
Münster is an independent city in North Rhine-Westphalia, Germany. It is in the northern part of the state and is considered to be the cultural centre of the Westphalia region. It is also a state district capital. Münster was the location of the Anabaptist rebellion during the Protestant Reformation and the site of the signing of the Treaty of Westphalia ending the Thirty Years' War in 1648. Today it is known as the bicycle capital of Germany.
Siegen-Wittgenstein is a Kreis (district) in the southeast of North Rhine-Westphalia, Germany. Neighboring districts are Olpe, Hochsauerlandkreis, Waldeck-Frankenberg, Marburg-Biedenkopf, Lahn-Dill, Westerwaldkreis, and Altenkirchen.
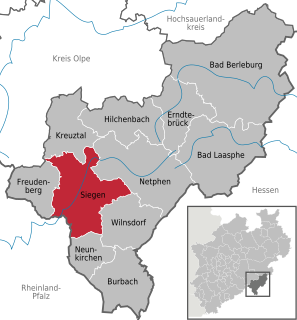
Siegen is a city in Germany, in the south Westphalian part of North Rhine-Westphalia.

Meschede is a town in the Hochsauerland district, in North Rhine-Westphalia, Germany. It is the capital of the district Hochsauerlandkreis.

Rheda-Wiedenbrück is a city in the district of Gütersloh, in North Rhine-Westphalia, Germany.

Schmallenberg is a town and a climatic health resort in the High Sauerland District, Germany. By area, it is the third biggest of all cities and towns of the state of North Rhine-Westphalia and the second biggest of the region of Westphalia.

Lennestadt lies in the Sauerland in southeast North Rhine-Westphalia and is a community in Olpe district. It is the district's most populous municipality. Lennestadt itself is not an actual town but a community which comprises several towns and villages.

Olpe is a town situated in the foothills of the Ebbegebirge in North Rhine-Westphalia, roughly 60 km east of Cologne and 20 km northwest of Siegen. It is part of the Regierungsbezirk of Arnsberg and is the seat of the district of Olpe.

Freudenberg is a town in the Siegen-Wittgenstein district, in North Rhine-Westphalia, Germany.

Hilchenbach is a town in the Siegen-Wittgenstein Kreis (district) of North Rhine-Westphalia, Germany.
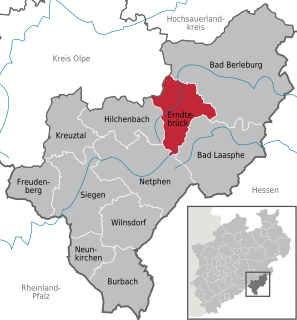
Erndtebrück is a municipality in the Siegen-Wittgenstein district, in North Rhine-Westphalia, Germany.
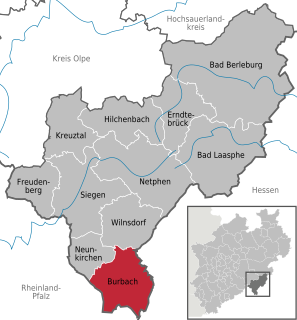
Burbach is a municipality in the Siegen-Wittgenstein district, in North Rhine-Westphalia, Germany.

Siegen Hauptbahnhof is the main station of the town of Siegen, in the German state of North Rhine-Westphalia. It is in close to the modern centre of Siegen, which includes the bus station and the Sieg Carré and City Galerie shopping centres.
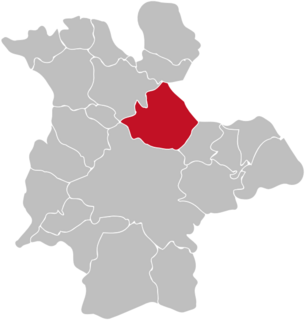
Weidenau is a suburban part (Stadtteil) of the city Siegen in Germany.

The Soest Feud, or Feud of Soest, was a feud that took place from 1444 to 1449 in which the town of Soest claimed its freedom from Archbishop Dietrich of Cologne (1414–1463), who tried to restore his rule. The town of Soest opposed this attempt on 5 June 1444 by accepting a new suzerain, John I, the Duke of Cleves-Mark, who guaranteed the town its old rights as well as new ones. As a result Emperor Frederick III imposed the imperial ban on the town. The victory of the town meant that Soest had de facto more freedom than a free imperial city until it was annexed by Prussia, but at the same time it had to forfeit its economic power because it was now an enclave within Cologne's territory.

The Westphalia Football and Athletics Association is the umbrella organization of football and athletics clubs in the German Westphalia area, and comprises 29 districts. The FLVW was created in 1954 through the merger of the Football Association of Westphalia, founded in 1946, with the Athletics Association of Westphalia. The FLVW has its headquarters in Kamen. President of the FLVW is Gundolf Walaschewski.
The following is a timeline of the history of the city of Münster, North Rhine-Westphalia, Germany.

Annette Kurschus is a German Protestant theologian and pastor. Since March 2012 she has been Praeses of the Evangelical Church of Westphalia and since November 2015 she has also been Vice-President of the Council of the Evangelical Church in Germany (EKD).
Neue Stimmen is an international singing competition. Initiated by Liz Mohn, it was launched in 1987 to provide support for young opera singers. It is considered an important forum for new talent, one that has marked the beginning of international careers for many participants. The competition is organized every two years by the Bertelsmann Stiftung in Gütersloh. It is one of the foundation's oldest projects.

Oberholzklau is a constituent community of Freudenberg, Siegen-Wittgenstein, North Rhine-Westphalia, Germany.




















