A nephelescope is a device invented by James Pollard Espy to measure the drop in temperature of a gas from a reduction in pressure; originally used to explore the formation of clouds.
A nephelescope is a device invented by James Pollard Espy to measure the drop in temperature of a gas from a reduction in pressure; originally used to explore the formation of clouds.

The original design [1] consisted of an air compression pump (a), a vessel (b), and a barometer (c).
Air is pumped into the vessel until a desired pressure is reached, the stopclock is then closed and the temperature allowed to equilibriate. The stopclock is then opened, allowing the pressure of the container to equilibriate the atmosphere, and then closed again.
The air inside of the container would now be colder. As it warms up, pressure inside the container once again increases above atmosphere. This increase in pressure can be used to work out the number of degrees which the container had been cooled by.

A later design [2] consisted of an air pump receiver (a) connected to a flask (c) by an intervening stopclock (b). Air was pumped out of the receiver, then the stopclock was opened. One advantage of using negative pressure was that a glass vessel could be used, which allowed the observation of condensation and droplets resulting from the drop in temperature. To observe this in a dry atmosphere, air would have needed to first be moistened by exposure to water.
The nephelescope enabled Epsy to predict the change in heat of air as water vapor became cloud. He showed that when dry air was used instead of moist air, temperature was reduced by about twice as much as moist air. In other words, latent heat released from the condensation of water mitigated some of the cooling from expansion of moist air. Since moist air is already lighter than dry air, the warmer and lighter moist air in clouds would continue to rise and cool, forcing more vapor to condense, which had consequences for meteorological theories at that time. [3]
The nephelescope has been described as an "early cloud-chamber". [4]

Condensation is the change of the state of matter from the gas phase into the liquid phase, and is the reverse of vaporization. The word most often refers to the water cycle. It can also be defined as the change in the state of water vapor to liquid water when in contact with a liquid or solid surface or cloud condensation nuclei within the atmosphere. When the transition happens from the gaseous phase into the solid phase directly, the change is called deposition.

Convection is single or multiphase fluid flow that occurs spontaneously due to the combined effects of material property heterogeneity and body forces on a fluid, most commonly density and gravity. When the cause of the convection is unspecified, convection due to the effects of thermal expansion and buoyancy can be assumed. Convection may also take place in soft solids or mixtures where particles can flow.

Humidity is the concentration of water vapour present in the air. Water vapor, the gaseous state of water, is generally invisible to the human eye. Humidity indicates the likelihood for precipitation, dew, or fog to be present.

Fog is a visible aerosol consisting of tiny water droplets or ice crystals suspended in the air at or near the Earth's surface. Fog can be considered a type of low-lying cloud usually resembling stratus, and is heavily influenced by nearby bodies of water, topography, and wind conditions. In turn, fog affects many human activities, such as shipping, travel, and warfare.

Water vapor, water vapour or aqueous vapor is the gaseous phase of water. It is one state of water within the hydrosphere. Water vapor can be produced from the evaporation or boiling of liquid water or from the sublimation of ice. Water vapor is transparent, like most constituents of the atmosphere. Under typical atmospheric conditions, water vapor is continuously generated by evaporation and removed by condensation. It is less dense than most of the other constituents of air and triggers convection currents that can lead to clouds.
A cryopump or a "cryogenic pump" is a vacuum pump that traps gases and vapours by condensing them on a cold surface, but are only effective on some gases. The effectiveness depends on the freezing and boiling points of the gas relative to the cryopump's temperature. They are sometimes used to block particular contaminants, for example in front of a diffusion pump to trap backstreaming oil, or in front of a McLeod gauge to keep out water. In this function, they are called a cryotrap, waterpump or cold trap, even though the physical mechanism is the same as for a cryopump.

The lapse rate is the rate at which an atmospheric variable, normally temperature in Earth's atmosphere, falls with altitude. Lapse rate arises from the word lapse, in the sense of a gradual fall. In dry air, the adiabatic lapse rate is 9.8 °C/km.

A dehumidifier is an air conditioning device which reduces and maintains the level of humidity in the air. This is done usually for health or comfort reasons, or to eliminate musty odor and to prevent the growth of mildew by extracting water from the air. It can be used for household, commercial, or industrial applications. Large dehumidifiers are used in commercial buildings such as indoor ice rinks and swimming pools, as well as manufacturing plants or storage warehouses.
Equivalent potential temperature, commonly referred to as theta-e, is a quantity that is conserved during changes to an air parcel's pressure, even if water vapor condenses during that pressure change. It is therefore more conserved than the ordinary potential temperature, which remains constant only for unsaturated vertical motions.

An evaporative cooler is a device that cools air through the evaporation of water. Evaporative cooling differs from other air conditioning systems, which use vapor-compression or absorption refrigeration cycles. Evaporative cooling uses the fact that water will absorb a relatively large amount of heat in order to evaporate. The temperature of dry air can be dropped significantly through the phase transition of liquid water to water vapor (evaporation). This can cool air using much less energy than refrigeration. In extremely dry climates, evaporative cooling of air has the added benefit of conditioning the air with more moisture for the comfort of building occupants.

Cloud physics is the study of the physical processes that lead to the formation, growth and precipitation of atmospheric clouds. These aerosols are found in the troposphere, stratosphere, and mesosphere, which collectively make up the greatest part of the homosphere. Clouds consist of microscopic droplets of liquid water, tiny crystals of ice, or both. Cloud droplets initially form by the condensation of water vapor onto condensation nuclei when the supersaturation of air exceeds a critical value according to Köhler theory. Cloud condensation nuclei are necessary for cloud droplets formation because of the Kelvin effect, which describes the change in saturation vapor pressure due to a curved surface. At small radii, the amount of supersaturation needed for condensation to occur is so large, that it does not happen naturally. Raoult's law describes how the vapor pressure is dependent on the amount of solute in a solution. At high concentrations, when the cloud droplets are small, the supersaturation required is smaller than without the presence of a nucleus.

Psychrometrics, psychrometry, and hygrometry are names for the field of engineering concerned with the physical and thermodynamic properties of gas-vapor mixtures. The term comes from the Greek psuchron (ψυχρόν) meaning "cold" and metron (μέτρον) meaning "means of measurement".

Thermosiphon is a method of passive heat exchange, based on natural convection, which circulates a fluid without the necessity of a mechanical pump. Thermosiphoning is used for circulation of liquids and volatile gases in heating and cooling applications such as heat pumps, water heaters, boilers and furnaces. Thermosiphoning also occurs across air temperature gradients such as those utilized in a wood fire chimney or solar chimney.
The sorption pump is a vacuum pump that creates a vacuum by adsorbing molecules on a very porous material like molecular sieve which is cooled by a cryogen, typically liquid nitrogen. The ultimate pressure is about 10−2 mbar. With special techniques this can be lowered till 10−7 mbar. The main advantages are the absence of oil or other contaminants, low cost and vibration free operation because there are no moving parts. The main disadvantages are that it cannot operate continuously and cannot effectively pump hydrogen, helium and neon, all gases with lower condensation temperature than liquid nitrogen. The main application is as a roughing pump for a sputter-ion pump in ultra-high vacuum experiments, for example in surface physics.

In meteorology, convective instability or stability of an air mass refers to its ability to resist vertical motion. A stable atmosphere makes vertical movement difficult, and small vertical disturbances dampen out and disappear. In an unstable atmosphere, vertical air movements tend to become larger, resulting in turbulent airflow and convective activity. Instability can lead to significant turbulence, extensive vertical clouds, and severe weather such as thunderstorms.
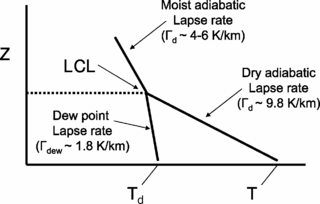
The lifted condensation level or lifting condensation level (LCL) is formally defined as the height at which the relative humidity (RH) of an air parcel will reach 100% with respect to liquid water when it is cooled by dry adiabatic lifting. The RH of air increases when it is cooled, since the amount of water vapor in the air remains constant, while the saturation vapor pressure decreases almost exponentially with decreasing temperature. If the air parcel is lifting further beyond the LCL, water vapor in the air parcel will begin condensing, forming cloud droplets. The LCL is a good approximation of the height of the cloud base which will be observed on days when air is lifted mechanically from the surface to the cloud base.
Atmospheric thermodynamics is the study of heat-to-work transformations that take place in the earth's atmosphere and manifest as weather or climate. Atmospheric thermodynamics use the laws of classical thermodynamics, to describe and explain such phenomena as the properties of moist air, the formation of clouds, atmospheric convection, boundary layer meteorology, and vertical instabilities in the atmosphere. Atmospheric thermodynamic diagrams are used as tools in the forecasting of storm development. Atmospheric thermodynamics forms a basis for cloud microphysics and convection parameterizations used in numerical weather models and is used in many climate considerations, including convective-equilibrium climate models.

A transient condensation cloud, also called a Wilson cloud, is observable surrounding large explosions in humid air.
Compressed air dryers are special types of filter systems that are specifically designed to remove the water that is inherent in compressed air. The process of compressing air raises its temperature and concentrates atmospheric contaminants, primarily water vapor. Consequently, the compressed air is generally at an elevated temperature and 100% relative humidity. As the compressed air cools, water vapor condenses into the tank(s), pipes, hoses and tools that are downstream from the compressor. Water vapor is removed from compressed air to prevent condensation from occurring and to prevent moisture from interfering in sensitive industrial processes.

This glossary of meteorology is a list of terms and concepts relevant to meteorology and atmospheric science, their sub-disciplines, and related fields.
nephelescope.
draper, john william.