
Meknes is one of the four Imperial cities of Morocco, located in northern central Morocco and the sixth largest city by population in the kingdom. Founded in the 11th century by the Almoravids as a military settlement, Meknes became capital of Morocco under the reign of Sultan Moulay Ismaïl (1672–1727), son of the founder of the Alaouite dynasty. Moulay Ismaïl turned Meknes into an impressive city in Spanish-Moorish style, surrounded by high walls with great doors, where the harmonious blending of the Islamic and European styles of the 17th century Maghreb are still evident today. The city recorded a population of 632,079 in the 2014 Moroccan census. It is the seat of Meknès Prefecture and an important economic pole in the region of Fès-Meknès.Before, Meknès was part of the region Meknès-Tafilelt.

Volubilis is a partly excavated Berber city in Morocco situated near the city of Meknes, and commonly considered as the ancient capital of the kingdom of Mauretania. Built in a fertile agricultural area, it developed from the 3rd century BC onward as a Berber, then proto-Carthaginian, settlement before being the capital of the kingdom of Mauretania. It grew rapidly under Roman rule from the 1st century AD onward and expanded to cover about 42 hectares with a 2.6 km (1.6 mi) circuit of walls. The city gained a number of major public buildings in the 2nd century, including a basilica, temple and triumphal arch. Its prosperity, which was derived principally from olive growing, prompted the construction of many fine town-houses with large mosaic floors.
Mauritania Tingitana was a Roman province located in the Maghreb, coinciding roughly with the northern part of present-day Morocco. The territory stretched from the northern peninsula opposite Gibraltar, to Sala Colonia and Volubilis to the south, and as far east as the Mulucha river. Its capital city was Tingis, which is the modern Tangier. Other major cities of the province were Iulia Valentia Banasa, Septem, Rusadir, Lixus and Tamuda.

The Idrisids were an Arab Zaydi-Shia dynasty of Morocco, ruling from 788 to 974. Named after the founder Idriss I, the great grandchild of Hasan ibn Ali, the Idrisids and the Hamroun are considered to be the founders of the first Moroccan state.

Zerhoun is a mountain in Morocco, north of Meknes. On the hill is the Moulay Idris Zarhona town, named after Moulay Idris I, the founder of the Idrisid dynasty who was buried there in 791 AD.

Sidi Kacem is a city in Rabat-Salé-Kénitra, Morocco. It is the capital of Sidi Kacem Province.

Moulay Idriss or Moulay Idriss Zerhoun, a town in northern Morocco located at 34°3′15″N5°31′38″W, is spread over two hills at the base of Mount Zerhoun, the holy town of Moulay Idriss Zerhoune holds a special place in the hearts of the Moroccan people. It was here that Moulay Idriss I arrived in 789, bringing with him the religion of Shiism, and starting a new dynasty. In addition to founding the town named after him, he also initiated construction of Fez, continued later by his son, Moulay Idriss II.

Bou Assel is a settlement in northwestern Morocco situated north of the city of Meknes. Bou Assel is situated slightly south of the ancient city of Volubilis, initially settled by the Phoenicians and Romans over 2000 years ago. The settlement is close to the river of the same name, Oued Bou Assel.
Douar Doukkara is a settlement in the western part of Morocco. Douar Doukkara is situated in the vicinity of the ancient city of Volubilis, initially settled by the Phoenicians and Romans over 2000 years ago.Alternative spellings for this community are Douar Doukara and Douar Dokkara.
Douar Ain Chami is a settlement in northwestern Morocco somewhat to the north of the city of Meknes. Douar Ain Chami is situated slightly west of the ancient city of Volubilis, where the earliest recorded history of this locale is embedded; Volubilis was initially settled by the Phoenicians and Romans over 2000 years ago.

The Capitoline Temple is an ancient monument located in the old city of Volubilis in Fès-Meknès, Morocco. It dates from the Roman era, and was situated in the ancient Kingdom of Mauretania.
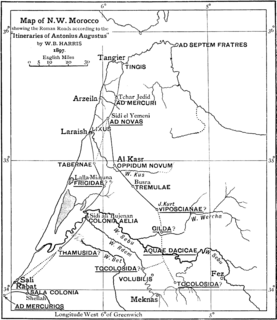
Roman roads in Morocco were the western roads of Roman Africa.

Rabat Archaeological Museum is an archaeological museum in Rabat, Morocco. Opened in 1932, it contains the most extensive collection of archaeological artifacts found in the country. The museum holds prehistoric and pre-Islamic collections, including many objects uncovered by archaeologists working in Volubilis, Banasa and Thamusida, which were first put on display in 1930-1932. This includes human remains from the middle Palaeolithic period to the Neolithic. A further find in 1957 saw the museum expand considerably, after which it became a National Museum and it has housed the National Museum collections since 1986. Pre-Roman and Roman civilisations are well represented in the museum with a number of notable Hellenistic-style bronzes such as the Dog of Volubilis, and the marble 'Ephebe Crowned With Ivy and Head of a Young Berber.

Altava was an ancient Roman-Berber city in present-day Algeria. It served as the capital of the ancient Berber Kingdom of Altava. During the French presence, the town was called Lamoriciere. It was situated in the modern Ouled Mimoun near Tlemcen.

Tifelt is a town in northwestern Morocco, west of Khemisset and east of Rabat. Tifelt is in a region of Morocco that is rich with ancient history including settlement by Berbers, Phoenicians and Romans during the first millennium BC. The nearest such major settlements are in Rabat and Volubilis. Tiflet is between the cities of Rabat and Khemisset

Sidi Said, Morocco is a hamlet in Morocco located at 28° 27' 36" North, 10° 34' 12" was during the Roman Empire one of five Castra (fort) that guarded the city of Volubilis from incursion over the nearby Limes Africanus. Sidi Said was the base for the Cohors IV Gallorum equitata, an auxiliary cavalry unit from Gaul. Rome's control over the area ended, however, following the chaos of the Crisis of the Third Century, when the empire nearly disintegrated as a series of generals seized and lost power through civil wars, palace coups and assassinations.
Aïn Schkor, Morocco is a hamlet in Morocco which served during the Roman Empire as one of five castra (forts) that guarded the city of Volubilis, located 3 kilometers to the south, from incursions from over the nearby Limes Africanus. In antiquity Aïn Schkor housed Spanish and Belgic cohorts.

Tocolsida is a site in modern Morocco, with the remains of an ancient castra from the Roman Province of Mauretania Tingitana, Roman Empire.
The following is a timeline of the history of the city of Meknes, Morocco.













