Quilp Rock is a small, isolated rock in Laubeuf Fjord, lying 6.5 kilometres (3.5 nmi) south-southeast of the south tip of Pinero Island and 2.4 kilometres (1.3 nmi) off the northwest side of Pourquoi Pas Island, off the west coast of Graham Land. First surveyed in 1948 by the Falkland Islands Dependencies Survey (FIDS), it was named by them after the dwarf, Daniel Quilp, a vicious, ill-tempered character in The Old Curiosity Shop, by Charles Dickens.
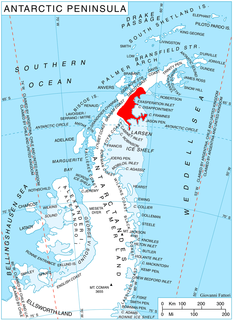
Flask Glacier, is a gently-sloping glacier, 25 nautical miles long, flowing east from Bruce Plateau to enter Scar Inlet between Daggoo Peak and Spouter Peak in Graham Land, Antarctica. The lower reaches of this glacier were surveyed and photographed by the Falklands Islands Dependencies Survey (FIDS) in 1947. The entire glacier was photographed by the Falkland Islands and Dependencies Aerial Survey Expedition in 1955–56, and mapped by the FIDS in 1957. It was named by the UK Antarctic Place-names Committee after the third mate on the Pequod in Herman Melville's Moby-Dick; or, The White Whale.

Wolseley Buttress is a high buttress on the southern edge of Detroit Plateau, forming the west side of Albone Glacier on Nordenskjöld Coast in Graham Land, Antarctica. Mapped from surveys by Falkland Islands Dependencies Survey (FIDS) (1960–61). Named by United Kingdom Antarctic Place-Names Committee (UK-APC) after Wolseley Tool and Motor Car Co. which, in 1908-10, designed the experimental motor sledge used by Captain Scott's 1910-13 expedition.
Woodbury Glacier is a glacier just west of Montgolfier Glacier, flowing into Piccard Cove, Wilhelmina Bay, on the west coast of Graham Land. Mapped by the Falkland Islands Dependencies Survey (FIDS) from air photos taken by Hunting Aerosurveys Ltd. in 1956-57. Named by the United Kingdom Antarctic Place-Names Committee (UK-APC) in 1960 for Walter B. Woodbury (1834–1885), English pioneer of photomechanical printing in 1865 and of serial film cameras for use in balloons and kites in 1877.

Andrew Glacier is a glacier 3 nautical miles (6 km) long, flowing northeast into Ognen Cove in Charcot Bay immediately west of the Webster Peaks on Trinity Peninsula, northern Graham Land.
Mount Arronax is an ice-covered, pointed peak, 1,585 m, standing 6 nautical miles (11 km) west-southwest of Nautilus Head and dominating the north part of Pourquoi Pas Island, off the west coast of Graham Land. Black Pass runs northeast–southwest, 3 nautical miles west of Mount Arronax.

Bevin Glacier is a glacier 5 nautical miles (9 km) long, which flows east from the plateau escarpment on the east side of Graham Land into the northwest end of Cabinet Inlet between Attlee Glacier and Anderson Glacier. During December 1947 it was charted by the Falkland Islands Dependencies Survey (FIDS) and photographed from the air by the Ronne Antarctic Research Expedition. It was named by the FIDS for Rt. Hon. Ernest Bevin, M.P., British Minister of Labour and National Service and member of the War Cabinet.

Bottrill Head is a rugged headland on the east side of Bourgeois Fjord which forms the southwest extremity of German Peninsula and the north side of the entrance to Dogs Leg Fjord in Fallières Coast, on the west side of Graham Land, Antarctica. It was first surveyed in 1936 by the British Graham Land Expedition (BGLE) under John Rymill. The headland was resurveyed in 1948 by the Falkland Islands Dependencies Survey (FIDS) who named it for Harold Bottrill, Chairman of the Board of Directors, later General Manager, of Maclean and Stapledon S.A., shipping agents at Montevideo, who gave great assistance to the BGLE, 1934–37, and to FIDS, 1943–48.
Contact Peak is a prominent rock peak, 1,005 metres (3,300 ft) high, which is the southeasternmost peak on Pourquoi Pas Island, off the west coast of Graham Land. It was first sighted and roughly charted in 1909 by the French Antarctic Expedition under Jean-Baptiste Charcot. It was surveyed in 1936 by the British Graham Land Expedition and in 1948 by the Falkland Islands Dependencies Survey (FIDS). It was so named by FIDS because the peak marks the granite-volcanic contact in the cliffs which is visible at a considerable distance.
Nautilus Head is a prominent headland rising to 975 m near the northeast extremity of Pourquoi Pas Island, off the west coast of Graham Land. It was first surveyed in 1936 by the British Graham Land Expedition (BGLE) under Rymill and resurveyed in 1948 by the Falkland Islands Dependencies Survey (FIDS) who named it after the submarine Nautilus in Jules Verne's Twenty Thousand Leagues Under The Sea. Other features on Pourquoi Pas Island are named after characters from that book.
Whistling Bay is an open bay, 4 nautical miles (7 km) wide and indenting 2.5 nautical miles (4.6 km), between Longridge Head and Cape Saenz along the west coast of Graham Land. First roughly surveyed in 1936 by the British Graham Land Expedition (BGLE) under Rymill. Resurveyed in 1948 by the Falkland Islands Dependencies Survey (FIDS) and so named by them because of the curious and unidentified whistling sounds heard there at the time of the survey.
Dalgliesh Bay is a bay, 1 nautical mile (2 km) wide and indenting 3 nautical miles (6 km), lying between Lainez Point and Bongrain Point on the west side of Pourquoi Pas Island, off the west coast of Graham Land. It was first roughly surveyed in 1936 by the British Graham Land Expedition under John Rymill. It was resurveyed in 1948 by the Falkland Islands Dependencies Survey (FIDS) and named for David G. Dalgliesh, FIDS medical officer at Stonington Island in 1948–49, who accompanied the 1948 sledge survey party to this area.
Stipple Rocks is a compact group of more than twenty rocks, lying 3 nautical miles (6 km) northwest of Millerand Island in Marguerite Bay, off the west coast of Graham Land. First surveyed in 1936 by the British Graham Land Expedition (BGLE) under Rymill, and resurveyed in 1949 by the Falkland Islands Dependencies Survey (FIDS). The name, applied by FIDS, is descriptive of the representation on a map of the numerous rocks in this group.
Powder Island is a small island lying 8 nautical miles (15 km) south-southeast of Cape Jeremy and 2 nautical miles (3.7 km) off the west coast of Palmer Land, in George VI Sound. First surveyed in 1948 by the Falkland Islands Dependencies Survey (FIDS), and so named by them because of the friable nature of the rock found on the island.
Perplex Ridge is a ridge, rising over 915 m, composed of four rocky masses separated by small glaciers, extending 6 nautical miles (11 km) northeastward from Lainez Point along the northwest side of Pourquoi Pas Island, off the west coast of Graham Land. First sighted and roughly charted in 1909 by the French Antarctic Expedition under Charcot. It was surveyed in 1936 by the British Graham Land Expedition (BGLE) and in 1948 by the Falkland Islands Dependencies Survey (FIDS). So named by FIDS because of confusion in attempting to identify this ridge from earlier maps.

Perutz Glacier is a glacier, 10 nautical miles (18 km) long and 2 nautical miles (3.7 km) wide, which flows west-northwest from Hemimont Plateau into Bourgeois Fjord, close east of Thomson Head, on the west coast of Graham Land, Antarctica. The mouth of the glacier was first surveyed in 1936 by the British Graham Land Expedition (BGLE) under Rymill. The entire glacier was surveyed in 1946-47 and 1948-49 by the Falkland Islands Dependencies Survey (FIDS), and named by them for Max F. Perutz of the Cavendish Laboratory, Cambridge, who has made important studies on the mechanism of glacier flow.
Harris Peak is a peak, 1,005 metres (3,300 ft) high, surmounting the base of Reclus Peninsula on the west coast of Graham Land, Antarctica. It was mapped by the Falkland Islands Dependencies Survey (FIDS) from photos taken by Hunting Aerosurveys Ltd in 1956–57, and was named by the UK Antarctic Place-Names Committee in 1960 for Leslie Harris, a FIDS carpenter and general assistant at the Danco Island station in 1956, who participated in the reconnaissance journeys from that station and from the nearby Portal Point hut.
Twig Rock is a small rocky mass, more than 90 m high, between Alamode Island and Hayrick Island in the Terra Firma Islands, off the west coast of Graham Land.

Thomson Head is a steep, rocky headland rising to 915 m at the east side of Bourgeois Fjord, between Perutz and Bader Glaciers, forming the north extremity of German Peninsula on Fallières Coast on the west side of Graham Land, Antarctica. First surveyed in 1936 by the British Graham Land Expedition (BGLE) under Rymill. Resurveyed in 1948-49 by the Falkland Islands Dependencies Survey (FIDS) and named for William H. Thomson, FIDS air pilot at Stonington Island in 1947.
The Forbidden Plateau is a long, narrow plateau extending southwestward from Charlotte Bay to Flandres Bay in Graham Land. It borders Bruce Plateau on the south and Foster Plateau on the north. The feature was mapped by the Falklands Islands Dependencies Survey (FIDS) from photos taken by Hunting Aerosurveys Ltd. in 1956-57. Its name was picked by the UK Antarctic Place-names Committee (UK-APC) because all attempts to reach the plateau failed until it was finally traversed by Falklands Islands Dependencies Survey (FIDS) members in 1957.


![]()







