Related Research Articles

Veterinary medicine is the branch of medicine that deals with the prevention, control, diagnosis, and treatment of disease, disorder, and injury in animals. Along with this, it deals with animal rearing, husbandry, breeding, research on nutrition, and product development. The scope of veterinary medicine is wide, covering all animal species, both domesticated and wild, with a wide range of conditions that can affect different species.

A veterinarian (vet), also known as a veterinary surgeon or veterinary physician, is a medical professional who practices veterinary medicine by treating diseases, disorders, managing reproductive health and injuries in non-human animals. Along with this, Vets also play vital role in animal reproduction, animal health management emphasizing on animal reproductive health, conservation, breeding and preventive medicine like animal nutrition, bio security.

Pet adoption is the process of transferring responsibility for a pet that was previously owned by another party such as a person, shelter, or rescue organization. Common sources for adoptable pets are animal shelters and rescue groups. Some organizations give adopters ownership of the pet, while others use a guardianship model wherein the organization retains some control over the animal's future use or care.

The Department for Environment, Food and Rural Affairs (Defra) is the government department responsible for environmental protection, food production and standards, agriculture, fisheries and rural communities in the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland. Concordats set out agreed frameworks for co operation, between it and the Scottish Government, Welsh Government and Northern Ireland Executive, which have devolved responsibilities for these matters in their respective nations.

A microchip implant is an identifying integrated circuit placed under the skin of an animal. The chip, about the size of a large grain of rice, uses passive radio-frequency identification (RFID) technology, and is also known as a PIT tag. Standard pet microchips are typically 11–13 mm long and 2 mm in diameter.
The Veterinary Medicines Directorate (VMD) is an Executive Agency of the Department for Environment, Food and Rural Affairs (Defra) seeking to protect public health, animal health, the environment and promoting animal welfare by assuring the safety, quality and efficacy of veterinary medicines in the United Kingdom.
Pet insurance pays, partly or in total, for veterinary treatment of the insured person's ill or injured pet. Some policies will pay out when the pet dies, or if the pet is lost or stolen.

Pet food is animal feed intended for consumption by pets. Typically sold in pet stores and supermarkets, it is usually specific to the type of animal, such as dog food or cat food. Most meat used for animals is a byproduct of the human food industry, and is not regarded as "human grade".
Docking is the intentional removal of part of an animal's tail or, sometimes, ears. The term cropping is more commonly used in reference to the cropping of ears, while docking more commonly—but not exclusively—refers to the tail. The term tailing is also commonly used. The term arises because the living flesh of the tail, from which the animal's tail hairs grow, commonly is known as the dock.
Animal Health was a UK government executive agency primarily responsible for ensuring that farmed animals in Great Britain were healthy, disease-free and well looked after.

The American Animal Hospital Association (AAHA) is a non-profit organization for companion animal veterinary hospitals. Established in 1933, the association is the only accrediting body for small animal hospitals in the U.S. and Canada. The association develops standards for veterinary business practices, publications, and educational programs. Any veterinary hospital can join AAHA as a member, but must then pass an evaluation in order to receive AAHA accreditation.

The Philippine Animal Welfare Society (PAWS) is a volunteer-based, non-government organization whose goal is to prevent animal cruelty through education, animal sheltering and advocacy, based in Quezon City, Philippines. PAWS believes that the creation of a more peaceful society starts with the widening of mankind's circle of compassion which includes animals, thereby envisions a nation that respects animals, practices responsible pet ownership and protects wildlife. The volunteer-based organization rehabilitates these animals in the hope of finding them new homes and a second chance at a good life. PAWS does not take in pets of other people, but only victims of cruelty or neglect where the animal offenders are charged with violation of the Animal Welfare Act in court.
The British Veterinary Association (BVA) is the national body for veterinary surgeons in the United Kingdom and is a not-for-profit organisation. Its purpose is that of knowledge dissemination, and not professional validation or academic competence. Knowledge dissemination is important in the veterinary profession to prevent a knowledge divide.

Mayhew, formerly known as The Mayhew Animal Home, is an animal welfare charity working to improve the lives of dogs, cats and the people in local communities – both in London and internationally. Mayhew's animal shelter, head office and Community Vet Clinic are based in Kensal Green, North London.
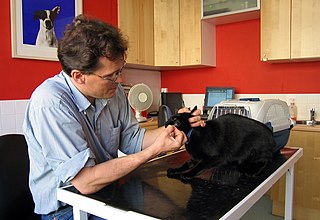
Veterinary medicine in the United Kingdom is the performance of veterinary medicine by licensed professionals. It is strictly regulated by the statute law, notably the Veterinary Surgeons Act 1966. Veterinary medicine is led by veterinary physicians, termed 'veterinary surgeons', normally referred to as 'vets'.
The Moredun Research Institute is a scientific research institution based at the Pentlands Science Park, in the Bush Estate area of Midlothian, Scotland. It conducts research into diseases of farm livestock and the promotion of animal health and welfare.
The Canadian Veterinary Medical Association (CVMA), founded in 1876, provides leadership on national veterinary issues, advocates for animal welfare, and works to encourage life balance in veterinary professionals.
Between 5% to 10% of homeless peoplein the United States own pets. Studies of homeless pet owners in urban settings show a sense of identity and community connection between pets and their owners. This topic is part of the Animals and Society branch of study in the field of Sociology, and is also an issue with the values and responsibility of pet ownership.
StreetVet is a registered charity that offers free accessible vet care to pets belonging to those experiencing homelessness in the United Kingdom. The organisation provides support for homeless pet owners who cannot afford private veterinary treatment and educates them on the responsibilities and care of animal ownership.
The pet industry is the market industry associated with companion animals. It includes things that are associated with the production, consumption and cultural activities linked to the market. Next to nutrition, toys and animal healthcare, new services and products like taxis, kindergartens, hotels, IT appliances, broadcasting, theme parks and funeral services are appearing on the market.