
A digital camera is a camera that captures photographs in digital memory. Most cameras produced today are digital, largely replacing those that capture images on photographic film. Digital cameras are now widely incorporated into mobile devices like smartphones with the same or more capabilities and features of dedicated cameras. High-end, high-definition dedicated cameras are still commonly used by professionals and those who desire to take higher-quality photographs.

Nikon Corporation, also known just as Nikon, is a Japanese multinational corporation headquartered in Tokyo, Japan; it specializes in creating and marketing optics and imaging products. The companies held by Nikon form the Nikon Group.

A digital single-lens reflex camera is a digital camera that combines the optics and the mechanisms of a single-lens reflex camera with a solid-state image sensor and digitally records the images from the sensor.

Mavica is a discontinued brand of Sony cameras which use removable disks as the main recording medium. On August 25th 1981, Sony unveiled a prototype of the Sony Mavica as the world's first electronic still video camera.
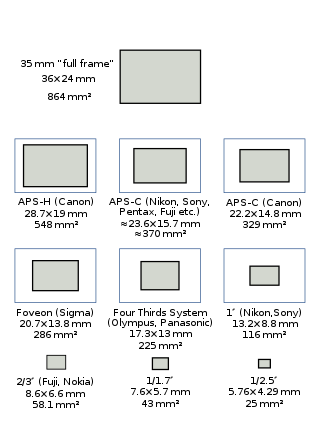
A full-frame DSLR is a digital single-lens reflex camera (DSLR) with a 35 mm image sensor format. Historically, 35 mm was one of the standard film formats, alongside larger ones, such as medium format and large format. The full-frame DSLR is in contrast to full-frame mirrorless interchangeable-lens cameras, and DSLR and mirrorless cameras with smaller sensors, much smaller than a full 35 mm frame. Many digital cameras, both compact and SLR models, use a smaller-than-35 mm frame as it is easier and cheaper to manufacture imaging sensors at a smaller size. Historically, the earliest digital SLR models, such as the Nikon NASA F4 or Kodak DCS 100, also used a smaller sensor.

Bridge cameras are cameras that fill the niche between relatively simple point-and-shoot cameras and interchangeable-lens cameras such as mirrorless cameras and single-lens reflex cameras (SLRs). They are often comparable in size and weight to the smallest digital SLRs (DSLR), but lack interchangeable lenses, and almost all digital bridge cameras lack an optical viewfinder system. The phrase "bridge camera" has been in use at least since the 1980s, and continues to be used with digital cameras. The term was originally used to refer to film cameras which "bridged the gap" between point-and-shoot cameras and SLRs.

The Coolpix 5400 was a 5.1 megapixel 'prosumer' digital camera produced by Nikon. Announced at the end of May 2003 as the immediate successor to the Nikon Coolpix 5000, it features 4x optical zoom, 4x digital zoom, and many other functions.

The Nikon D40 is Nikon F-mount entry-level digital SLR, announced November 16, 2006 and made until March 2009, when it was succeeded by the Nikon D3000. Compared to its predecessor, the D50, the D40 had several features removed, a few added, and a lower price: US$499.95 ESP as of November 2009 with the 18–55 mm G-II kit lens, positioning it as an entry-level model compared to the D80. The D40x has a 10-megapixel maximum resolution, up from 6 megapixels of the D40 and D50.

Sony Corporation produces professional, consumer, and prosumer camcorders such as studio and broadcast, digital cinema cameras, camcorders, pan-tilt-zoom and remote cameras.
General Imaging was a manufacturer of digital cameras headquartered in Torrance, California, established in 2006 by Hiroshi "Hugh" Komiya, a former executive of Olympus Corporation. General Imaging sold their cameras internationally under the General Electric name, used under license. General Imaging was licensed to manufacture and sell their cameras under the AgfaPhoto name in Japan. On October 5, 2015, General Imaging filed for bankruptcy.

The Coolpix S10 is a model of digital camera formerly produced by Nikon and first released in 2006 as part of the Coolpix Series. Its image sensor is a CCD with 6.0 million pixels. It has a 2.5-inch (64 mm) thin-film transistor liquid crystal display device with 230,000 pixels. The S10 incorporates Nikon's popular swivel design first seen in the Coolpix 900 which allows for a powerful Nikkor 10X Optical zoom lens while retaining a compact form. Other features include D-Lighting and Face-priority AF.

The Coolpix P6000 is a digital camera introduced by the Nikon Corporation in August 2008.

The Panasonic Lumix DMC-GH1 is a digital mirrorless interchangeable lens camera adhering to the Olympus and Panasonic developed Micro Four Thirds System (MFT) system design standard. Panasonic classified the GH1 as a hybrid stills/video camera and the GH1 was introduced and marketed as a higher end camera than Panasonic's first MFT camera, the stills only, non-video capable Lumix DMC-G1.

The Nikon Coolpix P90 was launched by Nikon on 3 February 2009 as an improved version of the Nikon Coolpix P80. It is a 12-megapixel CCD digital camera with a fixed 24× zoom lens giving more than twelve times image magnification fully extended.

The Panasonic Lumix DMC-LX5, or LX5, is a high-end compact "point and shoot" camera launched by Panasonic in 2010 to succeed the LX3.

The Olympus XZ-1 is a high-end 10.0 megapixel compact digital camera announced and released in January 2011. Its key features are a fast f/1.8-2.5 i.Zuiko Digital lens, a built in imager shift image stabilizer and Olympus' 6 Art Filters that are also present in the E-PEN series.

The Nikon D5600 is a 24.2 megapixel upper-entry level, APS-C sensor DSLR announced by Nikon on November 10, 2016, as the successor of the D5500. The camera has an F-mount.

















