
Heinrich Hermann Robert Koch was a German physician and microbiologist. As the discoverer of the specific causative agents of deadly infectious diseases including tuberculosis, cholera, and anthrax, he is regarded as one of the main founders of modern bacteriology. As such he is popularly nicknamed the father of microbiology, and as the father of medical bacteriology. His discovery of the anthrax bacterium in 1876 is considered as the birth of modern bacteriology. His discoveries directly provided proofs for the germ theory of diseases, and the scientific basis of public health.

Plasmodium vivax is a protozoal parasite and a human pathogen. This parasite is the most frequent and widely distributed cause of recurring malaria. Although it is less virulent than Plasmodium falciparum, the deadliest of the five human malaria parasites, P. vivax malaria infections can lead to severe disease and death, often due to splenomegaly. P. vivax is carried by the female Anopheles mosquito; the males do not bite.

The Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR), the apex body in India for the formulation, coordination and promotion of biomedical research, is one of the oldest and largest medical research bodies in the world. The ICMR is funded by the Government of India through the Department of Health Research, Ministry of Health and Family Welfare. In 2007 the organization established the Clinical Trials Registry - India, which is India's national registry for clinical trials.

The Walter Reed Army Institute of Research (WRAIR) is the largest biomedical research facility administered by the U.S. Department of Defense (DoD). The institute is centered at the Forest Glen Annex, in the Forest Glen Park part of the unincorporated Silver Spring urban area in Maryland just north of Washington, DC, but it is a subordinate unit of the U.S. Army Medical Research and Development Command (USAMRDC), headquartered at nearby Fort Detrick, Maryland. At Forest Glen, the WRAIR has shared a laboratory and administrative facility — the Sen Daniel K. Inouye Building, also known as Building 503 — with the Naval Medical Research Center since 1999.
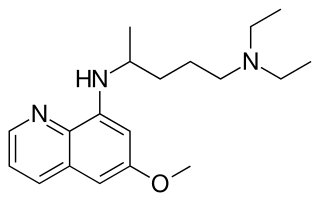
Pamaquine is an 8-aminoquinoline drug formerly used for the treatment of malaria. It is closely related to primaquine.

The Bureau of Medicine and Surgery (BUMED) is an agency of the United States Department of the Navy that manages health care activities for the United States Navy and United States Marine Corps. BUMED operates hospitals and other health care facilities as well as laboratories for biomedical research, and trains and manages the Navy's many staff corps related to medicine. Its headquarters is located at the Defense Health Headquarters in Fairfax County, Virginia. BUMED has 63,000 medical personnel and more than a million eligible beneficiaries.
Operation Pacific Angel is a recurring joint/combined humanitarian assistance mission sponsored by US Pacific Command (USPACOM) designed to bring humanitarian civic assistance (HCA) and civil-military operations (CMO) to areas in need in the Pacific region. It is conducted in locations throughout the Pacific theater to support the U.S. military charter of capacity building in partner nations. The operations contain elements of all four branches of the Department of Defense, including active duty, National Guard, and reserve members.
The quality of health in Cambodia is rising along with its growing economy. The public health care system has a high priority from the Cambodian government and with international help and assistance, Cambodia has seen some major and continuous improvements in the health profile of its population since the 1980s, with a steadily rising life expectancy.

Captain Gregory J. Martin, M.D., is an American medical doctor and captain in the United States Navy. Martin is a recognized expert in the fields of infectious diseases and bioterrorism.

The Iquitos Satellite Laboratory (IQTLAB) was established in 2002 in the city of Iquitos, Peru by doctor Margaret Kosek, biologist Maribel Paredes Olortegui, and nurse Pablo Peñataro Yori, with the collaboration of the Dr. Robert Gilman working group in Lima, Peru and the US Naval Medical Research Unit No. 6 (NAMRU-6).
Robert Allan Phillips MD was a research scientist during World War II who developed battlefield methods to evaluate hemoglobin levels using specific gravity saving many lives. This method is used in blood donor clinics to determine whether a person is healthy enough to donate blood. Continuing in the Navy his research turned to cholera where he spearheaded the efforts of Naval Medical Research Unit Two to develop a cure for the disease. He evaluated the course of the disease and developed the protocol for rehydration used today which has saved millions of lives. His research lead the Lasker Foundation to award him a prize in 1967. In his retirement, he collaborated with the University of Washington and the Chinese Government doing research in kidney failure again using hydration as a solution in remote areas of China where dialysis was not available.

The Walter Reed Tropical Medicine Course at Walter Reed Army Institute of Research (WRAIR) is one of the many Tropical Medicine Training Courses available in the US and worldwide. It is an intensive 5-day course and a 3-day short course, created to familiarize students with tropical diseases they may encounter overseas. The course is open to Physicians, Physician Assistants, Nurse Practitioners, ESO, 18D, or other medical personnel. The course is run by the military and designed for personnel of the US Military and several other US government agencies.
Naval Medical Research Unit One was a research laboratory of the US Navy which was founded as Naval Laboratory Research Unit 1, a Naval Reserve Unit at the University of California Berkeley in the life sciences building in 1934 after a campaign by a Berkeley scientist Albert P. Krueger to the Bureau of Medicine and Surgery to have a laboratory to study and prevent influenza and respiratory infections in naval forces. It was mobilized as an active duty naval unit in 1941 to study the epidemiological impact of diseases such as influenza, meningitis, and catarrhal fever, as well as tropical diseases such as malaria on the US Navy during World War II.

Naval Medical Research Unit Four (NAMRU-4) was a research laboratory of the US Navy which was commissioned 31 May 1946 at the Naval Hospital in Dublin, Georgia as the Mcintire Research Unit for Rheumatic Fever, which was named for the Surgeon General of the United States Navy Ross T. Mcintire. Initial staffing was 4 physicians, 4 laboratory technicians and 4 laboratory helpers under the command of LCDR John R. Seal. Eighteen months after commissioning the Navy transferred Dublin Naval Hospital to the Veterans Affairs system and the Secretary of the Navy re-established NAMRU-4 at Great Lakes Naval Base on the grounds of the Naval Hospital to study acute respiratory diseases in military personnel with a focus on their prevention. Lieutenant Commander Seal remained the Officer in Charge. The location at Great Lakes made it ideal as this was a large recruit training command with members arriving from all over the United States and being housed in military barracks and therefore would be expected to experience outbreaks of respiratory illness periodically. Diseases studied included:
Naval Medical Research Unit Five (NAMRU-5) was a research laboratory of the US Navy which was founded as a field facility of Naval Medical Research Unit 3 in Addis Ababa Ethiopia with a collecting station in Gambella on December 30, 1965 under an agreement between the US and Ethiopian governments. In 1974 NAMRU-5 was established as its own command and was housed in the Ethiopian Health and Nutrition Research Institute(former Imperial Central Laboratory Research Institute). The mission of NAMRU-5 was to conduct research and development on infectious diseases of military importance in sub-Sahara Africa. Gambella became the focus of a major malaria control effort and studies on malaria immunology. Applied research focused on the general areas of insect repellents, insecticide resistance, insect attractants and louse control. Members of the NAMRU-5 staff were also among the last Americans to ever see smallpox before its eradication. NAMRU-5 built collaborative research efforts with the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention; with local medical facilities, including the Haile Selassie University Medical School and various hospitals in Addis Ababa; and with the London School of Tropical Medicine, the University of Washington, Case Western Reserve University Department of Medicine and the University of Maryland School of Medicine. NAMRU-5 was disestablished in April 1977 following the communist takeover of the government of Ethiopia which ordered all members out of the country in 4 days. Fields of study included:

Naval Medical Research Unit Three (NAMRU-3) is a biomedical research laboratory of the US Navy located in Sigonella, Italy. Previously it was located in Cairo, Egypt. NAMRU-3 is the oldest US overseas military medical research facility that has remained in the same location, and one of the largest medical research laboratories in the North Africa-Middle East region. The laboratory has been in continuous operation despite periods of political tension and a seven-year lapse in U.S.-Egyptian relations (1967–1973) since 1942.

Naval Medical Research Unit Six (NAMRU-6) is a biomedical research laboratory of the US Navy located in Lima, Peru. It is the only US military command located in South America. Its mission is to identify infectious diseases threats of military and public health importance and to develop and evaluate interventions and products to mitigate those threats.

The Naval Medical Research Center (NMRC) is an agency that performs basic and applied biomedical research to meet the needs of the United States Navy and United States Marine Corps. Its areas of focus include study of infectious diseases, biodefense, military medicine, battlefield medicine, and bone marrow research. NMRC is under the United States Department of the Navy's Bureau of Medicine and Surgery.
The Armed Forces Research Institute of Medical Sciences — known as AFRIMS — is a United States Army project that started as a collaboration with the government of Thailand to fight a cholera outbreak in Bangkok in 1958 and '59. It subsequently expanded to cover military medical research projects across much of Southeast Asia and the Indian Subcontinent.

Naval Medical Research Unit Dayton (NAMRU-D) is a biomedical research laboratory of the United States Navy in Dayton, Ohio. It is one of seven subordinate commands of the Naval Medical Research Center and incorporates two research divisions. The Environmental Health Effects Laboratory was established in 1959 in Bethesda, Maryland, and moved to Dayton in 1976. The Naval Aerospace Medical Research Laboratory's predecessor activities date back to 1939 in Pensacola, Florida, and it moved to Dayton in 2010. Despite being a Navy activity, NAMRU-D was set up on the grounds of Wright-Patterson Air Force Base so it could be co-located with similar Air Force activities.














