
The substantia nigra (SN) is a basal ganglia structure located in the midbrain that plays an important role in reward and movement. Substantia nigra is Latin for "black substance", reflecting the fact that parts of the substantia nigra appear darker than neighboring areas due to high levels of neuromelanin in dopaminergic neurons. It was discovered in 1784 by Félix Vicq-d'Azyr, and Samuel Thomas von Sömmerring alluded to this structure in 1791. Parkinson's disease is characterized by the loss of dopaminergic neurons in the substantia nigra pars compacta.

Yareta or llareta is a flowering plant in the family Apiaceae native to South America. It grows in the Puna grasslands of the Andes in Peru, Bolivia, northern Chile, and western Argentina at altitudes between 3,200 and 5,200 metres.
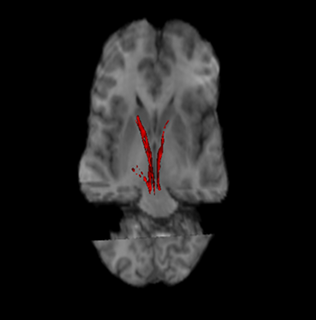
The nigrostriatal pathway or the nigrostriatal bundle (NSB), is a dopaminergic pathway that connects the substantia nigra pars compacta (SNc) with the dorsal striatum. It is one of the four major dopamine pathways in the brain, and is particularly involved in the production of movement, as part of a system called the basal ganglia motor loop. Dopaminergic neurons of this pathway synapse onto GABAergic neurons.
The pars compacta is a portion of the substantia nigra, located in the midbrain. It is formed by dopaminergic neurons and located medial to pars reticulata. Parkinson's disease is characterized by the death of dopaminergic neurons in this region.

The oblong rocksnail is a species of freshwater snail with an operculum, an aquatic gastropod mollusk in the family Pleuroceridae.
Victaphanta compacta, common name the Otway black snail, is a species of carnivorous air-breathing land snail, a terrestrial pulmonate gastropod mollusks in the family Rhytididae. The Otway Black Snail Victaphanta compacta is only found in cool temperate rainforests in the Otway Ranges, Victoria. It is one of four species of the carnivorous land snails in the genus Victaphanta and is endemic to the Otway Ranges.

Ayenia compacta is a species of shrub in the mallow family known by the common name California ayenia.
Compacta is a genus of moths of the family Crambidae.
Compacta, a Latin adjective for compact, may refer to:

Compacta is a condensed sans-serif typeface designed by Fred Lambert for Letraset in 1963. It is visually similar to the typefaces Impact and Haettenschweiler, though Compacta has a distinctively square shape in comparison. Letraset was a dry transfer system, widely used by amateur or small-scale lettering projects, although many professional designers used it as well. Compacta was Letraset's first original typeface design, and proved widely popular. Rights to it were acquired by Linotype and others, leading to it becoming available in other formats such as digitally.
C. compacta may refer to:
P. compacta may refer to:
Cyclophora compacta is a moth in the family Geometridae. It is found on the Kei Islands and in New Guinea and Queensland.

Hemithrinax compacta is a species of palm that is endemic to Cuba. Hemithrinax compacta flourishes on the mogotes of Cuba. Mogotes are dome-shaped hills in Cuba made up of coral rock. Hemithrinax compacta is the only species in its genus in Cuba that grows in the highlands, at an elevation of 450 metres (1,480 ft). Hemithrinax compacta needs to have more than 2,400 mm (94 in) per year of rainfall and a mean temperature of 22 degrees Celsius (72 °F). The leaves of the palm have an average length of 190 cm (75 in) and the inflorescence of the palm is tightly clustered, giving rise to the species name. A mature H. compacta can have a massive trunk of up to 10 cm (3.9 in) thick and more than 20 m (66 ft) in height. The genus Thrinax has been grown in gardens. In addition, in Thrinax the fruits are dispersed and eaten by red-bellied woodpeckers, birds, gray squirrels and lizards.
Niphosoma is a genus of longhorn beetles of the subfamily Lamiinae, containing the following species:
Fonsecaea compacta is a saprophytic fungal species found in the family Herpotrichiellaceae. It is a rare etiological agent of chromoblastomycosis, with low rates of correspondence observed from reports. The main active components of F. compacta are glycolipids, yet very little is known about its composition. F. compacta is widely regarded as a dysplastic variety of Fonsecaea pedrosoi, its morphological precursor. The genus Fonsecaea presently contains two species, F. pedrosoi and F. compacta. Over 100 strains of F. pedrosoi have been isolated but only two of F. compacta.

Cuscuta compacta, the compact dodder, is a parasitic plant that specializes on woody plants. This species is distributed across the Eastern and Midwestern USA, Eastern Canada, and Mexico.
Niphosoma sikkimensis is a species of beetle in the family Cerambycidae. It was described by Stephan von Breuning in 1957.
Coptosia compacta is a species of beetle in the family Cerambycidae. It was described by Ménétriés in 1832, originally under the genus Saperda. It is known from Israel, Iran, Syria, Armenia, Jordan, and Turkey.
Graciella compacta is a species of beetle in the family Cerambycidae. It was described by Jordan in 1894.









