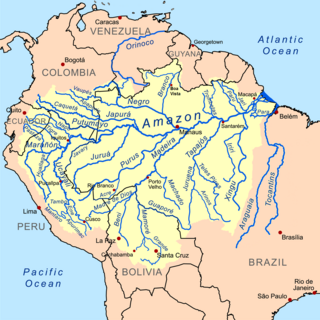
The Amazon basin is the part of South America drained by the Amazon River and its tributaries. The Amazon drainage basin covers an area of about 7,000,000 km2 (2,700,000 sq mi), or about 35.5 percent of the South American continent. It is located in the countries of Bolivia, Brazil, Colombia, Ecuador, Guyana, Peru, Suriname, and Venezuela, as well as the territory of French Guiana.

Loricariidae is the largest family of catfish, with over 90 genera and just over 680 species. Loricariids originate from freshwater habitats of Costa Rica, Panama, and tropical and subtropical South America. These fish are noted for the bony plates covering their bodies and their suckermouths. Several genera are sold as "plecos", notably the suckermouth catfish, Hypostomus plecostomus, and are popular as aquarium fish.

Hypostomus is a genus of catfish in the family Loricariidae. They are native to tropical and subtropical South America. H. plecostomus is the popular freshwater aquarium fish formerly known as Plecostomus plecostomus. The taxonomic structure of the Loricariidae is still being expanded by scientists. Hypostomus is a highly species-rich and widely distributed catfish genus.

Corydoras is a genus of freshwater catfish in the family Callichthyidae and subfamily Corydoradinae. The species usually have more restricted areas of endemism than other callichthyids, but the area of distribution of the entire genus almost equals the area of distribution of the family, except for Panama where Corydoras is not present. Corydoras species are distributed in South America where they can be found from the east of the Andes to the Atlantic coast, from Trinidad to the Río de la Plata drainage in northern Argentina.

The zebra oto or tiger oto is a fish of the genus Otocinclus of the family Loricariidae that originates from Peru.

Rineloricaria is a genus of freshwater tropical catfish belonging to the family Loricariidae. They are commonly called whiptail catfish because of the long filament that grows out of the tip of the caudal fin that is characteristic of the genus. With the exception of R. altipinnis from Panama, they are native to the rivers of northern and central South America. Some species are regularly seen in the aquarium trade.

Sorubim is a small genus of long-whiskered catfish native to tropical South America. A number of characteristics allows the differentiation of each species in the genus. Sorubim species are important food fish in South America and are highly significant to fisheries of some areas; however, harvests of these fish are not identified as much as other, more popular food fishes such as Colossoma, Arapaima, and Brachyplatystoma. Some species of this family are popular aquarium fish.

Hemiancistrus is a genus of suckermouth armored catfishes. These species are native to South America. The taxonomy of this genus is complex and unclear, and major work has to be done. Many of these fish are popular aquarium fish.
Epactionotus is a genus of armored catfishes native to South America.

The Hypoptopomatinae are a subfamily of catfishes of the family Loricariidae, composed of 17 genera and approximately 80 species. This subfamily represents about one-tenth of all loricariid species.
Harttia is a genus of armored catfishes native to South America.

Neoplecostomus is a genus of fish in the family Loricariidae native to South America. Neoplecostomus can be distinguished from all other loricariids by a modified shield of small plates on the abdomen with posteriorly directed odontodes; the shield appears to act as a holdfast. The color pattern is generally mottled brown with the abdomen white. The head is long, rounded, and shovel-shaped. The fin spines are weak. They range from about 8 to 11 cm (3.1–4.3 in) SL. The species of Neoplecostomus live in fast-flowing water.
Isbrueckerichthys is a genus of armored catfishes which are endemic to Brazil.
Ammoglanis is a genus of pencil catfishes native to South America.
The Sarcoglanidinae are a subfamily of catfishes of the family Trichomycteridae. It includes six genera: Ammoglanis, Malacoglanis, Microcambeva, Sarcoglanis, Stauroglanis, and Stenolicmus.
The Copionodontinae are a subfamily of catfishes of the family Trichomycteridae. It includes two genera, Copionodon and Glaphyropoma.

Myloplus is a genus of freshwater fish in the family Serrasalmidae found in tropical and subtropical South America, where they inhabit rivers and streams. They are primarily herbivores, but also take some animal matter. Depending on the exact species, they reach up to 16–56 cm (0.5–1.8 ft) in standard length. Adult males have a double-lobed anal fin and filamentous extensions on the dorsal fin, and both sexes can be brightly colored when breeding.
Sturisoma reisi is a species of catfish in the family Loricariidae. It is native to South America, where it occurs in the Cautário River, the Guaporé River, the Ji-Paraná River, the Mamoré River, and the Sotério River in the Madeira River basin in Bolivia and Brazil. It was described in 2022 by Alejandro Londoño-Burbano and Marcelo Ribeiro de Britto of the Federal University of Rio de Janeiro on the basis of distinctive genetic and morphological characteristics.

Corydoras arcuatus is a species of freshwater fish in the armored catfish family Callichthyidae. It is restricted to the western Amazon basin, where only known from small blackwater or clearwater streams in the middle Juruá River basin, the Javari River basin and streams near Leticia in western Brazil, far northeastern Peru and far southeastern Colombia.

Neoplecostomus sapucai, also known as the Sapucaí River armored catfish, is a species of catfish found in the Sapucaí River. The fish can reach about 3.5 inches in length and has elongated bodies, covered in bony plates. They have a broad head, bumpy lips, and tons of copper colored teeth. It is golden yellow and brown, and has blotches of color on it's sides and fins.










