
RDX (abbreviation of "Research Department eXplosive" or Royal Demolition eXplosive) or hexogen, among other names, is an organic compound with the formula (CH2N2O2)3. It is white, odorless and tasteless, widely used as an explosive. Chemically, it is classified as a nitroamine alongside HMX, which is a more energetic explosive than TNT. It was used widely in World War II and remains common in military applications.

Dynamite is an explosive made of nitroglycerin, sorbents, and stabilizers. It was invented by the Swedish chemist and engineer Alfred Nobel in Geesthacht, Northern Germany, and was patented in 1867. It rapidly gained wide-scale use as a more robust alternative to the traditional black powder explosives. It allows the use of nitroglycerine's favorable explosive properties while greatly reducing its risk of accidental detonation.

An explosive is a reactive substance that contains a great amount of potential energy that can produce an explosion if released suddenly, usually accompanied by the production of light, heat, sound, and pressure. An explosive charge is a measured quantity of explosive material, which may either be composed solely of one ingredient or be a mixture containing at least two substances.

Paraffin wax is a soft colorless solid derived from petroleum, coal, or oil shale that consists of a mixture of hydrocarbon molecules containing between 20 and 40 carbon atoms. It is solid at room temperature and begins to melt above approximately 37 °C (99 °F), and its boiling point is above 370 °C (698 °F). Common applications for paraffin wax include lubrication, electrical insulation, and candles; dyed paraffin wax can be made into crayons. It is distinct from kerosene and other petroleum products that are sometimes called paraffin.

Trinitrotoluene, more commonly known as TNT, more specifically 2,4,6-trinitrotoluene, and by its preferred IUPAC name 2-methyl-1,3,5-trinitrobenzene, is a chemical compound with the formula C6H2(NO2)3CH3. TNT is occasionally used as a reagent in chemical synthesis, but it is best known as an explosive material with convenient handling properties. The explosive yield of TNT is considered to be the standard comparative convention of bombs and asteroid impacts. In chemistry, TNT is used to generate charge transfer salts.
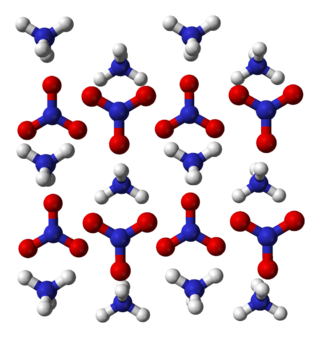
Ammonium nitrate is a chemical compound with the formula NH4NO3. It is a white crystalline salt consisting of ions of ammonium and nitrate. It is highly soluble in water and hygroscopic as a solid, although it does not form hydrates. It is predominantly used in agriculture as a high-nitrogen fertilizer.

ANFO ( AN-foh) (or AN/FO, for ammonium nitrate/fuel oil) is a widely used bulk industrial explosive. It consists of 94% porous prilled ammonium nitrate (NH4NO3) (AN), which acts as the oxidizing agent and absorbent for the fuel, and 6% number 2 fuel oil (FO). The use of ANFO originated in the 1950s.
Nitromethane, sometimes shortened to simply "nitro", is an organic compound with the chemical formula CH
3NO
2. It is the simplest organic nitro compound. It is a polar liquid commonly used as a solvent in a variety of industrial applications such as in extractions, as a reaction medium, and as a cleaning solvent. As an intermediate in organic synthesis, it is used widely in the manufacture of pesticides, explosives, fibers, and coatings. Nitromethane is used as a fuel additive in various motorsports and hobbies, e.g. Top Fuel drag racing and miniature internal combustion engines in radio control, control line and free flight model aircraft.

Smokeless powder is a type of propellant used in firearms and artillery that produces less smoke and less fouling when fired compared to black powder. Because of their similar use, both the original black powder formulation and the smokeless propellant which replaced it are commonly described as gunpowder. The combustion products of smokeless powder are mainly gaseous, compared to around 55% solid products for black powder. In addition, smokeless powder does not leave the thick, heavy fouling of hygroscopic material associated with black powder that causes rusting of the barrel.

Torpex is a secondary explosive, 50% more powerful than TNT by mass. Torpex comprises 42% RDX, 40% TNT and 18% powdered aluminium. It was used in the Second World War from late 1942, at which time some used the names Torpex and RDX interchangeably, much to the confusion of today's historical researchers. Torpex proved to be particularly useful in underwater munitions because the aluminium component had the effect of making the explosive pulse last longer, which increased the destructive power. Besides torpedoes, naval mines, and depth charges, Torpex was only used in the Upkeep, Tallboy and Grand Slam bombs as well as the drones employed in Operation Aphrodite. Torpex has long been superseded by H6 and Polymer-bonded explosive (PBX) compositions. It is therefore regarded as obsolete and Torpex is unlikely to be encountered except in old munitions or unexploded ordnance, although a notable exception to this is the Sting Ray lightweight torpedo, which as of October 2020 remains in service with the Royal Navy and several foreign militaries. The German equivalent of Torpex was Trialen.
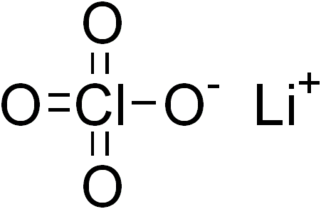
Lithium perchlorate is the inorganic compound with the formula LiClO4. This white or colourless crystalline salt is noteworthy for its high solubility in many solvents. It exists both in anhydrous form and as a trihydrate.
Minol is a military explosive developed by the Admiralty early in the Second World War to augment supplies of trinitrotoluene (TNT) and RDX, which were in short supply. The aluminium component in Minol significantly prolongs the explosive pulse, making it ideal for use in underwater naval weapons where munitions with a longer explosive pulse are more destructive than those with high brisance. Minol cannot be used in weapons fired from gun barrels because there is a risk of detonation when subjected to over 250 gs of acceleration. Initially, three Minol formulas were used. All percentages shown are by weight:
A-IX-2 is a Russian explosive used in modern Russian military shells. It consists of 73% RDX with 23% aluminium powder, phlegmatized with 4% wax. Its relative effectiveness factor is 1.54.

Tovex is a water-gel explosive composed of ammonium nitrate and methylammonium nitrate that has several advantages over traditional dynamite, including lower toxicity and safer manufacture, transport, and storage. It has thus almost entirely replaced dynamite. There are numerous versions ranging from shearing charges to aluminized common blasting agents. Tovex is used by 80% of international oil companies for seismic exploration.

Urea nitrate is a fertilizer-based high explosive that has been used in improvised explosive devices in Afghanistan, Pakistan, Iraq, and various terrorist acts elsewhere in the world such as in the 1993 World Trade Center bombings. It has a destructive power similar to better-known ammonium nitrate explosives, with a velocity of detonation between 3,400 m/s (11,155 ft/s) and 4,700 m/s (15,420 ft/s). It has chemical formula of CH5N3O4 or (NH2)2COHNO3.

The 1924 Nixon Nitration Works disaster was an explosion and fire that claimed many lives and destroyed several square miles of New Jersey factories. It began on March 1, 1924, about 11:15 a.m., when an explosion destroyed a building in Nixon, New Jersey used for processing ammonium nitrate. The explosion touched off fires in surrounding buildings in the Nixon Nitration Works that contained other highly flammable materials. The disaster killed twenty people, destroyed forty buildings, and demolished the "tiny industrial town of Nixon, New Jersey."

Ammonium permanganate is the chemical compound NH4MnO4, or NH3·HMnO4. It is a water soluble, violet-brown or dark purple salt.

Potassium picrate, or potassium 2,4,6-trinitrophenolate, is an organic chemical, a picrate of potassium. It is a reddish yellow or green crystalline material. It is a primary explosive. Anhydrous potassium picrate forms orthorhombic crystals.

Trinitroanisole is a chemical compound that exists as pale yellow crystals with a melting point of 68 °C. It is highly toxic. It is an explosive with a detonation velocity of 7200 meters per second. The compound's primary hazard is a blast of an instantaneous explosion, not flying projectiles or fragments.
This timeline lists the development of explosives and related events.















