Related Research Articles
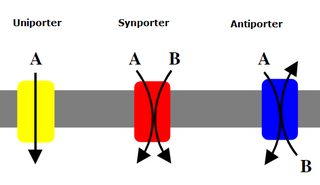
An antiporter (also called exchanger or counter-transporter) is a cotransporter and integral membrane protein involved in secondary active transport of two or more different molecules or ions across a phospholipid membrane such as the plasma membrane in opposite directions, one into the cell and one out of the cell. Na+/H+ antiporters have been reviewed.

Multidrug and toxin extrusion protein 2 is a protein which in humans is encoded by the SLC47A2 gene.
Multi-antimicrobial extrusion protein (MATE) also known as multidrug and toxin extrusion or multidrug and toxic compound extrusion is a family of proteins which function as drug/sodium or proton antiporters.

Members of the Solute:Sodium Symporter (SSS) Family (TC# 2.A.21) catalyze solute:Na+ symport. The SSS family is within the APC Superfamily. The solutes transported may be sugars, amino acids, organo cations such as choline, nucleosides, inositols, vitamins, urea or anions, depending on the system. Members of the SSS family have been identified in bacteria, archaea and eukaryotes. Almost all functionally well-characterized members normally catalyze solute uptake via Na+ symport.
Phosphate permeases are membrane transport proteins that facilitate the diffusion of phosphate into and out of a cell or organelle. Some of these families include:
The Holin superfamily II is a superfamily of putative pore-forming proteins. It is one of the seven different holin superfamilies in total. In general, these proteins are thought to play a role in regulated cell death, although functionality varies between families and individual members. The Holin superfamily II includes the TC families:
The Holin Superfamily III is a superfamily of integral membrane transport proteins. It is one of the seven different holin superfamilies in total. In general, these proteins are thought to play a role in regulated cell death, although functionality varies between families and individual members.
The LydA Holin Family, named after the lydA gene which codes for its prototype member, belongs to the Holin Superfamily III. Members of this family have 3 transmembrane segments (TMSs) and appear to possess between 90 and 120 amino acyl residues (aas). A representative list of proteins belonging to this family can be found in the Transporter Classification Database.
The PRD1 Phage P35 Holin Family is a member of Holin Superfamily III. The prototype for this family is the lipid-containing PRD1 enterobacterial phage holin protein P35 encoded by gene XXXV (orfT). It is a component of a typical holin-endolysin system which functions to lyse the host bacterial cell.
The ion transporter (IT) superfamily is a superfamily of secondary carriers that transport charged substrates.
The arsenical resistance-3 (ACR3) family is a member of the BART superfamily. Based on operon analyses, ARC3 homologues may function either as secondary carriers or as primary active transporters, similarly to the ArsB and ArsAB families. In the latter case ATP hydrolysis again energizes transport. ARC3 homologues transport the same anions as ArsA/AB homologues, though ArsB homologues are members of the IT Superfamily and homologues of the ARC3 family are within the BART Superfamily suggesting they may not be evolutionarily related.
The Malonate Uptake (MatC) family is a constituent of the ion transporter (IT) superfamily. It consists of proteins from Gram-negative and Gram-positive bacteria, simple eukaryotes and archaea. The proteins are of about 450 amino acyl residues in length with 12-14 putative transmembrane segments (TMSs). Closest functionally-characterized homologues are in the DASS family. One member of this family is a putative malonate transporter.
The Basic Amino Acid Antiporter (ArcD) family is a constituent of the IT superfamily. This family consists of proteins from Gram-negative and Gram-positive bacteria. The proteins are of about 480 amino acyl residues (aas) in length and have 10-12 putative transmembrane segments (TMSs). Functionally characterized homologues are in the DcuC and ArsB families. Some members of the family probably catalyze arginine/ornithine or citrulline/ornithine antiport.
Na+/H+ antiporter A (NhaA) family (TC# 2.A.33) contains a number of bacterial sodium-proton antiporter (SPAP) proteins. These are integral membrane proteins that catalyse the exchange of H+ for Na+ in a manner that is highly pH dependent. Homologues have been sequenced from a number of bacteria and archaea. Prokaryotes possess multiple paralogues. A representative list of the proteins that belong to the NhaA family can be found in the Transporter Classification Database.
The NhaB family belongs to the ion transporter (IT) superfamily. A representative list of proteins belonging to the NhaB family can be found in the Transporter Classification Database.
The NhaC family belongs to the Ion Transporter (IT) Superfamily. A representative list of proteins belonging to the NhaC family can be found in the Transporter Classification Database.
The NhaE family belongs to the Ion Transporter (IT) Superfamily. A representative list of proteins belonging to the NhaE family can be found in the Transporter Classification Database.

The Monovalent Cation:Proton Antiporter-1 (CPA1) Family (TC# 2.A.36) is a large family of proteins derived from Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria, blue-green bacteria, archaea, yeast, plants and animals. The CPA1 family belongs to the VIC superfamily. Transporters from eukaryotes have been functionally characterized to catalyze Na+:H+ exchange. Their primary physiological functions are thought to be in (1) cytoplasmic pH regulation, extruding the H+ generated during metabolism, and (2) salt tolerance (in plants), due to Na+ uptake into vacuoles. Bacterial homologues have also been found to facilitate Na+:H+ antiport, but some also catalyze Li+:H+ antiport or Ca2+:H+ antiport under certain conditions.
The Monovalent Cation (K+ or Na+):Proton Antiporter-3 (CPA3) Family (TC# 2.A.63) is a member of the Na+ transporting Mrp superfamily. The CPA3 family consists of bacterial multicomponent K+:H+ and Na+:H+ antiporters. The best characterized systems are the PhaABCDEFG system of Sinorhizobium meliloti (TC# 2.A.63.1.1) that functions in pH adaptation and as a K+ efflux system, and the MnhABCDEFG system of Staphylococcus aureus (TC# 2.A.63.1.3) that functions as a Na+ efflux Na+:H+ antiporter.
The inorganic phosphate transporter (PiT) family is a group of carrier proteins derived from Gram-negative and Gram-positive bacteria, archaea, and eukaryotes.
References
- ↑ Prakash, Shraddha; Cooper, Garret; Singhi, Soumya; Saier, Milton H. (2003-12-03). "The ion transporter superfamily". Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Biomembranes. 1618 (1): 79–92. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamem.2003.10.010 . ISSN 0006-3002. PMID 14643936.
- ↑ Nozaki, K.; Kuroda, T.; Mizushima, T.; Tsuchiya, T. (1998-03-02). "A new Na+/H+ antiporter, NhaD, of Vibrio parahaemolyticus". Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Biomembranes. 1369 (2): 213–220. doi: 10.1016/s0005-2736(97)00223-x . ISSN 0006-3002. PMID 9518619.
- ↑ Ostroumov, Elena; Dzioba, Judith; Loewen, Peter C.; Dibrov, Pavel (2002-08-19). "Asp(344) and Thr(345) are critical for cation exchange mediated by NhaD, Na(+)/H(+) antiporter of Vibrio cholerae". Biochimica et Biophysica Acta. 1564 (1): 99–106. doi: 10.1016/s0005-2736(02)00407-8 . ISSN 0006-3002. PMID 12101001.
As of this edit, this article uses content from "2.A.62 The NhaD Na+:H+ Antiporter (NhaD) Family" , which is licensed in a way that permits reuse under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported License, but not under the GFDL. All relevant terms must be followed.