
Alboin was king of the Lombards from about 560 until 572. During his reign the Lombards ended their migrations by settling in Italy, the northern part of which Alboin conquered between 569 and 572. He had a lasting effect on Italy and the Pannonian Basin; in the former his invasion marked the beginning of centuries of Lombard rule, and in the latter his defeat of the Gepids and his departure from Pannonia ended the dominance there of the Germanic peoples.

The Lombards or Longobards were a Germanic people who conquered most of the Italian Peninsula between 568 and 774.
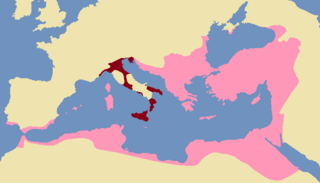
The Exarchate of Ravenna, also known as the Exarchate of Italy, was a lordship of the Eastern Roman Empire in Italy, from 584 to 751, when the last exarch was put to death by the Lombards. It was one of two exarchates established following the western reconquests under Emperor Justinian to more effectively administer the territories, along with the Exarchate of Africa.

Ratchis was the Duke of Friuli (739–744) and then King of the Lombards (744–749).

Agilulf, called the Thuringian and nicknamed Ago, was a duke of Turin and king of the Lombards from 591 until his death.

The History of the Lombards or the History of the Langobards is the chief work by Paul the Deacon, written in the late 8th century. This incomplete history in six books was written after 787 and at any rate no later than 796, maybe at Montecassino.

The Donation of Sutri was an agreement reached at Sutri by Liutprand, King of the Lombards and Pope Gregory II in 728. At Sutri, the two reached an agreement by which the city and some hill towns in Latium were given to the Papacy, "as a gift to the blessed Apostles Peter and Paul" according to the Liber Pontificalis. The pact formed the first extension of papal territory beyond the confines of the Duchy of Rome and was the first of two land transfers from Liutprand to the Church of Rome.

The Kingdom of Italy, also called Imperial Italy, was one of the constituent kingdoms of the Holy Roman Empire, along with the kingdoms of Germany, Bohemia, and Burgundy. It originally comprised large parts of northern and central Italy. Its original capital was Pavia until the 11th century.

Langobardia Minor was the name that, in the Early Middle Ages, was given to the Lombard domains in central and southern Italy, corresponding to the duchies of Spoleto and Benevento. After the conquest of the Lombard kingdom by Charlemagne in 774, it remained under Lombard control.

The Kingdom of the Lombards, also known as the Lombard Kingdom and later as the Kingdom of all Italy, was an early medieval state established by the Lombards, a Germanic people, on the Italian Peninsula in the latter part of the 6th century. The king was traditionally elected by the very highest-ranking aristocrats, the dukes, as several attempts to establish a hereditary dynasty failed. The kingdom was subdivided into a varying number of duchies, ruled by semi-autonomous dukes, which were in turn subdivided into gastaldates at the municipal level. The capital of the kingdom and the center of its political life was Pavia in the modern northern Italian region of Lombardy.

The Duchy of Friuli was a Lombard duchy in present-day Friuli, the first to be established after the conquest of the Italian peninsula in 568. It was one of the largest domains in Langobardia Major and an important buffer between the Lombard kingdom and the Slavs, Avars, and the Byzantine Empire. The original chief city in the province was Roman Aquileia, but the Lombard capital of Friuli was Forum Julii, modern Cividale.
Ferdulf or Fardulf, originally from the territories of Liguria, was the Duke of Friuli at some point between the end of the reign of Cunincpert (688-700) and the beginning of that of Aripert II (701-12). There is no evidence to associate his tenure to the year 705 alone or indeed to suggest that it was very brief.. Paul the Deacon described him as 'a man tricky and conceited' who had obtained the dukedom after the death of Duke Ado.
Euin, also Ewin or Eoin, was the first Lombard Duke of Trent during the Rule of the Dukes, an interregnum (575–585) during which the Kingdom of Italy was ruled by its regional magnates, the dukes of the thirty or so cities. Euin participated in several significant wars during his long reign. The primary source for his career is Paul the Deacon's Historia Langobardorum.
Albsuinda was the only child of Alboin, King of the Lombards in Pannonia, and his first wife Chlothsind, daughter of the Merovingian king of the Franks Chlothar. While still young Albsuinda had lost her mother shortly before the final clash in 567 with the people of the Gepids in Pannonia, in which the Gepids were completely destroyed. After the victory her father had promptly remarried, taking as second wife Rosamund, daughter of the Gepid king Cunimund that Alboin had personally killed on the battlefield.
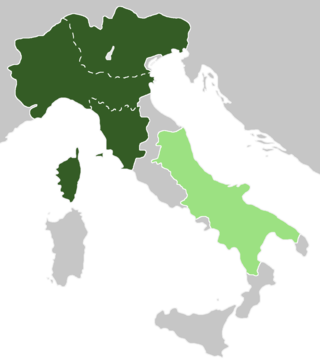
Austria was, according to the early medieval geographical classification, the eastern portion of Langobardia Major, the north-central part of the Lombard Kingdom, extended from the Adda to Friuli and opposite to Neustria. The partition had not only been territorial, but also implied significant cultural and political differences.
Among the Lombards, the duke or dux was the man who acted as political and military commander of a set of "military families", irrespective of any territorial appropriation.

Helmichis was a Lombard noble who killed his king, Alboin, in 572 and unsuccessfully attempted to usurp his throne. Alboin's queen, Rosamund, supported or at least did not oppose Helmichis' plan to remove the king, and after the assassination Helmichis married her. The assassination was assisted by Peredeo, the king's chamber-guard, who in some sources becomes the material executer of the murder. Helmichis is first mentioned by the contemporary chronicler Marius of Avenches, but the most detailed account of his endeavours derives from Paul the Deacon's late 8th-century Historia Langobardorum.
Thurisind was king of the Gepids, an East Germanic Gothic people, from c. 548 to 560. He was the penultimate Gepid king, and succeeded King Elemund by staging a coup d'état and forcing the king's son into exile. Thurisind's kingdom, known as Gepidia, was located in Central Europe and had its centre in Sirmium, a former Roman city on the Sava River.

The coinage of the Lombards refers to the autonomous productions of coins by the Lombards. It constitutes part of the coinage produced by Germanic peoples occupying the former territory of the Roman Empire during the Migration Period. All known Lombard coinage was produced after their settlement of Italy. The coinage originates from two distinct areas, in Langobardia Major between the last decades of the sixth century and 774, and in Langobardia Minor, in the duchy of Benevento, between approximately 680 and the end of the 9th century.
Theodota was a Byzantine noblewoman, most notable for her association with the Lombard king Cunipert (688-700). The Plutei of Theodota are named after her.












