
The Neandertal is a small valley of the river Düssel in the German state of North Rhine-Westphalia, located about 12 km (7.5 mi) east of Düsseldorf, the capital city of North Rhine-Westphalia. The valley lies within the limits of the towns of Erkrath and Mettmann. In August 1856, the area became famous for the discovery of Neanderthal 1, one of the first specimens of Homo neanderthalensis to be found.
The Middle Paleolithic is the second subdivision of the Paleolithic or Old Stone Age as it is understood in Europe, Africa and Asia. The term Middle Stone Age is used as an equivalent or a synonym for the Middle Paleolithic in African archeology. The Middle Paleolithic broadly spanned from 300,000 to 50,000 years ago. There are considerable dating differences between regions. The Middle Paleolithic was succeeded by the Upper Paleolithic subdivision which first began between 50,000 and 40,000 years ago. Pettit and White date the Early Middle Paleolithic in Great Britain to about 325,000 to 180,000 years ago, and the Late Middle Paleolithic as about 60,000 to 35,000 years ago. The Middle Paleolithic was in the geological Chibanian and Late Pleistocene ages.
Neanderthals became extinct around 40,000 years ago. Hypotheses on the causes of the extinction include violence, transmission of diseases from modern humans which Neanderthals had no immunity to, competitive replacement, extinction by interbreeding with early modern human populations, natural catastrophes, climate change and inbreeding depression. It is likely that multiple factors caused the demise of an already low population.

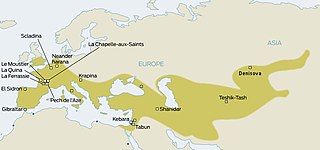
Johann Carl Fuhlrott was an early German paleoanthropologist. He is famous for recognizing the significance of the bones of Neanderthal 1, a Neanderthal specimen discovered by German laborers who were digging for limestone in Neander valley in August 1856. Originally disregarded, Fuhlrott, to his eternal credit, had the insight to recognize them for what they were: the remains of a previously unknown type of human.

Kebara Cave is a limestone cave locality in Wadi Kebara, situated at 60 to 65 m above sea level on the western escarpment of the Carmel Range, in the Ramat HaNadiv preserve of Zichron Yaakov.
The Neanderthal genome project is an effort, founded in July 2006, of a group of scientists to sequence the Neanderthal genome.

Feldhofer 1 or Neanderthal 1 is the scientific name of the 40,000-year-old type specimen fossil of the species Homo neanderthalensis. The fossil was discovered in August 1856 in the Kleine Feldhofer Grotte cave in the Neander Valley (Neandertal), located 13 km (8.1 mi) east of Düsseldorf, Germany.
Homo sapiens is the taxonomic binomial species name for modern humans.

Vindija Cave is an archaeological site associated with Neanderthals and modern humans, located in the municipality of Donja Voća, northern Croatia. Remains of three Neanderthals were selected as the primary sources for the first draft sequence of the Neanderthal genome project in 2010. Additional research was done on the samples and published in 2017.
The multiregional hypothesis, multiregional evolution (MRE), or polycentric hypothesis, is a scientific model that provides an alternative explanation to the more widely accepted "Out of Africa" model of monogenesis for the pattern of human evolution.

Neanderthals are an extinct group of archaic humans who lived in Eurasia until about 40,000 years ago. The type specimen, Neanderthal 1, was found in 1856 in the Neander Valley in present-day Germany.

Neanderthal anatomy differed from modern humans in that they had a more robust build and distinctive morphological features, especially on the cranium, which gradually accumulated more derived aspects, particularly in certain isolated geographic regions. This robust build was an effective adaptation for Neanderthals, as they lived in the cold environments of Europe. In which they also had to operate in Europe's dense forest landscape that was extremely different from the environments of the African grassland plains that Homo sapiens adapted to with a different anatomical build.
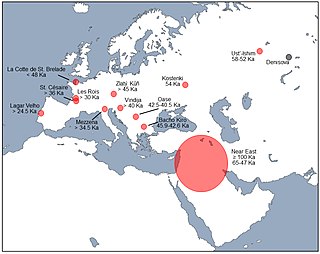
Interbreeding between archaic and modern humans occurred during the Middle Paleolithic and early Upper Paleolithic. The interbreeding happened in several independent events that included Neanderthals and Denisovans, as well as several unidentified hominins.
Mezmaiskaya Cave is a prehistoric cave site overlooking the right bank of the Sukhoi Kurdzhips in the southern Russian Republic of Adygea, located in the northwestern foothills of the North Caucasus in the Caucasus Mountains system.

Forbes' Quarry is located on the northern face of the Rock of Gibraltar within the Upper Rock Nature Reserve in the British Overseas Territory of Gibraltar. The area was quarried during the 19th century to supply stone for reinforcing the fortress' military installations. In the course of the quarrying, a limestone cave was found. The second ever Neanderthal discovery was made within this cave when Cpt. Edmund Flint found the skull of an adult female Neanderthal in 1848.

The Obi-Rakhmat Grotto is a Middle Paleolithic prehistoric site that yielded Neanderthal fossils. It is a shallow karst cave near the junction of the Chatkal and Pskem Rivers at the southwestern end of the Talassky Alatau Range in the Tien Shan Mountains, 100 km (62 mi) northeast of Tashkent, Uzbekistan.

The Goyet Caves are a series of connected caves located in Belgium in a limestone cliff about 15 m (50 ft) above the river Samson near the village of Mozet in the Gesves municipality of the Namur province. The site is a significant locality of regional Neanderthal and European early modern human occupation, as thousands of fossils and artifacts were discovered that are all attributed to a long and contiguous stratigraphic sequence from 120,000 years ago, the Middle Paleolithic to less than 5,000 years ago, the late Neolithic. A robust sequence of sediments was identified during extensive excavations by geologist Edouard Dupont, who undertook the first probings as early as 1867. The site was added to the Belgian National Heritage register in 1976.

Amud 1 is a nearly complete but poorly preserved adult Southwest Asian Neanderthal skeleton thought to be about 55,000 years old. It was discovered at Amud in Israel by Hisashi Suzuki in July 1961, who described it as male. With an estimated height of 1.78 m, it is considerably taller than any other known Neanderthal, and its skull has by far the largest cranial capacity of any human skull in the fossil record. According to Ralph Holloway, this makes it one of the most famous Neanderthal specimens.

Krapina Neanderthal site, also known as Hušnjakovo Hill is a Paleolithic archaeological site located near Krapina, Croatia.

Cueva Antón is a paleoanthropological and archeological site in the Region of Murcia of southeast Spain. The cave is located about 60 kilometers from the Mediterranean port city of Cartagena inland in the territory of the municipality of Mula. It was eroded by the Río Mula and served as a cave in the Middle Palaeolithic inhabited by Neanderthals. The cave became internationally known in 2010, after a shell at least 43,000 years old with adhering orange pigment was discovered there. The pigment found was interpreted as evidence that the shell was used "in an aesthetic and probably symbolic" way. The find from the Cueva Antón was published together with similar finds from the Cave of Los Aviones; they were named as the first such Neanderthal jewelry found in Europe. The colonization of the Iberian Peninsula by modern man took place only several thousand years after the creation of the jewelry from the Cueva Antón. This site is the last known place where Neanderthal people resided.














