is a dwarf who represents spiritual ignorance and nonsensical speech. He is also known as Muyalaka or Muyalakan. To preserve knowledge in the world, Apasmāra must be subdued, not killed, as to do so would disturb the necessary balance between spiritual knowledge and ignorance. Killing Apasmāra would symbolise the attainment of knowledge without the (essential) effort, dedication and hard work involved, and this would lead to the devaluing of knowledge in all its forms. To subdue Apasmāra, Lord Shiva adopted the form of Nataraja – the Lord of Dance – and performed the cosmic dance of Tāṇḍava. During this dance, Nataraja suppressed Apasmāra by crushing him with his right foot. As Apasmāra is one of the few demons destined to immortality, it is believed that Lord Shiva forever remains in his Nataraja form suppressing Apasmāra for eternity.
Nataraja's right foot is planted squarely on a horrible little subhuman creature - the demon, Muyalaka. A dwarf, but immensely powerful in his malignity, Muyalaka is the embodiment of ignorance, the manifestation of greedy, possessive selfhood. Stamp on him, break his back! And that's precisely what Nataraja is doing. Trampling the little monster down under his right foot. But notice that it isn't at this trampling foot that he points his finger; it's at the left foot, the foot that, as he dances, he's in the act of raising from the ground. And why does he point at it? Why? That lifted foot, that dancing defiance of the force of gravity - it's the symbol of release, of moksha, of liberation.
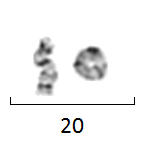
Ring chromosome 20, ring-shaped chromosome 20 or r(20) syndrome is a rare human chromosome abnormality where the two arms of chromosome 20 fuse to form a ring chromosome. The syndrome is associated with epileptic seizures, behaviour disorders and intellectual disability.

Generalized epilepsy is a form of epilepsy characterised by generalised seizures with no apparent cause. Generalized seizures, as opposed to focal seizures, are a type of seizure that impairs consciousness and distorts the electrical activity of the whole or a larger portion of the brain. Generalized seizure occurs due to abnormalities in both hemispheres.

Kv7.3 (KvLQT3) is a potassium channel protein coded for by the gene KCNQ3.

Calcium channel, voltage-dependent, T type, alpha 1H subunit, also known as CACNA1H, is a protein which in humans is encoded by the CACNA1H gene.

Central nervous system diseases, also known as central nervous system disorders, are a group of neurological disorders that affect the structure or function of the brain or spinal cord, which collectively form the central nervous system (CNS). These disorders may be caused by such things as infection, injury, blood clots, age related degeneration, cancer, autoimmune disfunction, and birth defects. The symptoms vary widely, as do the treatments.
Epilepsy can affect employment for a variety of reasons. Many employers are reluctant to hire a person they know has epilepsy, even if the seizures are controlled by medication. If the employee has a seizure while at work, they could harm themselves depending on the nature of the work. Employers are often unwilling to bear any financial costs that may come from employing a person with epilepsy, i.e. insurance costs, paid sick leave etc. Many people whose seizures are successfully controlled by a medication experience a variety of side effects, most notably drowsiness, which may affect job performance. Many laws prohibit or restrict people with epilepsy from performing certain duties, most notably driving or operating dangerous machinery, thereby lowering the pool of jobs available to people with epilepsy. People with epilepsy are also prohibited from joining the armed forces, though they may work in certain civilian military positions.

Gap junction delta-2 protein (GJD2) also known as connexin-36 (Cx36) or gap junction alpha-9 protein (GJA9) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the GJD2 gene.

Seizure: European Journal of Epilepsy is a peer-reviewed medical journal covering epilepsy established in 1992. The editor-in-chief is Markus Reuber. It is the official journal of Epilepsy Action. It is published ten times a year by Elsevier.










