
Southwest Australia is a biogeographic region in Western Australia. It includes the Mediterranean-climate area of southwestern Australia, which is home to a diverse and distinctive flora and fauna.
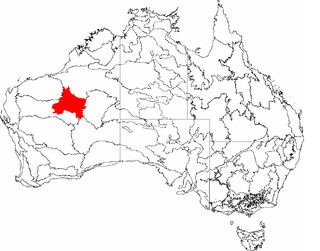
The Little Sandy Desert (LSD) is a desert region in the state of Western Australia, lying to the east of the Pilbara and north of the Gascoyne regions. It is part of the Western Desert cultural region, and was declared an interim Australian bioregion in the 1990s.

The Murchison is an interim Australian bioregion located within the Mid West of Western Australia. The bioregion is loosely related to the catchment area of the Murchison River and has an area of 281,205 square kilometres (108,574 sq mi). Traditionally the region is known as The Murchison.

The yellow-footed rock-wallaby, formerly known as the ring-tailed rock-wallaby, is a member of the macropod family.

Nuytsland Nature Reserve is a protected area of Western Australia in the south-eastern part of the state, on the south coast.

Esperance Plains, also known as Eyre Botanical District, is a biogeographic region in southern Western Australia on the south coast between the Avon Wheatbelt and Hampton bioregions, and bordered to the north by the Mallee region. It is a plain punctuated by granite and quartz outcrops and ranges, with a semi-arid Mediterranean climate and vegetation consisting mostly of mallee-heath and proteaceous scrub. About half of the region has been cleared for intensive agriculture. Recognised as a bioregion under the Interim Biogeographic Regionalisation for Australia (IBRA), it was first defined by John Stanley Beard in 1980.

Mallee, also known as Roe Botanical District, is a biogeographic region in southern Western Australia. Located between the Esperance Plains, Avon Wheatbelt and Coolgardie bioregions, it has a low, gently undulating topography, a semi-arid mediterranean climate, and extensive Eucalyptus mallee vegetation. It has an area of 73,975.59 square kilometres (28,562.13 sq mi). About half of the region has been cleared for intensive agriculture. Recognised as a region under the Interim Biogeographic Regionalisation for Australia (IBRA), it was first defined by John Stanley Beard in 1980.

The Avon Wheatbelt is a bioregion in Western Australia. It has an area of 9,517,104 hectares. It is considered part of the larger Southwest Australia savanna ecoregion.
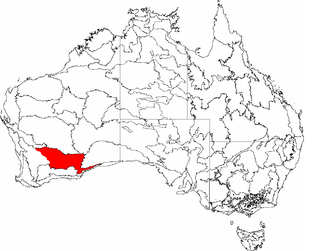
Coolgardie is an Australian bioregion consisting of an area of low hills and plains of infertile sandy soil in Western Australia. It has an area of 129,122.09 square kilometres (49,854.32 sq mi). It includes much of the Great Western Woodlands.

Hampton is an interim Australian bioregion located in southeastern coastal Western Australia, with a small portion (4%) extending into adjacent South Australia. It has an area of 1,088,198 hectares. The Hampton bioregion is part of the Coolgardie woodlands ecoregion.

Yalgoo is an interim Australian bioregion located in Western Australia. It has an area of 5,087,577 hectares. The bioregion, together with the Avon Wheatbelt and Geraldton Sandplains bioregions, is part of the larger Southwest Australia savanna ecoregion as classified by the World Wildlife Fund.
Nepabunna, also spelt Nipapanha, is a small community in the northern Flinders Ranges in north-eastern South Australia, about 600 kilometres (370 mi) north of Adelaide. It is located just west of the Gammon Ranges, and the traditional owners are the Adnyamathanha people.

An Indigenous Protected Area (IPA) is a class of protected area used in Australia; each is formed by voluntary agreement with Indigenous Australians, and declared by Aboriginal Australians and Torres Strait Islander representative organisations. Each is formally recognised by the Australian Government as being part of its National Reserve System. The areas may comprise land and sea, and are managed by Indigenous groups for the conservation of biodiversity. Managing IPAs also helps to protect the cultural values of their country for future generations, and has benefits for Indigenous health, education, economic and social cohesion.

The Coolgardie woodlands is an ecoregion in southern Western Australia. The predominant vegetation is woodlands and mallee scrub. The ecoregion is a transitional zone between the Mediterranean-climate forests, woodlands, and shrublands of Southwest Australia and the deserts and dry scrublands of the Australian interior.
Budj Bim, also known as Mount Eccles, is a dormant volcano near Macarthur in southwestern Victoria, Australia. It lies within the geologically-defined area known as the Newer Volcanics Province, which is the youngest volcanic area in Australia and stretches from western Victoria to south-eastern South Australia.

The Great Western Woodlands is located in the southwest of Australia. The woodlands cover almost 16,000,000 hectares, a region larger in size than England and Wales. The boundary of the Great Western Woodlands runs from the Nullarbor Plain in the east to the Western Australian Wheatbelt in the west; from north of Esperance through to the inland mulga country and deserts that are found north of Kalgoorlie.
The Ngadju are an indigenous Australian people of the Goldfields-Esperance region of the Western Australia.

Budj Bim heritage areas includes several protected areas in Victoria, Australia, the largest two being Budj Bim National Heritage Landscape and the Budj Bim Cultural Landscape. Within the latter, there are three Indigenous Protected Areas: the Tyrendarra Indigenous Protected Area, Kurtonitj Indigenous Protected Area, and the Lake Condah Indigenous Protected Area.
The Ngururrpa Indigenous Protected Area, covering an area of 29,000 square kilometres (11,000 sq mi) in the far eastern area of the Pilbara region, in the Great Sandy Desert of Western Australia, was declared in October 2020. It includes all of the land included in the Ngururrpa native title area, as determined in 2007.

Gawler is an interim Australian bioregion located in South Australia. It has an area of 12,002,883 hectares. Gawler bioregion is part of the Tirari–Sturt stony desert ecoregion.
















